Clin Endosc.
2017 Jul;50(4):328-333. 10.5946/ce.2017.089.
Training in Endoscopy: Enteroscopy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. jinsoo@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2389237
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2017.089
Abstract
- The balloon-assisted enteroscope has been regarded as the standard device for direct visualization of deep small bowels and allows for the diagnosis and treatment of small bowel disease. At the beginning, its application was focused on the diagnosis of obscure gastrointestinal bleeding, inflammatory bowel disease, and small bowel tumor. However, the indications are being expanded to various therapeutic procedures, not only confined to bleeding control. With the expansion of the indications, the need to perform enteroscopy effectively and safely is increasing. Recent studies have been focused on the diagnostic yield, therapeutic yield, and long-term outcomes of the device. However, with the increasing number of procedures, procedural guidelines and quality indicators are also needed.
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Clinicopathological Features of Small Bowel Tumors Diagnosed by Video Capsule Endoscopy and Balloon-Assisted Enteroscopy: A Single Center Experience
Ah Young Yoo, Beom Jae Lee, Won Shik Kim, Seong Min Kim, Seung Han Kim, Moon Kyung Joo, Hyo Jung Kim, Jong-Jae Park
Clin Endosc. 2021;54(1):85-91. doi: 10.5946/ce.2020.047.Balloon-Assisted Enteroscopy and Capsule Endoscopy in Suspected Small Bowel Crohn’s Disease
Hsu-Heng Yen, Chen-Wang Chang, Jen-Wei Chou, Shu-Chen Wei
Clin Endosc. 2017;50(5):417-423. doi: 10.5946/ce.2017.142.
Reference
-
1. Hounnou G, Destrieux C, Desmé J, Bertrand P, Velut S. Anatomical study of the length of the human intestine. Surg Radiol Anat. 2002; 24:290–294.2. Hiratsuka H, Hasegawa M, Ushiromachi K, Endo T, Suzuki S, Nishikawa F. Endoscopic diagnosis in the small intestine. Stomach Intestine. 1972; 7:1679–1685.3. Tada M, Akasaka Y, Misaki F, Kwaie K. Clinical evaluation of a sondetype small intestinal fiberscope. Endoscopy. 1977; 9:33–38.
Article4. Pennazio M, Spada C, Eliakim R, et al. Small-bowel capsule endoscopy and device-assisted enteroscopy for diagnosis and treatment of small-bowel disorders: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) clinical guideline. Endoscopy. 2015; 47:352–376.
Article5. Yamamoto H, Sekine Y, Sato Y, et al. Total enteroscopy with a nonsurgical steerable double-balloon method. Gastrointest Endosc. 2001; 53:216–220.
Article6. Tsujikawa T, Saitoh Y, Andoh A, et al. Novel single-balloon enteroscopy for diagnosis and treatment of the small intestine: preliminary experiences. Endoscopy. 2008; 40:11–15.
Article7. Matsushita M, Shimatani M, Okazaki K. Clockwise insertion: a risk factor of pancreatic hyperamylasemia and acute pancreatitis after peroral balloon-assisted enteroscopy. Dig Endosc. 2016; 28:482.
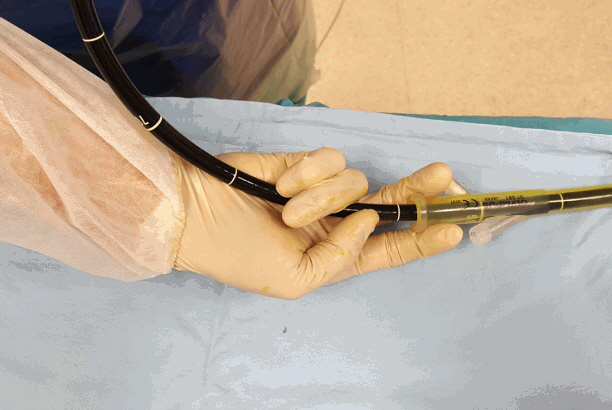
Article8. Araki A, Tsuchiya K, Okada E, et al. Single-operator double-balloon endoscopy (DBE) is as effective as dual-operator DBE. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009; 24:770–775.
