Ann Rehabil Med.
2012 Oct;36(5):688-695.
The Factors Associated with Contact Burns from Therapeutic Modalities
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Hallym University Burn Institute, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul 150-719, Korea. pmrseo@hallym.or.kr
- 2Department of Burn Surgery, Hallym Burn Center, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul 150-719, Korea.
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To understand the injury pattern of contact burns from therapeutic physical modalities. METHOD: A retrospective study was done in 864 patients with contact burns who discharged from our hospital from January 2005 to December 2008. The following parameters were compared between patients with contact burns from therapeutic modalities and from other causes: general characteristics, burn extent, cause of burn injury, place of occurrence, burn injury site, treatment methods, prevalence of underlying disease, and length of hospital stay were compared between patients with contact burns.
RESULTS
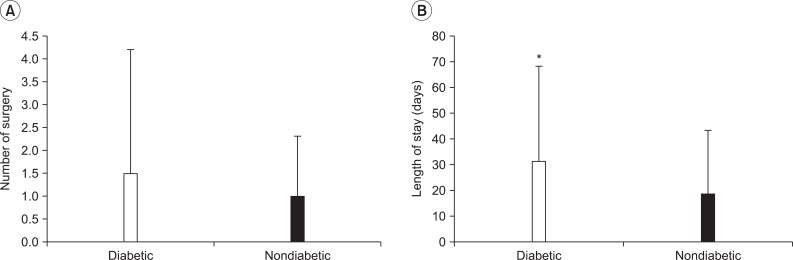
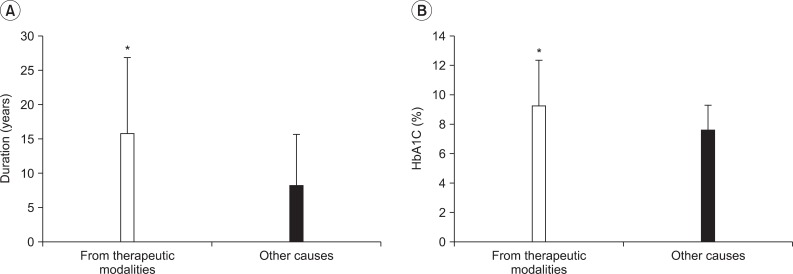
Of the 864 subjects, 94 patients were injured from therapeutic modalities. A hot pack (n=51) was the most common type of therapeutic modality causing contact burn followed by moxibustion (n=21), electric heating pad (n=16), and radiant heat (n=4). The lower leg (n=31) was the most common injury site followed by the foot & ankle (n=24), buttock & coccyx (n=9), knee (n=8), trunk (n=8), back (n=6), shoulder (n=4), and arm (n=4). Diabetes mellitus was associated with contact burns from therapeutic modalities; the odds ratio was 3.99. Injuries took place most commonly at home (n=56), followed by the hospital (n=33), and in other places (n=5).
CONCLUSION
A hot pack was the most common cause of contact burns from therapeutic modalities, and the lower leg was the most common injury site. Injuries took place most commonly at home. The patients with contact burns from therapeutic modalities showed high correlation to presence of diabetes mellitus. These results would be helpful for the prevention of contact burns due to therapeutic modalities.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Han TR, Bang MS. Rehabilitation medicine. 2008. 3rd ed. Seoul: Kunja Publishing Co.;p. 159–161.2. Basford JR. Delisa JA, Gans BM, Walsh NE, editors. Therapeutic physical agents. Physical medicine and rehabilitation: principles and practice. 2005. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;p. 252–253.3. Han CH, Shin MS, Kang KW, Kang BK, Park SH, Choi SM. An in-depth interview for use of moxibustion therapy in Korea. Korean J Acupunct. 2008; 25:85–97.4. Nadler SF, Prybicien M, Malanga GA, Sicher D. Complications from therapeutic modalities: results of national survey of athletic trainers. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2003; 84:849–853. PMID: 12808537.5. Nam YH, Ko DH, Yoon TJ. A case of moxibustion-induced keloid. Korean J Dermatol. 2006; 44:1091–1093.6. Song DS, Kim HC, Woo GW. A retrospective epidemiologic analysis of burn patients at Hanil Hospital. J Korean Burn Soc. 2009; 12:21–37.7. Weber DC, Hoppe KM. Braddom RL, editor. Physical agent modalities. Physical medicine and rehabilitation. 2007. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Saunders;p. 459–477.
Article8. Bill TJ, Edlich RF, Himel HN. Electric heating pad burns. J Emerg Med. 1994; 12:819–824. PMID: 7533807.
Article9. Satter EK. Third-degree burns incurred as a result of interferential current therapy. Am J Dermatopathol. 2008; 30:281–283. PMID: 18496434.
Article10. Balmaseda MT Jr, Fatehi MT, Koozekanani SH, Sheppard JS. Burns in functional electric stimulation: two case reports. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1987; 68:452–453. PMID: 3496867.11. Ford KS, Shrader MW, Smith J, Mclean TJ, Dahm DL. Full-thickness burn formation after the use of electrical stimulation for rehabilitation of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2005; 20:950–953. PMID: 16230253.
Article12. Smith MA, Munster AM, Spence RJ. Burns of the hand and upper limb-a review. Burns. 1998; 24:493–505. PMID: 9776087.
Article13. Kim DC, Na DS. Epidemiology of burns in Korea. J Korean Burn Soc. 2011; 14:6–11.14. The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. The effect of intensive diabetes therapy on the development and progression of neuropathy. Ann Intern Med. 1995; 122:561–568. PMID: 7887548.15. Park JM, An GY. Factors affecting diabetic neuropathy and significance of nerve conduction study. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 1993; 17:578–584.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effects of Morgan Therapeutic Lens in Chemical Corneal Burn
- Knee joint reconstruction using regional flaps: an aesthetic approach to extensive defects following fourth-degree contact burns
- Phototherapeutic Keratectomy for the Treatment of Persistent Epithelial Defect
- Treatment of Burns Exposed to Glacial Acetic Acid Dough
- Mayonnaise and the Treatment of Molten Polyethylene Burns: A Case Report