J Cardiovasc Ultrasound.
2013 Jun;21(2):96-99.
Prosthetic Mitral Valve Leaflet Escape
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cardiology, Severance Cardiovascular Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. GRHONG@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Chest Surgery, Yonsei Cardiovascular Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Cardiology Division, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
Abstract
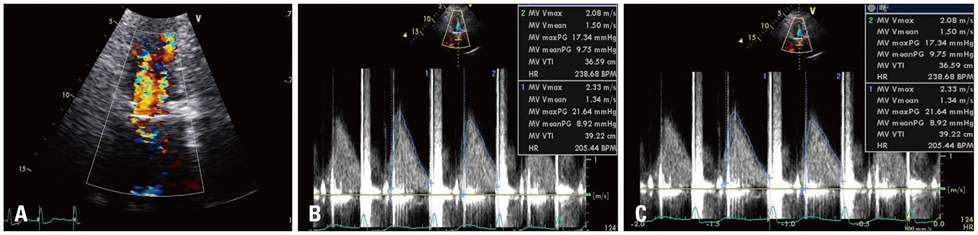
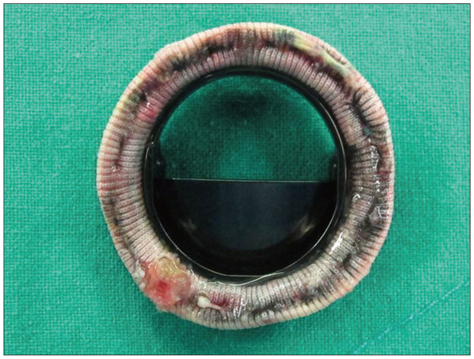
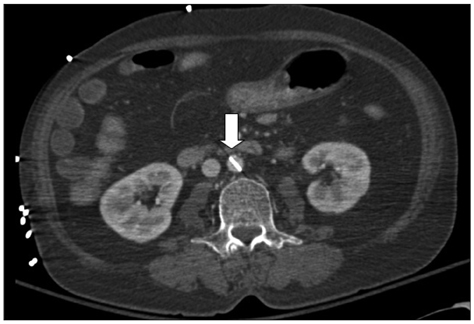
- Leaflet escape of prosthetic valve is rare but potentially life threatening. It is essential to make timely diagnosis in order to avoid mortality. Transesophageal echocardiography and cinefluoroscopy is usually diagnostic and the location of the missing leaflet can be identified by computed tomography (CT). Emergent surgical correction is mandatory. We report a case of fractured escape of Edward-Duromedics mitral valve 27 years after the surgery. The patient presented with symptoms of acute decompensated heart failure and cardiogenic shock. She was instantly intubated and mechanically ventilated. After prompt evaluation including transthoracic echocardiography and CT, the escape of the leaflet was confirmed. The patient underwent emergent surgery for replacement of the damaged prosthetic valves immediately. Eleven days after the surgery, the dislodged leaflet in iliac artery was removed safely and the patient recovered well.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Deuvaert FE, Devriendt J, Massaut J, Van Nooten G, De Paepe J, Primo G. Leaflet escape of a mitral Duromedics prosthesis. Case report. Acta Chir Belg. 1989; 89:15–18.2. Klepetko W, Moritz A, Mlczoch J, Schurawitzki H, Domanig E, Wolner E. Leaflet fracture in Edwards-Duromedics bileaflet valves. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1989; 97:90–94.
Article3. Alvarez J, Deal CW. Leaflet escape from a Duromedics valve. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1990; 99:372.
Article4. Kumar N, Balasundaram S, Rickard M, al Halees Z, Duran CM. Leaflet embolisation from Duromedics valves: a report of two cases. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1991; 39:382–383.
Article5. Tatou E, Saleh M, Eicher C, Brenot R, David M. Fracture-embolization of duromedics valve prosthesis and microscopic uncommon lesions. Ann Thorac Surg. 2001; 71:1366–1369.
Article6. Baudet E, Roques X, McBride J, Panès F, Grimaud JP. A 8-year follow-up of the Edwards-Duromedics bileaflet prosthesis. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 1995; 36:437–442.7. Eichler MJ, Reul HM. Mechanical heart valve cavitation: valve specific parameters. Int J Artif Organs. 2004; 27:855–867.
Article8. Fragoulis S, Palatianos GM. Fractured prosthetic valve leaflet. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2008; 34:907.
Article9. Devbhandari MP, Woo EB, Hooper TL. Long-term event-free survival with an embolised prosthetic valve leaflet in the thoracic aorta. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2008; 3:34.
Article10. Vogel W, Stoll HP, Bay W, Fröhlig G, Schieffer H. Cineradiography for determination of normal and abnormal function in mechanical heart valves. Am J Cardiol. 1993; 71:225–232.
Article11. Bottio T, Casarotto D, Thiene G, Caprili L, Angelini A, Gerosa G. Leaflet escape in a new bileaflet mechanical valve: TRI technologies. Circulation. 2003; 107:2303–2306.12. Lee SY, Choi JB. Escape of mechanical valve: a case report. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2007; 40:63–65.13. Kim JH, Oh SS, Na CY, Baek MJ, Seo HJ, Kim CW. Leaflet escape of edwards duromedics mechanical heart valve: report of 1 case. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2004; 37:373–375.14. Youn YN, Yoo KJ. Valve leaflet escape of edwards duromedics mechanical valve. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2002; 35:60–63.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Leaflet Escape of Edwards Duromedics Mechanical Heart Valve: Report of 1 case
- Leaflet Fracture and Embolization of a CarboMedics Prosthetic Mitral Valve: Case Report
- Mitral Valve Replacement with Chordal Preservation in Mitral Stenotic Disease
- Valve Leaflet Escape of Edwards Duromedics Mechanical Valve
- Escape of Mechanical Valve: A case report