J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2017 Aug;52(4):298-304. 10.4055/jkoa.2017.52.4.298.
Morton's Neuroma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Foot and Ankle Surgery, Nowon Eulji Medical Center, Eulji University, Seoul, Korea. youngkw1@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2387787
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2017.52.4.298
Abstract
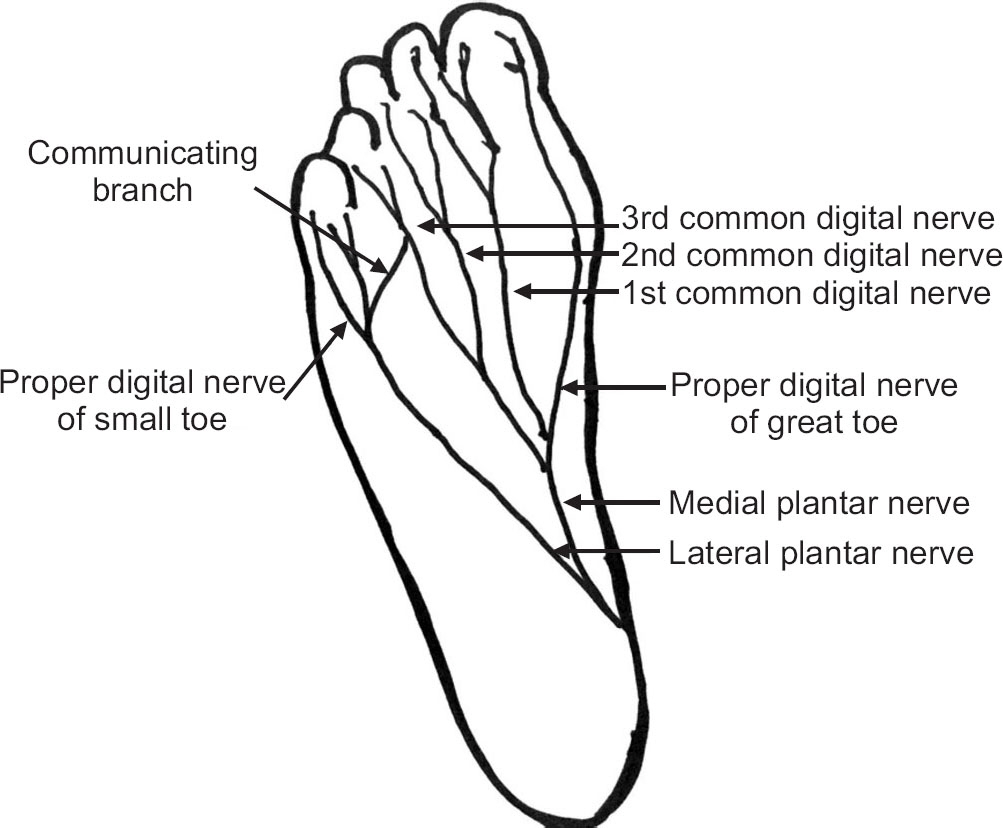
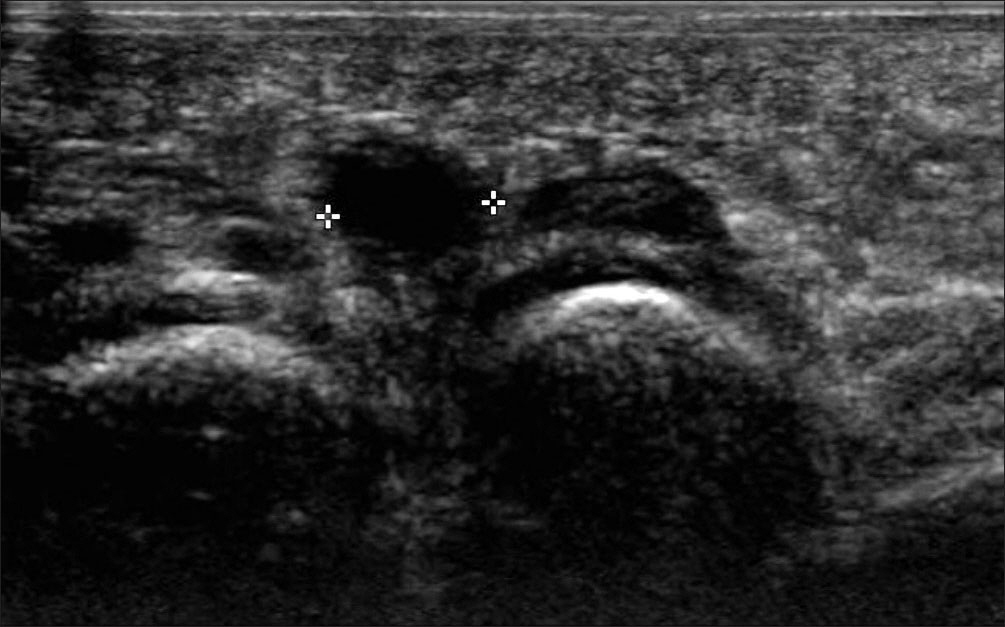
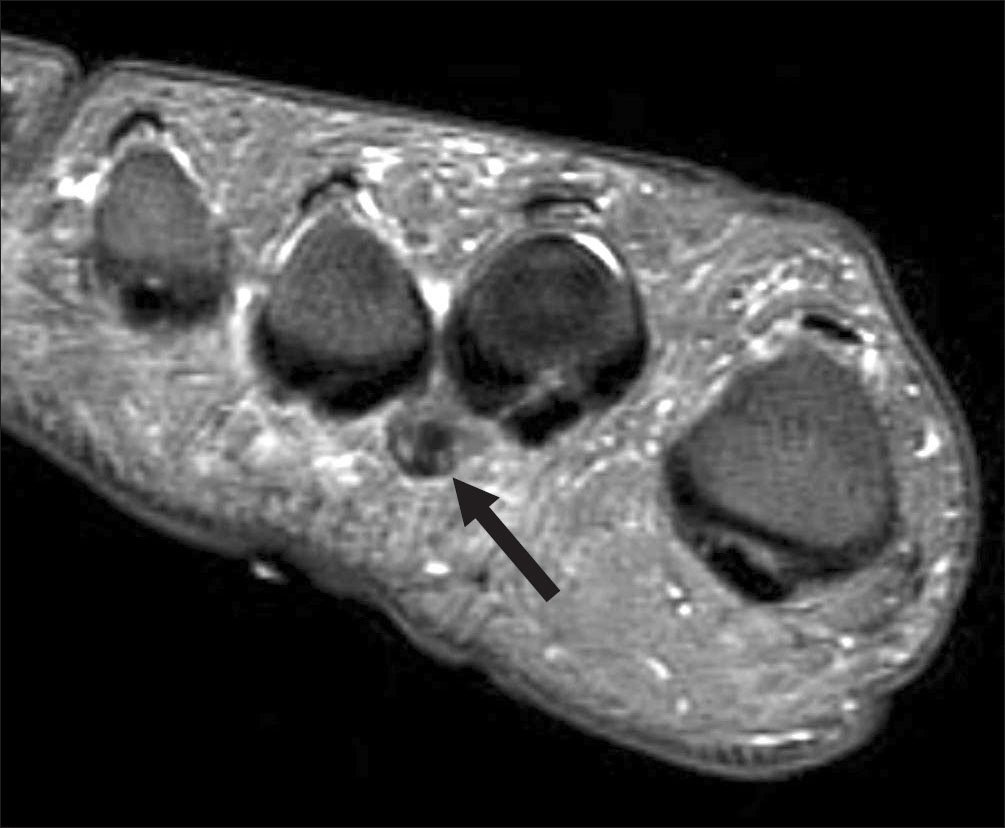
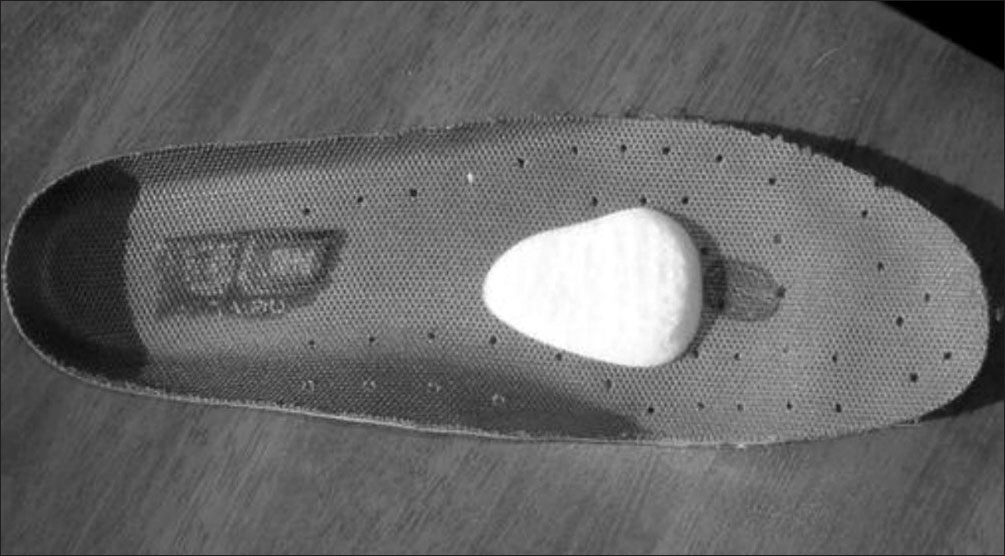
- Morton's neuroma, also known as interdigital neuroma, is a common cause of forefoot pain. It is a compressive neuropathy of the interdigital nerve, which is compressed by the overlying transverse metatarsal ligament. It is not a true tumor. The symptoms are forefoot pain that radiates into the toes, according to the involved nerve branches. Its histological findings are fibrosis around the nerve, demyelination. The clinical diagnosis can be obtained from a detailed history and physical examination, such as the compressive test. Moreover, ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging can also be used. Conservative treatment is the common initial treatment modality for interdigital neuroma. Surgical excision or decompression is indicated after a failure of conservative treatments.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kim JY, Lee KT, Young KW, Son SW. The comparison of ultrasonographic size of Morton's neuroma measured to actual size. J Korean Foot Ankle Soc. 2006; 10:80–3.2. Bennett GL, Graham CE, Mauldin DM. Morton's interdigital neuroma: a comprehensive treatment protocol. Foot Ankle Int. 1995; 16:760–3.
