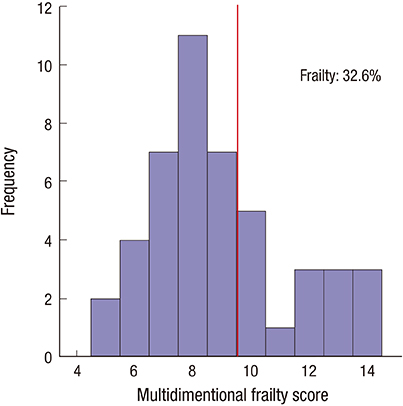
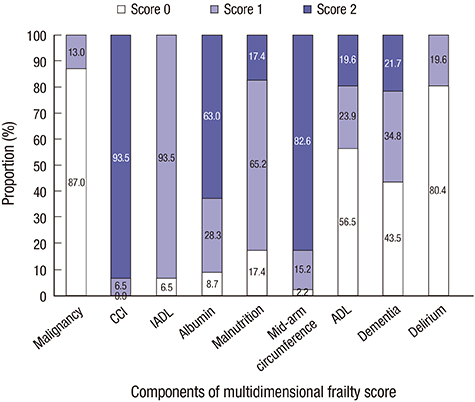
J Korean Med Sci.
2017 Nov;32(11):1800-1806. 10.3346/jkms.2017.32.11.1800.
Is Frailty a Modifiable Risk Factor of Future Adverse Outcomes in Elderly Patients with Incident End-Stage Renal Disease?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Postgraduate School, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Eulji General Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. mednep@snubh.org
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2390306
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2017.32.11.1800
Abstract
- Little is known about the clinical significance of frailty and changes of frailty after dialysis initiation in elderly patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD). We prospectively enrolled 46 elderly patients with incident ESRD at a dialysis center of a tertiary hospital between May 2013 and March 2015. Frailty was assessed by using a comprehensive geriatric assessment protocol and defined as a multidimensional frailty score of ≥ 10. The main outcome was the composite of all-cause death or cardiovascular hospitalization, as determined in June 2016. The median age of the 46 participants was 71.5 years, and 63.0% of them were men. During the median 17.7 months follow-up, the rate of composite outcome was 17.4%. In multivariate logistic regression analysis, after adjusting for age, sex, diabetes, body mass index (BMI), and time of predialytic nephrologic care, female sex, and increased BMI were associated with increased and decreased odds of frailty, respectively. In multivariate Cox proportional hazards analysis, after adjusting for age, sex, diabetes, BMI, and time of predialytic nephrologic care, frailty was significantly associated with the composite adverse outcome. In repeated frailty assessments, the multidimensional frailty score significantly improved 12 months after the initiation of dialysis, which largely relied on improved nutrition. Therefore, frailty needs to be assessed for risk stratification in elderly patients with incident ESRD.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Williams ME, Sandeep J, Catic A. Aging and ESRD demographics: consequences for the practice of dialysis. Semin Dial. 2012; 25:617–622.2. Jin DC. Major changes and improvements of dialysis therapy in Korea: review of end-stage renal disease registry. Korean J Intern Med. 2015; 30:17–22.3. Chandna SM, Da Silva-Gane M, Marshall C, Warwicker P, Greenwood RN, Farrington K. Survival of elderly patients with stage 5 CKD: comparison of conservative management and renal replacement therapy. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011; 26:1608–1614.4. Murtagh FE, Marsh JE, Donohoe P, Ekbal NJ, Sheerin NS, Harris FE. Dialysis or not? A comparative survival study of patients over 75 years with chronic kidney disease stage 5. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2007; 22:1955–1962.5. Kurella Tamura M, Covinsky KE, Chertow GM, Yaffe K, Landefeld CS, McCulloch CE. Functional status of elderly adults before and after initiation of dialysis. N Engl J Med. 2009; 361:1539–1547.6. Fried LP, Tangen CM, Walston J, Newman AB, Hirsch C, Gottdiener J, Seeman T, Tracy R, Kop WJ, Burke G, et al. Frailty in older adults: evidence for a phenotype. