J Korean Med Sci.
2017 Sep;32(9):1460-1467. 10.3346/jkms.2017.32.9.1460.
Risk of Stroke in Elderly Dialysis Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. dkkim73@gmail.com
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul Metropolitan Government-Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea.
- 5Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2385952
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2017.32.9.1460
Abstract
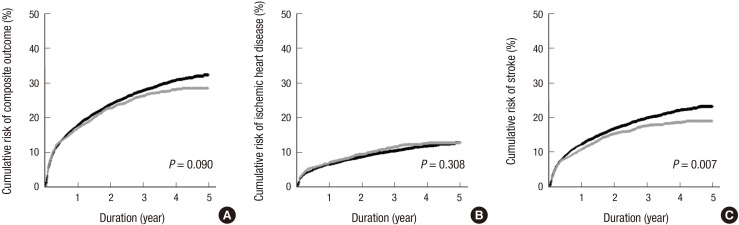
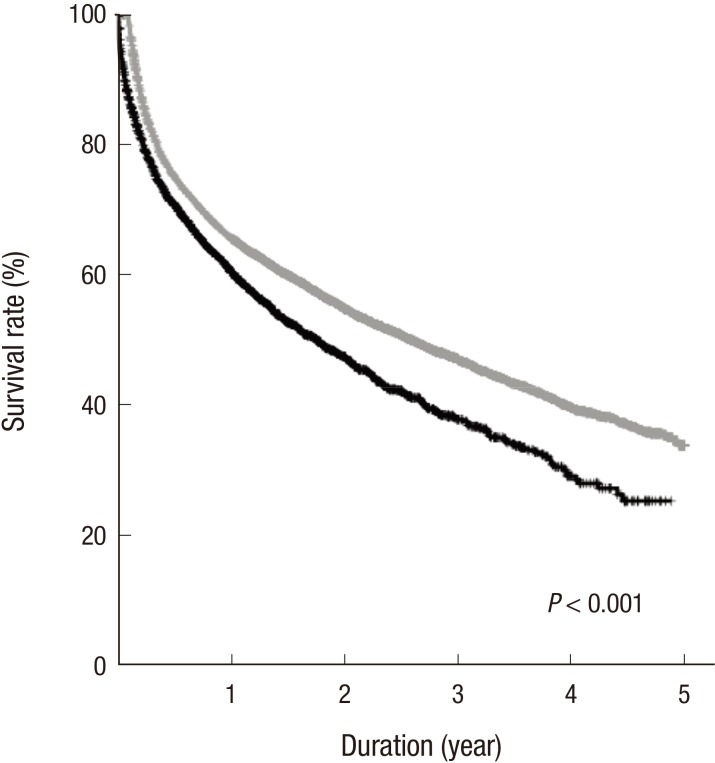
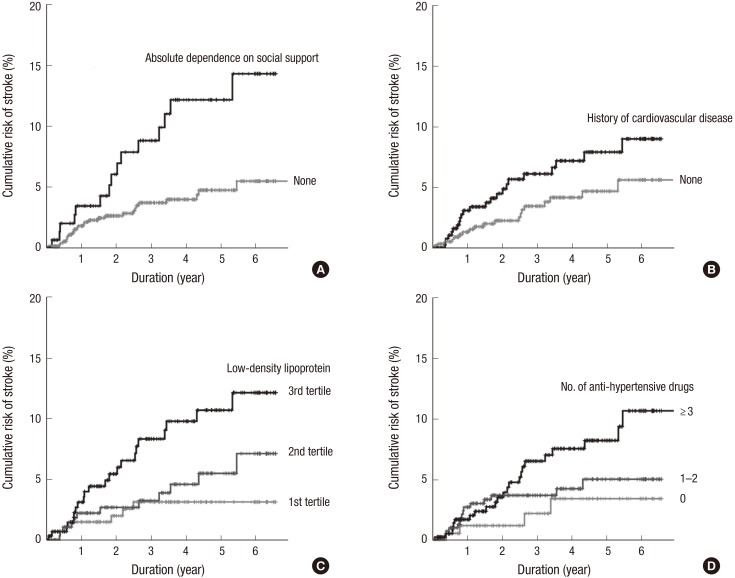
- Despite the current knowledge about the risk of stroke and its related factors in general population, this issue in elderly patients receiving dialysis remains unresolved. Firstly, to compare the risk of stroke between hemodialysis (HD) and peritoneal dialysis (PD), data on 13,065 incident dialysis patients (aged ≥ 65 years; 10,675 in HD and 2,390 in PD) were retrieved from the Korean Health Insurance dataset. Secondly, to identify the risk factors of stroke amongst various clinical and laboratory parameters in HD, 980 elderly patients were retrospectively analyzed using an independent prospective cohort from 31 dialysis centers. For a mean duration of 1.8 years (maximum of 5 years), the risk of all cardiovascular diseases (ischemic heart disease and stroke) did not differ between HD and PD. However, when analyses were conducted separately by subtype, the risk of stroke, not ischemic heart disease, was significantly higher in HD patients than in PD patients. When the risk factors of stroke were probed after HD for a mean duration of 2.6 years (maximum of 7 years), the absolute dependence on social support, a previous history of cardiovascular disease, high levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and the use of a high number of anti-hypertensive drugs were identified as being significant. Based on the discrepancy of stroke risk between modalities and the HD-tailored risk factors of stroke, the monitoring and management of these factors may be a key strategy to reduce the risk of stroke in elderly patients receiving dialysis.
