Ann Rehabil Med.
2017 Apr;41(2):323-327. 10.5535/arm.2017.41.2.323.
Extravasation of the Contrast Material During Voiding Cystourethrography in a Chronic Spinal Cord Injury Patient: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea. jseok337@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Daegu Fatima Hospital, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2389493
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2017.41.2.323
Abstract
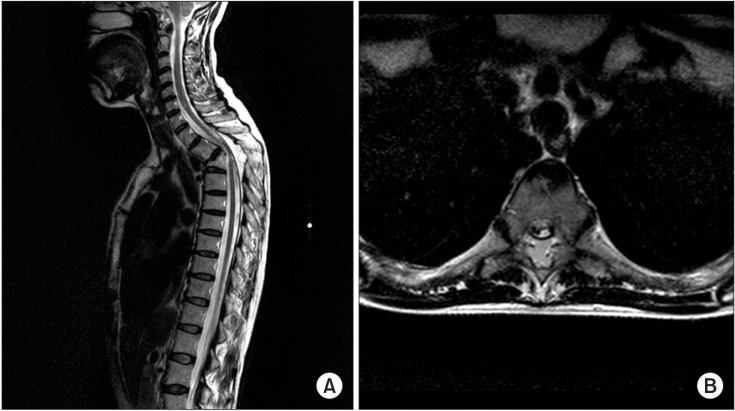
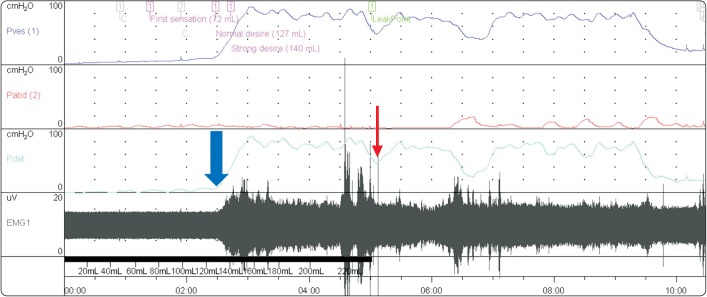
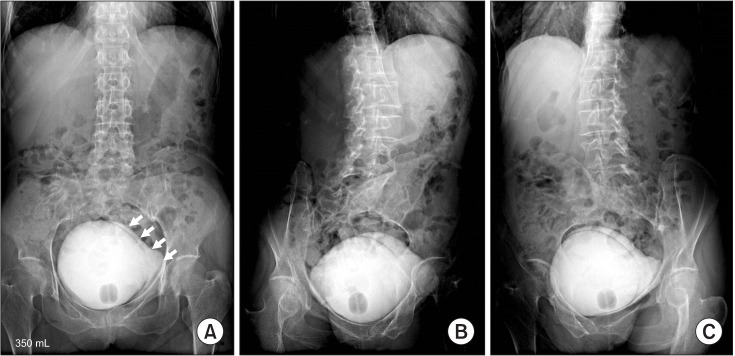
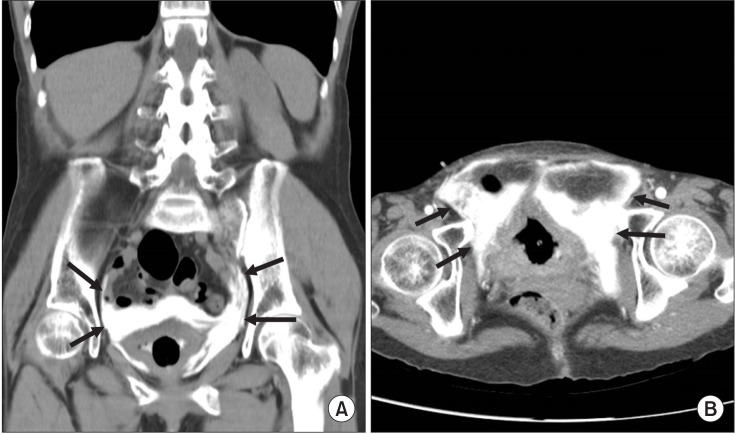
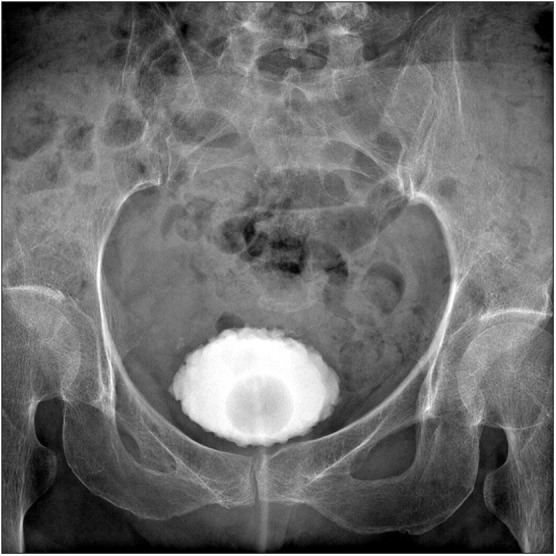
- Neurogenic bladder is common in most spinal cord injury patients. Voiding cystourethrography (VCUG) is recommended in these patients to detect urinary tract complications. However, rare but serious complications may occur during VCUG, although VCUG is generally safe. There are several case reports of bladder rupture occurring in pediatric patients. Here, we report the first case of iatrogenic bladder rupture in an adult spinal cord injury patient in Korea. Particularly, extravasation of contrast without manual instillation has hardly ever been reported. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first reported case of bladder rupture without manual instillation during VCUG. We report a case of a 59-year-old female with paraplegia due to tuberculous spondylitis who underwent VCUG as a part of routine evaluation of neurogenic bladder. Extravasation of the contrast media during VCUG developed as a complication and the patient recovered spontaneously without any intervention. Therefore, VCUG should be performed properly in chronic spinal cord injury patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Perkash I. Long-term urologic management of the patient with spinal cord injury. Urol Clin North Am. 1993; 20:423–434. PMID: 8351768.
