Ann Dermatol.
2017 Oct;29(5):655-657. 10.5021/ad.2017.29.5.655.
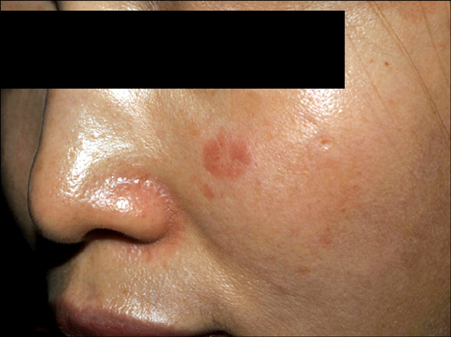
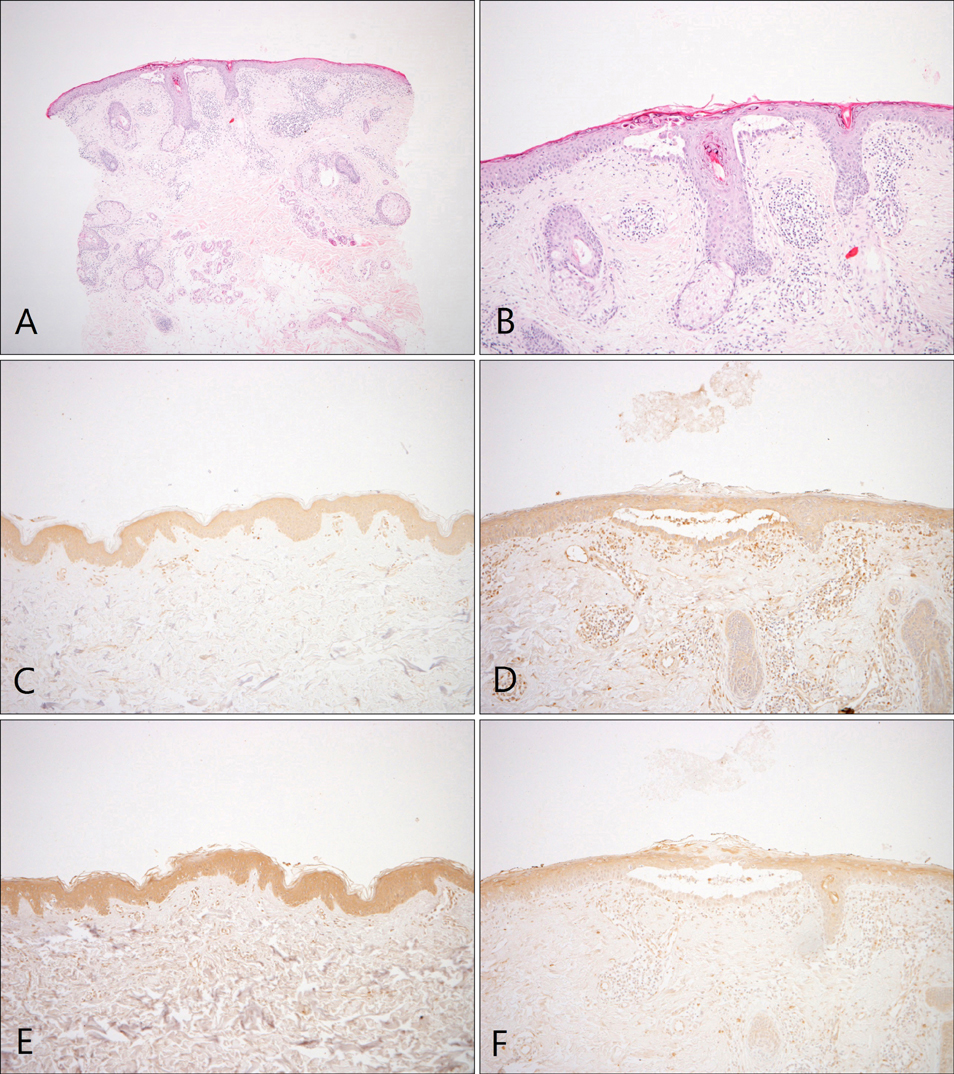
Incidental Focal Acantholytic Dyskeratosis in a Patient with Discoid Lupus Erythematosus: A Possible Role for SPCA1 in the Pathogenesis of the Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. Jhoon@cnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2388929
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2017.29.5.655
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Park SY, Lee HJ, Shin JY, Ahn SK. Incidental focal acantholytic dyskeratosis in the setting of rosacea. Ann Dermatol. 2013; 25:518–520.
Article2. Ackerman AB. Focal acantholytic dyskeratosis. Arch Dermatol. 1972; 106:702–706.
Article3. Dhitavat J, Fairclough RJ, Hovnanian A, Burge SM. Calcium pumps and keratinocytes: lessons from Darier's disease and Hailey-Hailey disease. Br J Dermatol. 2004; 150:821–828.
Article4. Porgpermdee S, Yu X, Takagi A, Mayuzumi N, Ogawa H, Ikeda S. Expression of SPCA1 (Hailey-Hailey disease gene product) in acantholytic dermatoses. J Dermatol Sci. 2005; 40:137–140.
Article5. Porgpermdee S, Takagi A, Mayuzumi N, Ogawa H, Ikeda S, Nakamura S. Expression of SERCA2 (Darier's disease gene product) in acantholytic dermatoses. J Dermatol Sci. 2006; 43:146–149.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Focal Acantholytic Dyskeratosis Presenting as a Solitary Papule
- A Case of Focal Acantholytic Dyskeratosis Occurring on both the Lip and the Anal Canal
- Two Cases of Hypertrophic Discoid Erythemas in Patients with Chronic Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus
- Vitiligo Developed in a Patient with Discoid Lupus Erythematosus
- A Case of Acantholytic Dyskeratotic Epidermal Nevus