Article3. Park HW. A clinical result of treatment of interdigital neuroma with decompression (4 cases report). J Korean Foot Ankle Soc. 2008; 12:106–10.4. Park HW. Morton's neuroma (interdigital neuritis). J Korean Foot Ankle Soc. 2011; 15:58–61.5. Kay D, Bennett GL. Morton's neuroma. Foot Ankle Clin. 2003; 8:49–59.
Article6. Yoo SH, Kim BH, Chu IT, Chang YJ. Factors affecting on conservative treatment of Morton's neuroma. J Korean Foot Ankle Soc. 2005; 9:131–4.7. Guiloff RJ, Scadding JW, Klenerman L. Morton's metatarsalgia. Clinical, electrophysiological and histological observations. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1984; 66:586–91.
Article8. Thompson FM, Deland JT. Occurrence of two interdigital neuromas in one foot. Foot Ankle. 1993; 14:15–7.
Article9. Lee KT, Kim HC, Choi YS, Kim DH. The ultrasonographic diagnosis of interdigital neuroma and result of surgical excision. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 1999; 34:963–7.
Article10. Weinfeld SB, Myerson MS. Interdigital neuritis: diagnosis and treatment. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 1996; 4:328–35.
Article11. Iagnocco A, Coari G, Palombi G, Valesini G. Sonography in the study of metatarsalgia. J Rheumatol. 2001; 28:1338–40.12. Zanetti M, Weishaupt D. MR imaging of the forefoot: Morton neuroma and differential diagnoses. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2005; 9:175–86.
Article13. Sharp RJ, Wade CM, Hennessy MS, Saxby TS. The role of MRI and ultrasound imaging in Morton's neuroma and the effect of size of lesion on symptoms. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2003; 85:999–1005.
Article14. Rowbotham M, Harden N, Stacey B, Bernstein P, Magnus-Miller L. Gabapentin for the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 1998; 280:1837–42.15. Lee JW, Han SH, Suh DS. Clinical result of conservative treatment and operative treatment for interdigital neuroma. J Korean Foot Ankle Soc. 2006; 10:31–6.16. Mahadevan D, Attwal M, Bhatt R, Bhatia M. Corticosteroid injection for Morton's neuroma with or without ultrasound guidance: a randomised controlled trial. Bone Joint J. 2016; 98:498–503.17. Perini L, Perini C, Tagliapietra M. . Percutaneous alcohol injection under sonographic guidance in Morton's neuroma: follow-up in 220 treated lesions. Radiol Med. 2016; 121:597–604.
Article18. Greenfield J, Rea J Jr, Ilfeld FW. Morton's interdigital neuroma. Indications for treatment by local injections versus surgery. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1984; 185:142–4.19. Mann RA, Reynolds JC. Interdigital neuromaa critical clinical analysis. Foot Ankle. 1983; 3:238–43.20. Basadonna PT, Rucco V, Gasparini D, Onorato A. Plantar fat pad atrophy after corticosteroid injection for an interdigital neuroma: a case report. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 1999; 78:283–5.21. Pasquali C, Vulcano E, Novario R, Varotto D, Montoli C, Volpe A. Ultrasound-guided alcohol injection for Morton's neuroma. Foot Ankle Int. 2015; 36:55–9.
Article22. Seok H, Kim SH, Lee SY, Park SW. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy in patients with Morton's neuroma a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2016; 106:93–9.23. Stamatis ED, Karabalis C. Interdigital neuromas: current state of the art: surgical. Foot Ankle Clin. 2004; 9:287–96.24. Amis JA, Siverhus SW, Liwnicz BH. An anatomic basis for recurrence after Morton's neuroma excision. Foot Ankle. 1992; 13:153–6.
Article25. Colgrove RC, Huang EY, Barth AH, Greene MA. Interdigital neuroma: intermuscular neuroma transposition compared with resection. Foot Ankle Int. 2000; 21:206–11.
Article26. Zelent ME, Kane RM, Neese DJ, Lockner WB. Minimally invasive Morton's intermetatarsal neuroma decompression. Foot Ankle Int. 2007; 28:263–5.
Article27. Chu IT, Jang HS, Park HW. Corrective osteotomy of metatarsal bone for surgical treatment of Morton's neuroma. J Korean Foot Ankle Soc. 2015; 19:58–62.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Clinical Result of Treatment of Interdigital Neuroma with Decompression (4 Cases Report)
- Ultrasonography of Morton's Neuroma Accompanied with Interdigital Bursitis
- The Comparison of Ultrasonographic Size of Morton's Neuroma measured to Actual Size
- Clinical Result of Conservative Treatment and Operative Treatment for Interdigital Neuroma
- Morton's Neuroma (Interdigital Neuritis)