Article9. Kav T, Balaban Y, Bayraktar Y. The power suction maneuver in single-balloon enteroscopy. Endoscopy. 2008; 40:961–962. author reply 962.
Article10. Manno M, Mussetto A, Conigliaro R. Preliminary results of alternative “simultaneous” technique for single-balloon enteroscopy. Endoscopy. 2008; 40:538. author reply 539.
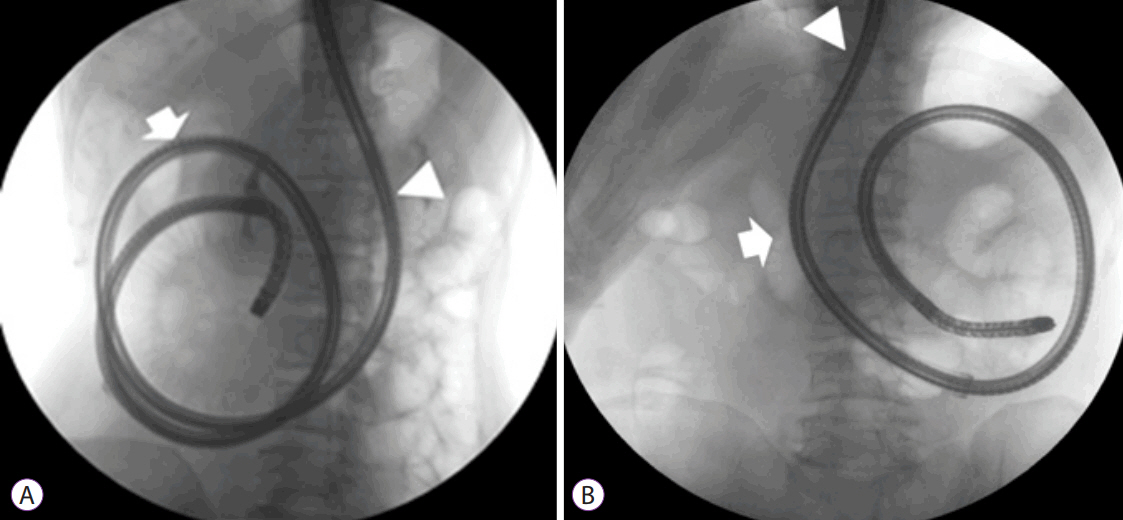
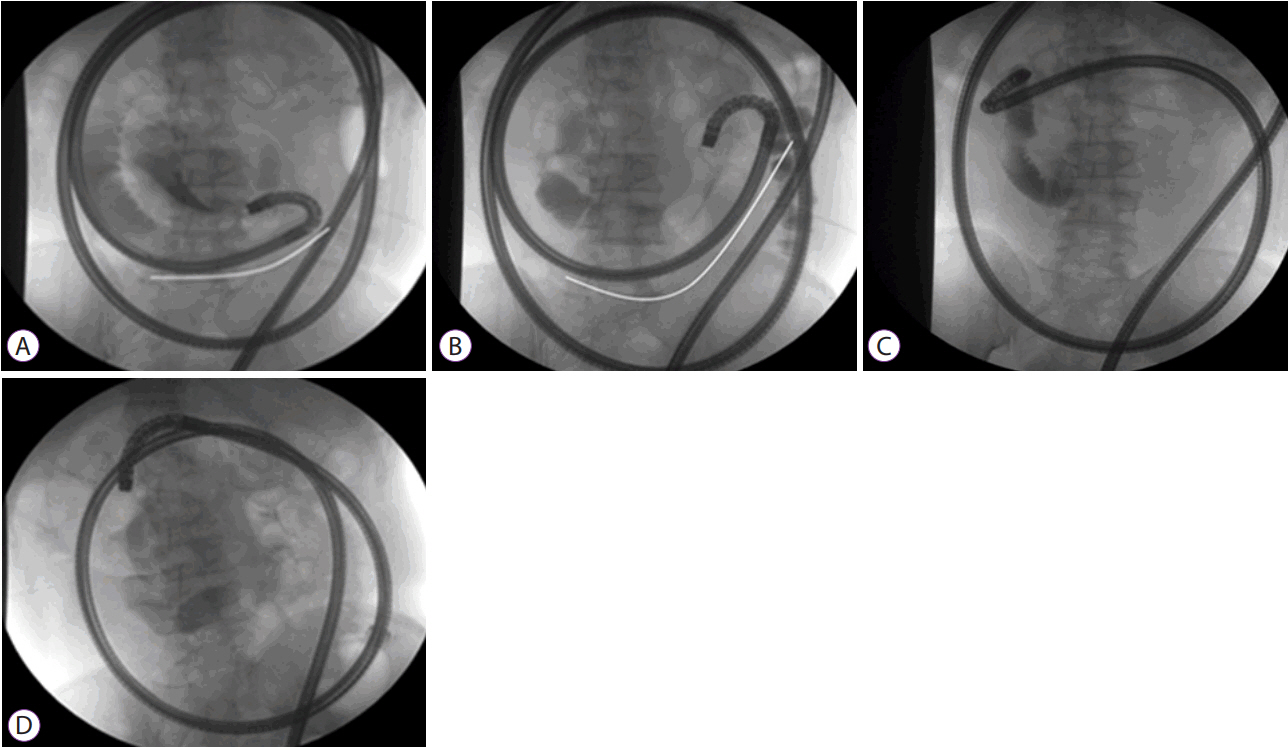
Article11. Despott EJ, Murino A, Fraser C. Management of deep looping when failing to progress at double-balloon enteroscopy. Endoscopy. 2011; 43 Suppl 2 UCTN:E275–E276.
Article12. Gay G, Delvaux M, Fassler I. Outcome of capsule endoscopy in determining indication and route for push-and-pull enteroscopy. Endoscopy. 2006; 38:49–58.
Article13. May A, Nachbar L, Schneider M, Neumann M, Ell C. Push-and-pull enteroscopy using the double-balloon technique: method of assessing depth of insertion and training of the enteroscopy technique using the Erlangen Endo-Trainer. Endoscopy. 2005; 37:66–70.
Article14. Li XB, Dai J, Chen HM, et al. A novel modality for the estimation of the enteroscope insertion depth during double-balloon enteroscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 72:999–1005.
