Anat Cell Biol.
2017 Sep;50(3):242-244. 10.5115/acb.2017.50.3.242.
Undescended cecum with accessory right colic artery: a rare case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomy, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Bhubaneswar, India. praveenkumar1059@gmail.com
- KMID: 2390487
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.2017.50.3.242
Abstract
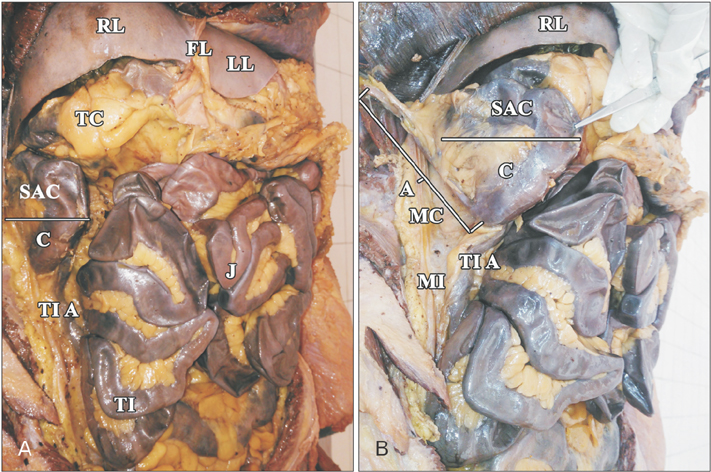
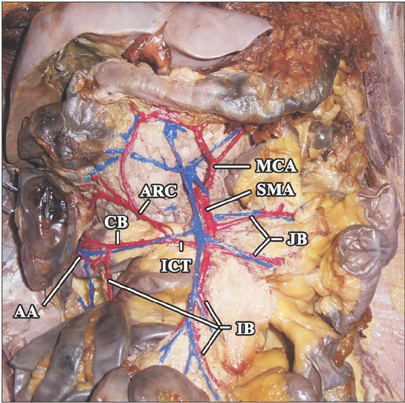
- Midgut malrotation and incomplete rotation are common causes of neonatal intestinal obstruction. At end of 10 week of intrauterine life, cecum will be placed in subhepatic region temporarily and descends to right lower quadrant by eleventh week. Arrest of cecum in subhepatic region or undescended cecum is a rare congenital anomaly of mid gut. Usually, it remains asymptomatic and is diagnosed incidentally. If any pathology occurs in anomalous part, like appendicitis then the diagnosis and treatment will be challenging in all age groups. Variation in blood supply have also been reported with anomalies leading to iatrogenic injuries during colonoscopy and surgeries. Lack of knowledge of these rare variations may lead to delayed diagnosis of appendicitis leading to perforation and surgical emergencies. In the present case, we describe an undescended cecum and its associated variation in branching pattern of superior mesenteric artery.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Standring S. Gray's anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice. 41st ed. New York: Elsevier Churchill Livingstone;2016.2. Moore KL, Persaud TV, Torchia MG. The developing human: clinically oriented embryology. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders;2013.3. Sadler TW. Langman's medical embryology. 13th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Wolters Kluwer;2016.4. Pickhardt PJ, Bhalla S. Intestinal malrotation in adolescents and adults: spectrum of clinical and imaging features. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002; 179:1429–1435.5. Schoenwolf GC, Bleyl SB, Brauer PR, Francis-West PH. Larsen's human embryology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Churchill Livingstone;2009.6. Moore KL, Agur AM, Dalley AF. Clinically oriented anatomy. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Wolters Kluwer;2014.7. Norris JM, Owusu D, Abdullah AA, Rajaratnam K. Subhepatic caecal tumour in an adult with intestinal malrotation. BMJ Case Rep. 2014; 2014:bcr2014207163.8. Nayak SB, George BM, Mishra S, Surendran S, Shetty P, Shetty SD. Sessile ileum, subhepatic cecum, and uncinate appendix that might lead to a diagnostic dilemma. Anat Cell Biol. 2013; 46:296–298.9. Brunicardi FC, Andersen DK, Billiar TR, Dunn DL, Hunter JG, Matthews JB, Pollock RE. Schwartz's principles of surgery. 10th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Medical;2015.10. M VN, Gireesh , Subhash LP, Pai V. Sub-hepatic caecum. J Clin Diagn Res. 2013; 7:1992–1993.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Accessory Left Colic Artery Arising from the Superior Mesenteric Artery: A Case Report
- A Rare Case of Coil Migration into the Duodenum after Embolization of a Right Colic Artery Pseudoaneurysm
- Accessory Middle Cerebral Artery
- Right sided descending and sigmoid colon: its embryological basis and clinical implications
- Unusual Course of the Accessory Meningeal Artery