Lab Med Online.
2017 Oct;7(4):206-210. 10.3343/lmo.2017.7.4.206.
Neutrophilic Leukemoid Reaction Associated with Malignancy Initially Suspected as Chronic Neutrophilic Leukemia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. JungWonH@ewha.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Dongguk University, Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea. hjhuh@duih.org
- KMID: 2389662
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/lmo.2017.7.4.206
Abstract
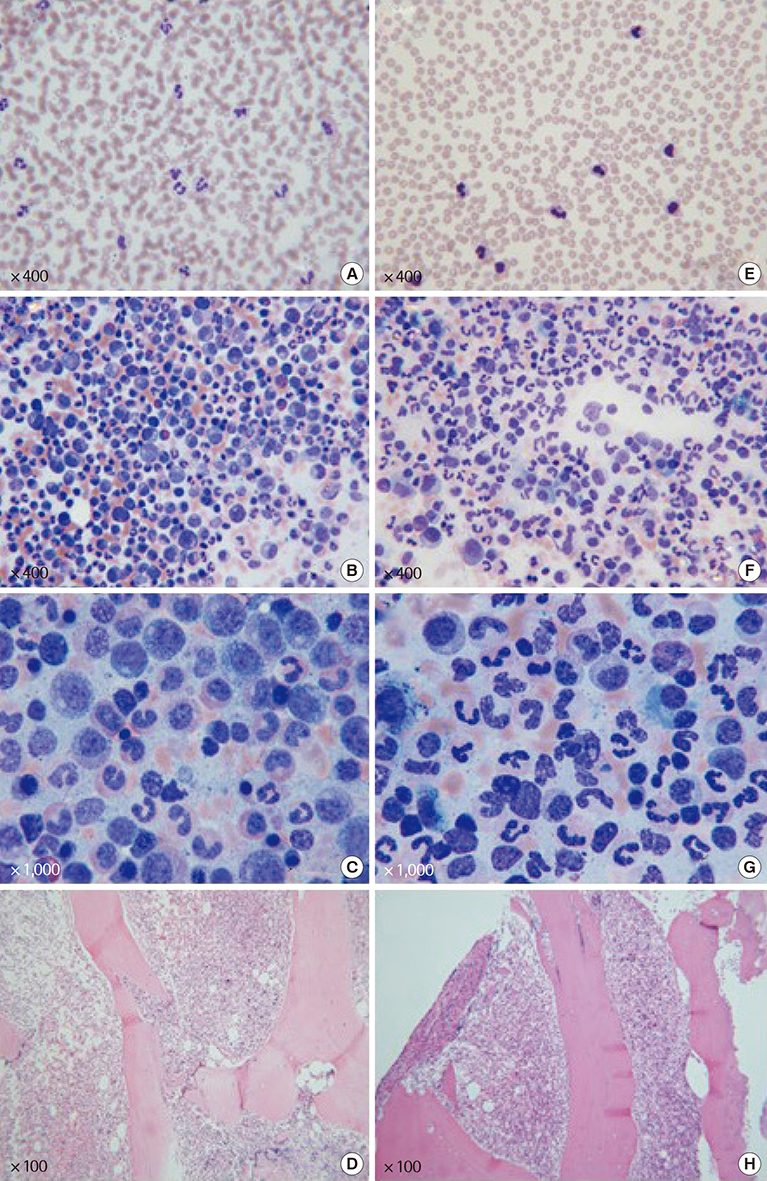
- Although neutrophilia can manifest from various causes, it is important to be able to distinguish chronic neutrophilic leukemia (CNL) from neutrophilic leukemoid reactions (NLR). In this paper, we describe four cases of leukocytosis with neutrophilia, including one case of CNL with a T618I mutation in colony stimulating factor 3 receptor (CSF3R) and three cases of NLR associated with malignancy or sepsis, which were initially suspected as CNL. Of the three NLR cases, one was associated with ovarian cancer, one with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance and one with multiple myeloma with sepsis. This study demonstrated that confirming the clonality of myeloid cells with CSF3R T618I could contribute to making an accurate differential diagnosis between CNL and NLR in patients with solid cancers or plasma cell neoplasms caused by paraneoplastic syndromes and/or infection.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Colony-Stimulating Factors
Diagnosis, Differential
Humans
Leukemia, Neutrophilic, Chronic*
Leukemoid Reaction*
Leukocytosis
Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance
Multiple Myeloma
Myeloid Cells
Neoplasms, Plasma Cell
Neutrophils*
Ovarian Neoplasms
Paraneoplastic Syndromes
Sepsis
Colony-Stimulating Factors
Figure
Reference
-
1. Granger JM, Kontoyiannis DP. Etiology and outcome of extreme leukocytosis in 758 nonhematologic cancer patients: a retrospective, single-institution study. Cancer. 2009; 115:3919–3923.