Article15. Efthymiou M, Desmond PV, Brown G, et al. SINGLE-01: a randomized, controlled trial comparing the efficacy and depth of insertion of single- and double-balloon enteroscopy by using a novel method to determine insertion depth. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012; 76:972–980.
Article16. Mehdizadeh S, Ross A, Gerson L, et al. What is the learning curve associated with double-balloon enteroscopy? Technical details and early experience in 6 U.S. tertiary care centers. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006; 64:740–750.
Article17. Mehdizadeh S, Han NJ, Cheng DW, Chen GC, Lo SK. Success rate of retrograde double-balloon enteroscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 65:633–639.
Article18. Tee HP, How SH, Kaffes AJ. Learning curve for double-balloon enteroscopy: findings from an analysis of 282 procedures. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2012; 4:368–372.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Does Single Balloon Enteroscopy Have Similar Efficacy and Endoscopic Performance Compared with Double Balloon Enteroscopy?
- Diagnostic and Therapeutic Capability of Double-Balloon Enteroscopy in Clinical Practice
- Recent developments in small bowel endoscopy: the “black box” is now open!
- Deep Enteroscopy: Which Technique Will Survive?
- A Case of Proximal Jejunal Diverticular Bleeding Diagnosed by Double Balloon Enteroscopy and Treated by Colonoscopic Hemoclipping