J Korean Soc Radiol.
2017 Aug;77(2):89-96. 10.3348/jksr.2017.77.2.89.
Effective Dose in Abdominal Digital Radiography: Patient Factors
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology and Research Institute of Radiology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. dokh@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Medical Physics, Korea University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2386744
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2017.77.2.89
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To identify independent patient factors associated with an increased radiation dose, and to evaluate the effect of patient position on the effective dose in abdominal digital radiography.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We retrospectively evaluated the effective dose for abdominal digital radiography in 222 patients. The patients were divided into two groups based on the cut-off dose value of 0.311 mSv (the upper third quartile of dose distribution): group A (n = 166) and group B (n = 56). Through logistic regression, independent factors associated with a larger effective dose were identified. The effect of patient position on the effective dose was evaluated using a paired t-test.
RESULTS
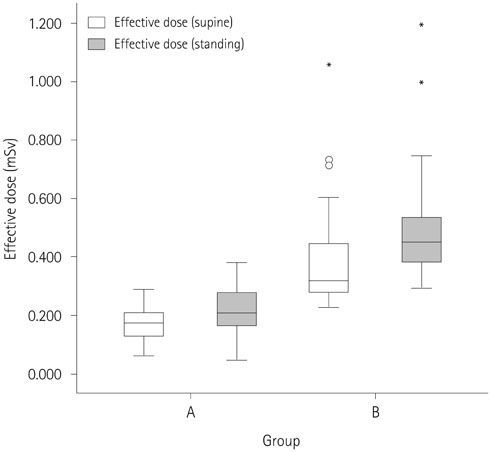
High body mass index (BMI) (≥ 23 kg/m²), presence of ascites, and spinal metallic instrumentation were significantly associated with a larger effective dose. Multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that high BMI [odds ratio (OR), 25.201; p < 0.001] and ascites (OR, 25.132; p < 0.001) were significantly associated with a larger effective dose. The effective dose was significantly lesser (22.6%) in the supine position than in the standing position (p < 0.001).
CONCLUSION
High BMI and ascites were independent factors associated with a larger effective dose in abdominal digital radiography. Significant dose reduction in patients with these factors may be achieved by placing the patient in the supine position during abdominal digital radiography.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mettler FA Jr, Thomadsen BR, Bhargavan M, Gilley DB, Gray JE, Lipoti JA, et al. Medical radiation exposure in the U.S. in 2006: preliminary results. Health Phys. 2008; 95:502–507.2. Bacher K, Smeets P, Bonnarens K, De Hauwere A, Verstraete K, Thierens H. Dose reduction in patients undergoing chest imaging: digital amorphous silicon flat-panel detector radiography versus conventional film-screen radiography and phosphor-based computed radiography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003; 181:923–929.3. Bacher K, Smeets P, Vereecken L, De Hauwere A, Duyck P, De Man R, et al. Image quality and radiation dose on digital chest imaging: comparison of amorphous silicon and amorphous selenium flat-panel systems. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006; 187:630–637.4. Grewal RK, Young N, Colins L, Karunnaratne N, Sabharwal N. Digital chest radiography image quality assessment with dose reduction. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med. 2012; 35:71–80.5. Schaefer-Prokop C, Neitzel U, Venema HW, Uffmann M, Prokop M. Digital chest radiography: an update on modern technology, dose containment and control of image quality. Eur Radiol. 2008; 18:1818–1830.6. Doyle P, Martin CJ. Calibrating automatic exposure control devices for digital radiography. Phys Med Biol. 2006; 51:5475–5485.7. Kim H, Park M, Park S, Jeong H, Kim J, Kim Y. Estimation of absorbed organ doses and effective dose based on body mass index in digital radiography. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2013; 153:92–99.8. Schindera ST, Nelson RC, Toth TL, Nguyen GT, Toncheva GI, DeLong DM, et al. Effect of patient size on radiation dose for abdominal MDCT with automatic tube current modulation: phantom study. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008; 190:W100–W105.9. Chan VO, McDermott S, Buckley O, Allen S, Casey M, O'Laoide R, et al. The relationship of body mass index and abdominal fat on the radiation dose received during routine computed tomographic imaging of the abdomen and pelvis. Can Assoc Radiol J. 2012; 63:260–266.10. Tung CJ, Lee CJ, Tsai HY, Tsai SF, Chen IJ. Body size-dependent patient effective dose for diagnostic radiography. Radiat Meas. 2008; 43:1008–1011.11. Ector J, Dragusin O, Adriaenssens B, Huybrechts W, Willems R, Ector H, et al. Obesity is a major determinant of radiation dose in patients undergoing pulmonary vein isolation for atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007; 50:234–242.12. Hsi RS, Zamora DA, Kanal KM, Harper JD. Severe obesity is associated with 3-fold higher radiation dose rate during ureteroscopy. Urology. 2013; 82:780–785.13. Guo H, Liu WY, He XY, Zhou XS, Zeng QL, Li BY. Optimizing imaging quality and radiation dose by the age-dependent setting of tube voltage in pediatric chest digital radiography. Korean J Radiol. 2013; 14:126–131.14. Nickoloff EL, Lu ZF, Dutta AK, So JC. Radiation dose descriptors: BERT, COD, DAP, and other strange creatures. Radiographics. 2008; 28:1439–1450.15. Khelassi-Toutaoui N, Berkani Y, Tsapaki V, Toutaoui AE, Merad A, Frahi-Amroun A, et al. Experimental evaluation of PCXMC and prepare codes used in conventional radiology. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2008; 131:374–378.16. Kiljunen T, Tietäväinen A, Parviainen T, Viitala A, Kortesniemi M. Organ doses and effective doses in pediatric radiography: patient-dose survey in Finland. Acta Radiol. 2009; 50:114–124.17. The 2007 Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection. ICRP publication 103. Ann ICRP. 2007; 37:1–332.18. Yanch JC, Behrman RH, Hendricks MJ, McCall JH. Increased radiation dose to overweight and obese patients from radiographic examinations. Radiology. 2009; 252:128–139.19. James B, Kelly B. The abdominal radiograph. Ulster Med J. 2013; 82:179–187.20. Levine MS, Scheiner JD, Rubesin SE, Laufer I, Herlinger H. Diagnosis of pneumoperitoneum on supine abdominal radiographs. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1991; 156:731–735.21. Smans K, Struelens L, Hoornaert MT, Bleeser F, Buls N, Berus D, et al. A study of the correlation between dose area product and effective dose in vascular radiology. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2008; 130:300–308.22. Doherty P, O'Leary D, Brennan PC. Do CEC guidelines under-utilise the full potential of increasing kVp as a dose-reducing tool? Eur Radiol. 2003; 13:1992–1999.23. Teeuwisse W, Geleijns J, Veldkamp W. An inter-hospital comparison of patient dose based on clinical indications. Eur Radiol. 2007; 17:1795–1805.24. Wall BF, Hart D. Revised radiation doses for typical X-ray examinations. Report on a recent review of doses to patients from medical X-ray examinations in the UK by NRPB. National Radiological Protection Board. Br J Radiol. 1997; 70:437–439.25. Chen TR, Tyan YS, Teng PS, Chou JH, Yeh CY, T WE, et al. Population dose from medical exposure in Taiwan for 2008. Med Phys. 2011; 38:3139–3148.26. Mettler FA Jr, Huda W, Yoshizumi TT, Mahesh M. Effective doses in radiology and diagnostic nuclear medicine: a catalog. Radiology. 2008; 248:254–263.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Abdominal Digital Radiography with a Novel Post-Processing Technique: Phantom and Patient Studies
- Absorbed and effective dose in direct and indirect digital panoramic radiography
- Absorbed and effective dose for periapical radiography using portable and wall type dental X-ray machines
- Skin entrance dose for digital and film radiography in Korean dental schools
- Effective dose from direct and indirect digital panoramic units