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2001; 56:M146–M156.7. Kim SW, Han HS, Jung HW, Kim KI, Hwang DW, Kang SB, Kim CH. Multidimensional frailty score for the prediction of postoperative mortality risk. JAMA Surg. 2014; 149:633–640.8. Baek SH, Lee SW, Kim SW, Ahn SY, Yu MY, Kim KI, Chin HJ, Na KY, Chae DW, Kim S. Frailty as a predictor of acute kidney injury in hospitalized elderly patients: a single center, retrospective cohort study. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0156444.9. Johansen KL. The frail dialysis population: a growing burden for the dialysis community. Blood Purif. 2015; 40:288–292.10. Johansen KL, Chertow GM, Jin C, Kutner NG. Significance of frailty among dialysis patients. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007; 18:2960–2967.11. McAdams-DeMarco MA, Law A, Salter ML, Boyarsky B, Gimenez L, Jaar BG, Walston JD, Segev DL. Frailty as a novel predictor of mortality and hospitalization in individuals of all ages undergoing hemodialysis. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2013; 61:896–901.12. McAdams-DeMarco MA, Suresh S, Law A, Salter ML, Gimenez LF, Jaar BG, Walston JD, Segev DL. Frailty and falls among adult patients undergoing chronic hemodialysis: a prospective cohort study. BMC Nephrol. 2013; 14:224.13. Kim YJ, Kim JH, Park MS, Lee KW, Kim KI, Bang SM, Lee JS, Kim CH. Comprehensive geriatric assessment in Korean elderly cancer patients receiving chemotherapy. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2011; 137:839–847.14. Charlson ME, Pompei P, Ales KL, MacKenzie CR. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation. J Chronic Dis. 1987; 40:373–383.15. Mahoney FI, Barthel DW. Functional evaluation: the Barthel Index. Md State Med J. 1965; 14:61–65.16. Lawton MP, Brody EM. Assessment of older people: self-maintaining and instrumental activities of daily living. Gerontologist. 1969; 9:179–186.17. Lee DY, Lee JH, Ju YS, Lee KU, Kim KW, Jhoo JH, Yoon JC, Ha J, Woo JI. The prevalence of dementia in older people in an urban population of Korea: the Seoul study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2002; 50:1233–1239.18. Gaudreau JD, Gagnon P, Harel F, Tremblay A, Roy MA. Fast, systematic, and continuous delirium assessment in hospitalized patients: the nursing delirium screening scale. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2005; 29:368–375.19. Vellas B, Guigoz Y, Garry PJ, Nourhashemi F, Bennahum D, Lauque S, Albarede JL. The Mini Nutritional Assessment (MNA) and its use in grading the nutritional state of elderly patients. Nutrition. 1999; 15:116–122.20. Choi JY, Cho KJ, Kim SW, Yoon SJ, Kang MG, Kim KI, Lee YK, Koo KH, Kim CH. Prediction of mortality and postoperative complications using the hip-multidimensional frailty score in elderly patients with hip fracture. Sci Rep. 2017; 7:42966.21. Choi JY, Yoon SJ, Kim SW, Jung HW, Kim KI, Kang E, Kim SW, Han HS, Kim CH. Prediction of postoperative complications using multidimensional frailty score in older female cancer patients with American Society of Anesthesiologists Physical Status Class 1 or 2. J Am Coll Surg. 2015; 221:652–660.e2.22. Levey AS, Stevens LA, Schmid CH, Zhang YL, Castro AF 3rd, Feldman HI, Kusek JW, Eggers P, Van Lente F, Greene T, et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med. 2009; 150:604–612.23. Johansen KL, Dalrymple LS, Glidden D, Delgado C, Kaysen GA, Grimes B, Chertow GM. Association of performance-based and self-reported function-based definitions of frailty with mortality among patients receiving hemodialysis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016; 11:626–632.24. Bao Y, Dalrymple L, Chertow GM, Kaysen GA, Johansen KL. Frailty, dialysis