Ann Rehabil Med.
2017 Jun;41(3):441-449. 10.5535/arm.2017.41.3.441.
A New Instrument for Measuring Tibial Torsion in Pediatric Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine and Christian Medical Research Center, Presbyterian Medical Center, Seonam University College of Medicine, Jeonju, Korea. gvcdr@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2389460
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2017.41.3.441
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To develop and test the validity and reliability of a new instrument for measuring the thigh-foot angle (TFA) for the patients with in-toeing and out-toeing gait.
METHODS
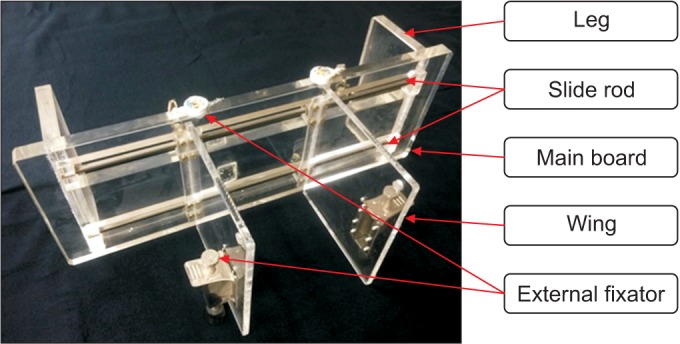
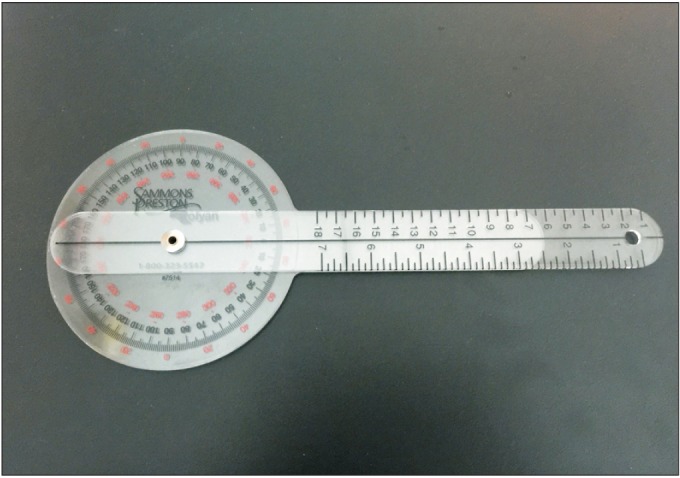
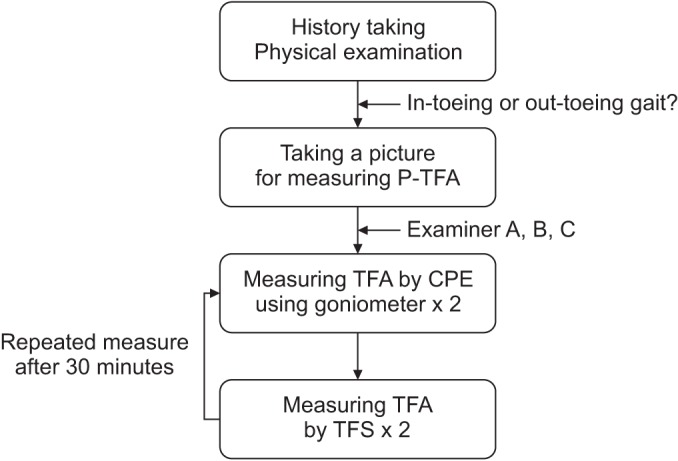
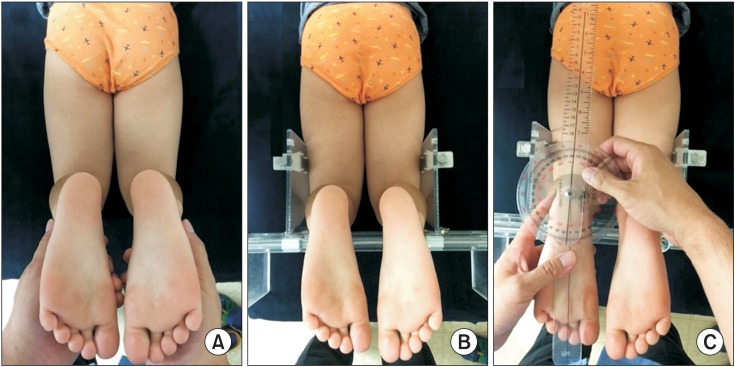
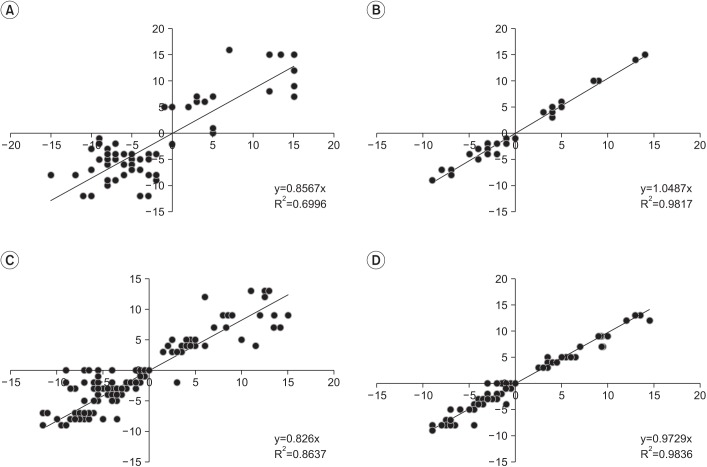
The new instrument (Thigh-Foot Supporter [TFS]) was developed by measuring the TFA during regular examination of the tibial torsional status. The study included 40 children who presented with in-toeing and out-toeing gaits. We took a picture of each case to measure photographic-TFA (P-TFA) in the proper position and to establish a criterion. Study participants were examined by three independent physicians (A, B, and C) who had one, three and ten years of experience in the field, respectively. Each examiner conducted a separate classical physical examination (CPE) of every participant using a gait goniometer followed by a TFA assessment of each pediatric patient with or without the TFS. Thirty minutes later, repeated in the same way was measured.