Article2. Halkes CJ, Dijstelbloem HM, Eelkman Rooda SJ, Kramer MH. Extreme leucocytosis: not always leukaemia. Neth J Med. 2007; 65:248–251.3. Pardanani A, Lasho TL, Laborde RR, Elliott M, Hanson CA, Knudson RA, et al. CSF3R T618I is a highly prevalent and specific mutation in chronic neutrophilic leukemia. Leukemia. 2013; 27:1870–1873.
Article4. Maxson JE, Gotlib J, Pollyea DA, Fleischman AG, Agarwal A, Eide CA, et al. Oncogenic CSF3R mutations in chronic neutrophilic leukemia and atypical CML. N Engl J Med. 2013; 368:1781–1790.
Article5. Aliper AM, Frieden-Korovkina VP, Buzdin A, Roumiantsev SA, Zhavoronkov A. A role for G-CSF and GM-CSF in nonmyeloid cancers. Cancer Med. 2014; 3:737–746.
Article6. Blombery P, Kothari J, Yong K, Allen C, Gale RE, Khwaja A. Plasma cell neoplasm associated chronic neutrophilic leukemia with membrane proximal and truncating CSF3R mutations. Leuk Lymphoma. 2014; 55:1661–1662.
Article7. Bain BJ, Ahmad S. Chronic neutrophilic leukaemia and plasma cell-related neutrophilic leukaemoid reactions. Br J Haematol. 2015; 171:400–410.
Article8. Kasuga I, Makino S, Kiyokawa H, Katoh H, Ebihara Y, Ohyashiki K. Tumor-related leukocytosis is linked with poor prognosis in patients with lung carcinoma. Cancer. 2001; 92:2399–2405.
Article9. Kitamura H, Kodama F, Odagiri S, Nagahara N, Inoue T, Kanisawa M. Granulocytosis associated with malignant neoplasms: a clinicopathologic study and demonstration of colony-stimulating activity in tumor extracts. Hum Pathol. 1989; 20:878–885.
Article10. Berdel WE, Danhauser-Riedl S, Steinhauser G, Winton EF. Various human hematopoietic growth factors (interleukin-3, GM-CSF, G-CSF) stimulate clonal growth of nonhematopoietic tumor cells. Blood. 1989; 73:80–83.
Article11. Nakayama S, Yokote T, Iwaki K, Hirata Y, Akioka T, Miyoshi T, et al. Co-expression of multiple cytokines and their receptors in primary clear cell sarcoma of the pubic bone with features of a small round cell tumor. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2012; 25:799–804.
Article12. Dorn C, Bugl S, Malenke E, Muller MR, Weisel KC, Vogel U, et al. Paraneoplastic granulocyte colony-stimulating factor secretion in soft tissue sarcoma mimicking myeloproliferative neoplasia: a case report. BMC Res Notes. 2014; 7:313.
Article13. Kumar AK, Satyan MT, Holzbeierlein J, Mirza M, Van Veldhuizen P. Leukemoid reaction and autocrine growth of bladder cancer induced by paraneoplastic production of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor--a potential neoplastic marker: a case report and review of the literature. J Med Case Rep. 2014; 8:147.14. Qing L, Xiang T, Guofu Z, Weiwei F. Leukemoid reaction in cervical cancer: a case report and review of the literature. BMC Cancer. 2014; 14:670.
Article15. Nimieri HS, Makoni SN, Madziwa FH, Nemiary DS. Leukemoid reaction response to chemotherapy and radiotherapy in a patient with cervical carcinoma. Ann Hematol. 2003; 82:316–317.
Article16. Elliott MA, Tefferi A. Chronic neutrophilic leukemia 2016: Update on diagnosis, molecular genetics, prognosis, and management. Am J Hematol. 2016; 91:341–349.
Article17. Nedeljkovic M, He S, Szer J, Juneja S. Chronic neutrophilia associated with myeloma: is it clonal. Leuk Lymphoma. 2014; 55:439–440.
Article