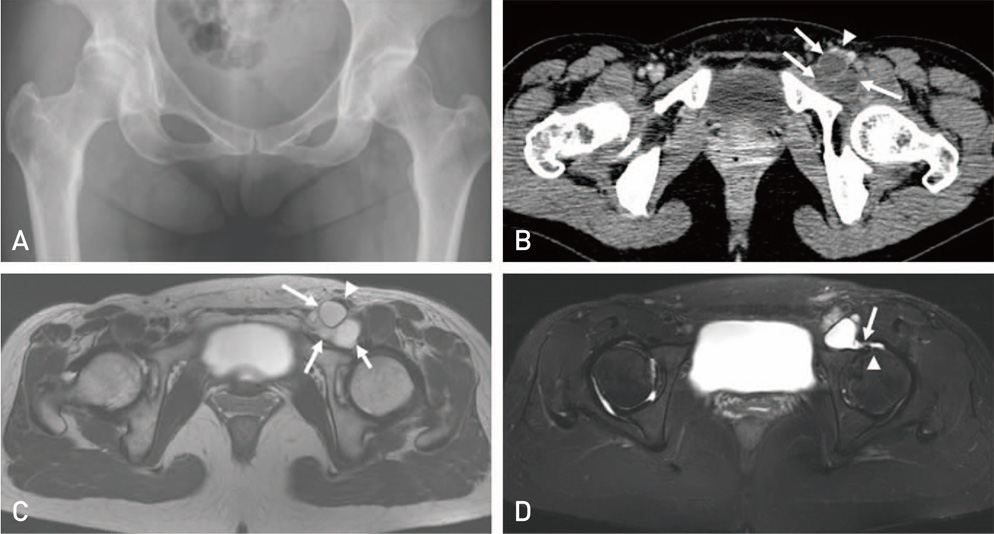
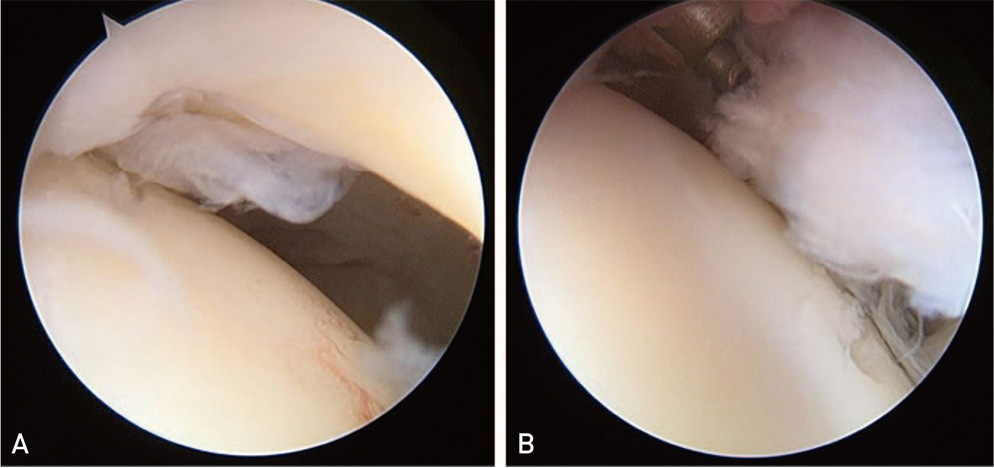
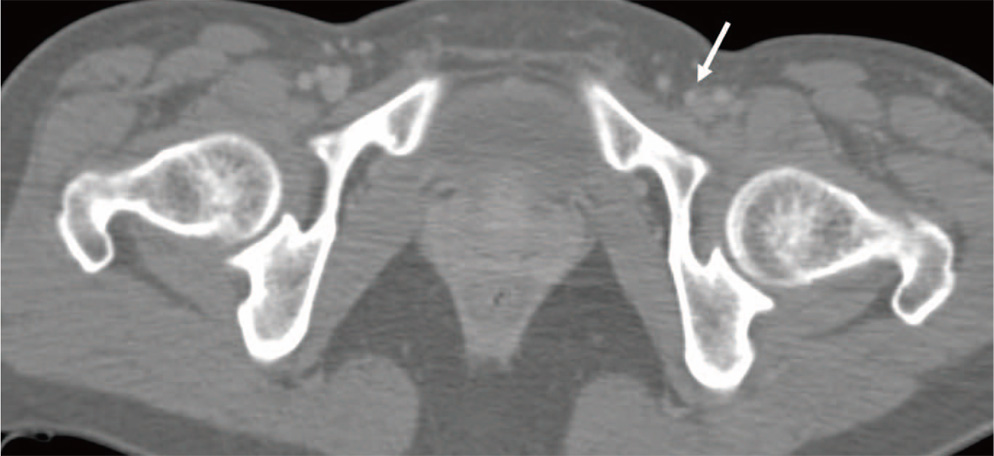
Hip Pelvis.