RESULTS
Less experienced examiner A showed significant differences between the TFA values depending on whether TFS used (left p=0.003 and right p=0.008). However, experienced examiners B and C did not show significant differences. Using TFS, less experienced examiner A showed a high validity and all examiner's inter-test and the inter-personal reliabilities increased.
CONCLUSION
TFS may increase validity and reliability in measuring tibial torsion in patients who has a rotational problem in lower extremities. It would be more useful in less experienced examiners.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jang SH, Woo BS, Park SB, Lee SG. Relationship between femoral anteversion and tibial torsion in intoeing gait. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 1999; 23:390–396.2. Kumar SJ, MacEwen GD. Torsional abnormalities in children's lower extremities. Orthop Clin North Am. 1982; 13:629–639. PMID: 7099592.
Article3. Sass P, Hassan G. Lower extremity abnormalities in children. Am Fam Physician. 2003; 68:461–468. PMID: 12924829.4. Fabry G, Cheng LX, Molenaers G. Normal and abnormal torsional development in children. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994; (302):22–26.
Article5. Butler-Manuel PA, Guy RL, Heatley FW. Measurement of tibial torsion: a new technique applicable to ultrasound and computed tomography. Br J Radiol. 1992; 65:119–126. PMID: 1540801.6. Clementz BG, Magnusson A. Assessment of tibial torsion employing fluoroscopy, computed tomography and the cryosectioning technique. Acta Radiol. 1989; 30:75–80. PMID: 2914121.