Article2. McAlister WH, Cacciarelli A, Shackelford GD. Complications associated with cystography in children. Radiology. 1974; 111:167–172. PMID: 4593165.
Article3. Wosnitzer M, Shusterman D, Barone JG. Bladder rupture in premature infant during voiding cystourethrography. Urology. 2005; 66:432.
Article4. Keihani S, Kajbafzadeh AM. Bladder rupture after voiding cystourethrography: a case report and literature review on pitfalls and bladder volume estimation. Can Urol Assoc J. 2015; 9:E826–E829. PMID: 26600895.
Article5. Kajbafzadeh AM, Saeedi P, Sina AR, Payabvash S, Salmasi AH. Infantile bladder rupture during voiding cystourethrography. Int Braz J Urol. 2007; 33:532–535. PMID: 17767759.
Article6. Santucci RA, McAninch JW. Bladder injuries: evaluation and management. Braz J Urol. 2000; 26:408–414.7. Matsumoto AH, Clark RL, Cuttino JT Jr. Bladder mucosal tears during voiding cystourethrography in chronic renal failure. Urol Radiol. 1986; 8:81–84. PMID: 3538606.
Article8. Landau EH, Jayanthi VR, Churchill BM, Shapiro E, Gilmour RF, Khoury AE, et al. Loss of elasticity in dysfunctional bladders: urodynamic and histochemical correlation. J Urol. 1994; 152:702–705. PMID: 8021999.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Bladder Rupture during Voiding Cystourethrography
- Changes of Voiding Methods in Patients with Spinal Cord Injury
- Extravasation Injury of Forearm by Computed Tomography Contrast Medium
- An objective score to predict upper tract deterioration in spinal cord injury patients
- Subcutaneous Injection Contrast Media Extravasation : 3D CT Appearance