2017 Sep;29(3):194-198. 10.5371/hp.2017.29.3.194.
Paralabral Cyst of the Hip Compressing Common Femoral Vein Treated with Sono-guided Cyst Aspiration Followed by Arthroscopic Labral Debridement: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea. wsleeos@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Bundang Jesaeng General Hospital, Daejin Medical Center, Seoungnam, Korea.
- KMID: 2389526
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5371/hp.2017.29.3.194
Abstract
- Paralabral cyst around hip is reported to be a cause of compression of the major neurovascular structures. Although, arthroscopic cyst and labral debridement is generally accepted as the effective treatment, there is limited literature available regarding treatment options for paralabral cysts in the hip. We present a case of paralabral cyst compressing left common femoral vein in the hip that was treated with sono-guided cyst aspiration followed by arthroscopic labral debridement.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Byström S, Adalberth G, Milbrink J. Giant synovial cyst of the hip: an unusual presentation with compression of the femoral vessels. Can J Surg. 1995; 38:368–370.2. Kullar RS, Kapron AL, Ihnat D, Aoki SK, Maak TG. Acetabular paralabral cyst: an unusual cause of femoral vein compression. Arthrosc Tech. 2015; 4:e35–e40.
Article3. Magee T, Hinson G. Association of paralabral cysts with acetabular disorders. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000; 174:1381–1384.
Article4. Tung GA, Entzian D, Stern JB, Green A. MR imaging and MR arthrography of paraglenoid labral cysts. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000; 174:1707–1715.
Article5. Lee WY, Hwang DS, Kang C, Zheng L. Entrapment neuropathy of the sciatic nerve caused by a paralabral cyst: three cases treated arthroscopically. JBJS Case Connect. 2016; 6:e82.
Article6. Hulet C, Souquet D, Alexandre P, Locker B, Beguin J, Vielpeau C. Arthroscopic treatment of 105 lateral meniscal cysts with 5-year average follow-up. Arthroscopy. 2004; 20:831–836.
Article7. Yukata K, Arai K, Yoshizumi Y, Tamano K, Imada K, Nakaima N. Obturator neuropathy caused by an acetabular labral cyst: MRI findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005; 184:3 Suppl. S112–S114.
Article8. Robertson WJ, Kadrmas WR, Kelly BT. Arthroscopic management of labral tears in the hip: a systematic review of the literature. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007; 455:88–92.9. Lee KH, Park YS, Lim SJ. Arthroscopic treatment of symptomatic paralabral cysts in the hip. Orthopedics. 2013; 36:e373–e376.
Article10. Kanauchi T, Suganuma J, Mochizuki R, Uchikawa S. Arthroscopic treatment of femoral nerve paresthesia caused by an acetabular paralabral cyst. Orthopedics. 2014; 37:e496–e499.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Paralabral Cysts and Their Correlation with Acetabular Disorder
- Multidirectional Instability Accompanying an Inferior Labral Cyst
- Arthroscopic Decompression of an Inferior Paralabral Cyst of the Shoulder in an Elderly Patient: A Case Report
- Unilateral Leg Swelling Caused by a Ganglion Cyst on the Hip Joint
- The Follow Up Results of Residual Spinoglenoid Ganglion Cyst after Arthroscopic Decompression and Superior Labral Repair: Cases Report