MeSH Terms
-
Aged*
Antihypertensive Agents
Cardiovascular Diseases
Cholesterol
Cohort Studies
Dataset
Dialysis*
Heart Diseases
Humans
Insurance, Health
Kidney Failure, Chronic
Lipoproteins
Myocardial Ischemia
Peritoneal Dialysis
Prospective Studies
Renal Dialysis
Retrospective Studies
Risk Factors
Stroke*
Antihypertensive Agents
Cholesterol
Lipoproteins
Figure
Reference
-
1. Brønnum-Hansen H, Davidsen M, Thorvaldsen P; Danish MONICA Study Group. Long-term survival and causes of death after stroke. Stroke. 2001; 32(9):2131–2136. PMID: 11546907.2. Di Carlo A. Human and economic burden of stroke. Age Ageing. 2009; 38:4–5. PMID: 19141505.3. Redón J, Cea-Calvo L, Lozano JV, Martí-Canales JC, Llisterri JL, Aznar J, González-Esteban J. Investigators of the PREV-ICTUS study. Blood pressure and estimated risk of stroke in the elderly population of Spain: the PREV-ICTUS study. Stroke. 2007; 38:1167–1173. PMID: 17322073.4. Chen X, Zhou L, Zhang Y, Yi D, Liu L, Rao W, Wu Y, Ma D, Liu X, Zhou XH, et al. Risk factors of stroke in Western and Asian countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. BMC Public Health. 2014; 14:776. PMID: 25081994.5. Schiffrin EL, Lipman ML, Mann JF. Chronic kidney disease: effects on the cardiovascular system. Circulation. 2007; 116:85–97. PMID: 17606856.6. Seliger SL, Gillen DL, Longstreth WT Jr, Kestenbaum B, Stehman-Breen CO. Elevated risk of stroke among patients with end-stage renal disease. Kidney Int. 2003; 64:603–609. PMID: 12846756.7. Stevens LA, Viswanathan G, Weiner DE. Chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease in the elderly population: current prevalence, future projections, and clinical significance. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2010; 17:293–301. PMID: 20610356.8. Han SS, Park JY, Kang S, Kim KH, Ryu DR, Kim H, Joo KW, Lim CS, Kim YS, Kim DK. Dialysis modality and mortality in the elderly: a meta-analysis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015; 10:983–993. PMID: 25941194.9. Quan H, Sundararajan V, Halfon P, Fong A, Burnand B, Luthi JC, Saunders LD, Beck CA, Feasby TE, Ghali WA. Coding algorithms for defining comorbidities in ICD-9-CM and ICD-10 administrative data. Med Care. 2005; 43:1130–1139. PMID: 16224307.10. Hemmelgarn BR, Manns BJ, Quan H, Ghali WA. Adapting the Charlson Comorbidity Index for use in patients with ESRD. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003; 42:125–132. PMID: 12830464.11. Davies SJ, Russell L, Bryan J, Phillips L, Russell GI. Comorbidity, urea kinetics, and appetite in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients: their interrelationship and prediction of survival. Am J Kidney Dis. 1995; 26:353–361. PMID: 7645541.12. Hemodialysis Adequacy 2006 Work Group. Clinical practice guidelines for hemodialysis adequacy, update 2006. Am J Kidney Dis. 2006; 48(Suppl 1):S2–S90. PMID: 16813990.13. Korevaar JC, Feith GW, Dekker FW, van Manen JG, Boeschoten EW, Bossuyt PM, Krediet RT; NECOSAD Study Group. Effect of starting with hemodialysis compared with peritoneal dialysis in patients new on dialysis treatment: a randomized controlled trial. Kidney Int. 2003; 64:2222–2228. PMID: 14633146.14. Selgas R, Cirugeda A, Fernandez-Perpén A, Sánchez-Tomero JA, Barril G, Alvarez V, Bajo MA. Comparisons of hemodialysis and CAPD in patients over 65 years of age: a meta-analysis. Int Urol Nephrol. 2001; 33:259–264. PMID: 12092638.15. Locatelli F, Marcelli D, Conte F, D’Amico M, Del Vecchio L, Limido A, Malberti F, Spotti D. Survival and development of cardiovascular disease by modality of treatment in patients with end-stage renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2001; 12:2411–2417. PMID: 11675417.16. Hiramatsu T, Furuta S, Kakuta H. Impact of dialysis modality on ultrasonographic cardiovascular parameters in elderly patients. Adv Perit Dial. 2007; 23:94–97. PMID: 17886611.17. Johnson DW, Dent H, Hawley CM, McDonald SP, Rosman JB, Brown FG, Bannister K, Wiggins KJ. Association of dialysis modality and cardiovascular mortality in incident dialysis patients. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009; 4:1620–1628. PMID: 19729428.18. Chavarria LA, Aguilar-Kitsu A, Rosas P, Fajardo A, Mendoza-Guevara L, Sanchez L, Zepeda C, Ibarra P, Luna A, Lindholm B, et al. Intima media thickness in children undergoing dialysis. Pediatr Nephrol. 2012; 27:1557–1564. PMID: 22552884.19. Marrón B, Remón C, Pérez-Fontán M, Quirós P, Ortíz A. Benefits of preserving residual renal function in peritoneal dialysis. Kidney Int Suppl. 2008; S42–S51. PMID: 18379546.20. McIntyre CW. Effects of hemodialysis on cardiac function. Kidney Int. 2009; 76:371–375. PMID: 19516249.21. Seliger SL, Gillen DL, Tirschwell D, Wasse H, Kestenbaum BR, Stehman-Breen CO. Risk factors for incident stroke among patients with end-stage renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003; 14:2623–2631. PMID: 14514741.22. Meschia JF, Bushnell C, Boden-Albala B, Braun LT, Bravata DM, Chaturvedi S, Creager MA, Eckel RH, Elkind MS, Fornage M, et al. Guidelines for the primary prevention of stroke: a statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2014; 45:3754–3832. PMID: 25355838.23. Phillips SJ. Pathophysiology and management of hypertension in acute ischemic stroke. Hypertension. 1994; 23:131–136. PMID: 8282324.24. Power A. Stroke in dialysis and chronic kidney disease. Blood Purif. 2013; 36:179–183. PMID: 24496188.25. Shroff RC, McNair R, Figg N, Skepper JN, Schurgers L, Gupta A, Hiorns M, Donald AE, Deanfield J, Rees L, et al. Dialysis accelerates medial vascular calcification in part by triggering smooth muscle cell apoptosis. Circulation. 2008; 118:1748–1757. PMID: 18838561.26. Demer LL, Tintut Y. Vascular calcification: pathobiology of a multifaceted disease. Circulation. 2008; 117:2938–2948. PMID: 18519861.27. Zhang X, Patel A, Horibe H, Wu Z, Barzi F, Rodgers A, MacMahon S, Woodward M; Asia Pacific Cohort Studies Collaboration. Cholesterol, coronary heart disease, and stroke in the Asia Pacific region. Int J Epidemiol. 2003; 32(9):563–572. PMID: 12913030.28. Iso H, Jacobs DR Jr, Wentworth D, Neaton JD, Cohen JD. Serum cholesterol levels and six-year mortality from stroke in 350,977 men screened for the multiple risk factor intervention trial. N Engl J Med. 1989; 320:904–910. PMID: 2619783.29. Russo T, Felzani G, Marini C. Stroke in the very old: a systematic review of studies on incidence, outcome, and resource use. J Aging Res. 2011; 2011:108785. PMID: 21876804.30. Fellström BC, Jardine AG, Schmieder RE, Holdaas H, Bannister K, Beutler J, Chae DW, Chevaile A, Cobbe SM, Grönhagen-Riska C, et al. Rosuvastatin and cardiovascular events in patients undergoing hemodialysis. N Engl J Med. 2009; 360:1395–1407. PMID: 19332456.31. Baigent C, Landray MJ, Reith C, Emberson J, Wheeler DC, Tomson C, Wanner C, Krane V, Cass A, Craig J, et al. The effects of lowering LDL cholesterol with simvastatin plus ezetimibe in patients with chronic kidney disease (Study of Heart and Renal Protection): a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2011; 377:2181–2192. PMID: 21663949.32. Clark AM, DesMeules M, Luo W, Duncan AS, Wielgosz A. Socioeconomic status and cardiovascular disease: risks and implications for care. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2009; 6:712–722. PMID: 19770848.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ischemic Stroke among the Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease Who Were Undergoing Maintenance Dialysis
- Clinical Features of Stroke in Patients Undergoing Dialysis
- Incidence and Pathophysiology of Cerebral Hemorrhagic Stroke in the Elderly
- Anticardiolipin Antibody in Elderly Ischemic Stroke
- Age Factor in Rehabilitation Outcome