Article7. Jakob RP, Haertel M, Stussi E. Tibial torsion calculated by computerized tomography and compared to other methods of measurement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1980; 62-B:238–242. PMID: 7364840.8. Staheli LT, Corbett M, Wyss C, King H. Lower-extremity rotational problems in children. Normal values to guide management. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1985; 67:39–47. PMID: 3968103.
Article9. Rethlefsen SA, Healy BS, Wren TA, Skaggs DL, Kay RM. Causes of intoeing gait in children with cerebral palsy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006; 88:2175–2180. PMID: 17015594.
Article10. Li YH, Leong JC. Intoeing gait in children. Hong Kong Med J. 1999; 5:360–366. PMID: 10870163.11. Kim SI, Park SB, Lee KM. Measurement of femoral anteversion using 3 dimensional imaging technique. J Korean Soc Picture Archiving Commun Syst. 1995; 1:53–58.12. Arnold AS, Komattu AV, Delp SL. Internal rotation gait: a compensatory mechanism to restore abduction capacity decreased by bone deformity. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1997; 39:40–44. PMID: 9003728.
Article13. Staheli LT. Rotational problems in children. Instr Course Lect. 1994; 43:199–209. PMID: 9097150.
Article14. Lincoln TL, Suen PW. Common rotational variations in children. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2003; 11:312–320. PMID: 14565753.
Article15. Kim SS, Kim SK. Derotational osteotomy and external fixation for increased femoral anteversion. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2004; 39:361–365.
Article16. Kwon OY, Tuttle LJ, Commean PK, Mueller MJ. Reliability and validity of measures of hammer toe deformity angle and tibial torsion. Foot (Edinb). 2009; 19:149–155. PMID: 20161156.
Article17. Hernandez RJ, Tachdjian MO, Poznanski AK, Dias LS. CT determination of femoral torsion. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1981; 137:97–101. PMID: 6787898.
Article18. Kitaoka HB, Weiner DS, Cook AJ, Hoyt WA Jr, Askew MJ. Relationship between femoral anteversion and osteoarthritis of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop. 1989; 9:396–404. PMID: 2732318.
Article19. Murphy SB, Simon SR, Kijewski PK, Wilkinson RH, Griscom NT. Femoral anteversion. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1987; 69:1169–1176. PMID: 3667647.
Article20. Staheli LT. In-toeing and out-toeing in children. J Fam Pract. 1983; 16:1005–1011. PMID: 6842143.21. Lee SH, Chung CY, Park MS, Choi IH, Cho TJ. Tibial torsion in cerebral palsy: validity and reliability of measurement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009; 467:2098–2104. PMID: 19159112.
Article22. Milner CE, Soames RW. A comparison of four in vivo methods of measuring tibial torsion. J Anat. 1998; 193(Pt 1):139–144. PMID: 9758144.
Article23. Kim HD, Lee DS, Eom MJ, Hwang JS, Han NM, Jo GY. Relationship between physical examinations and two-dimensional computed tomographic findings in children with intoeing gait. Ann Rehabil Med. 2011; 35:491–498. PMID: 22506164.
Article24. Fabry G. Normal and abnormal torsional development of the lower extremities. Acta Orthop Belg. 1997; 63:229–232. PMID: 9479773.25. Chung CY, Choi IH, Lee DY, Yoon KS, Lee DH, Sohn CS. Steel's gluteus medius and minimus advancement for in-toeing in spastic cerebral palsy. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 1996; 31:27–32.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Usefulness of tibia counter rotator (TCR) for treatment of tibial internal torsion in children
- Relationship between Femoral Anteversion and Tibial Torsion in Intoeing Gait
- Effect of the Tibia Counter Rotator Orthosis for Tibial Internal Torsion Children: A Preliminary Study
- The Availability of Radiological Measurement of Tibial Torsion: Three-Dimensional Computed Tomography Reconstruction
- Tibial Torsion in Children of the Jeju Area