initiation, and mortality in end-stage renal disease. Arch Intern Med. 2012; 172:1071–1077.25. Delgado C, Doyle JW, Johansen KL. Association of frailty with body composition among patients on hemodialysis. J Ren Nutr. 2013; 23:356–362.26. Painter P, Kuskowski M. A closer look at frailty in ESRD: getting the measure right. Hemodial Int. 2013; 17:41–49.27. Johansen KL, Dalrymple LS, Delgado C, Kaysen GA, Kornak J, Grimes B, Chertow GM. Association between body composition and frailty among prevalent hemodialysis patients: a US Renal Data System special study. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014; 25:381–389.28. Drost D, Kalf A, Vogtlander N, van Munster BC. High prevalence of frailty in end-stage renal disease. Int Urol Nephrol. 2016; 48:1357–1362.29. McAdams-DeMarco MA, Tan J, Salter ML, Gross A, Meoni LA, Jaar BG, Kao WH, Parekh RS, Segev DL, Sozio SM. Frailty and cognitive function in incident hemodialysis patients. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015; 10:2181–2189.30. Salter ML, Gupta N, Massie AB, McAdams-DeMarco MA, Law AH, Jacob RL, Gimenez LF, Jaar BG, Walston JD, Segev DL. Perceived frailty and measured frailty among adults undergoing hemodialysis: a cross-sectional analysis. BMC Geriatr. 2015; 15:52.31. Kalantar-Zadeh K, Block G, Humphreys MH, Kopple JD. Reverse epidemiology of cardiovascular risk factors in maintenance dialysis patients. Kidney Int. 2003; 63:793–808.32. Mansur HN, Lovisi JC, Colugnati FA, Raposo NR, Fernandes NM, Bastos MG. Association of frailty with endothelial dysfunction and its possible impact on negative outcomes in Brazilian predialysis patients with chronic kidney disease. BMC Nephrol. 2015; 16:157.33. Barzilay JI, Blaum C, Moore T, Xue QL, Hirsch CH, Walston JD, Fried LP. Insulin resistance and inflammation as precursors of frailty: the Cardiovascular Health Study. Arch Intern Med. 2007; 167:635–641.34. McAdams-DeMarco MA, Isaacs K, Darko L, Salter ML, Gupta N, King EA, Walston J, Segev DL. Changes in frailty after kidney transplantation. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2015; 63:2152–2157.35. Lee KH, Cho JH, Kwon O, Kim SU, Kim RH, Cho YW, Jung HY, Choi JY, Kim CD, Kim YL, et al. Low prealbumin levels are independently associated with higher mortality in patients on peritoneal dialysis. Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2016; 35:169–175.36. Chung W, Jung ES, Shin D, Choi SH, Jung JY, Chang JH, Lee HH, Kim DK, Kim S. Low resistin level is associated with poor hospitalization-free survival in hemodialysis patients. J Korean Med Sci. 2012; 27:377–381.37. Kang SS, Chang JW, Park Y. Nutritional status predicts 10-year mortality in patients with end-stage renal disease on hemodialysis. Nutrients. 2017; 9:E399.38. Jung HW, Jang IY, Lee YS, Lee CK, Cho EI, Kang WY, Chae JH, Lee EJ, Kim DH. Prevalence of frailty and aging-related health conditions in older Koreans in rural communities: a cross-sectional analysis of the aging study of Pyeongchang rural area. J Korean Med Sci. 2016; 31:345–352.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Therapeutic Consideration for the Elderly Patients with End Stage Renal Disease
- Cortical thickness of the rostral anterior cingulate gyrus is associated with frailty in patients with end-stage renal disease undergoing hemodialysis in Korea: a cross-sectional study
- Frailty in Geriatric Patients with Head and Neck Cancer and its Implication in Survivorship
- The Concept of Frailty: A Review of the Literature
- Social Frailty