J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2017 Jun;24(2):103-108. 10.4184/jkss.2017.24.2.103.
Kyphotic Deformity after Spinal Fusion in a Patient with Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Guri Hospital, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Guri, Korea. hyparkys@hanyang.ac.kr
- KMID: 2385646
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2017.24.2.103
Abstract
- STUDY DESIGN: Case report.
OBJECTIVES
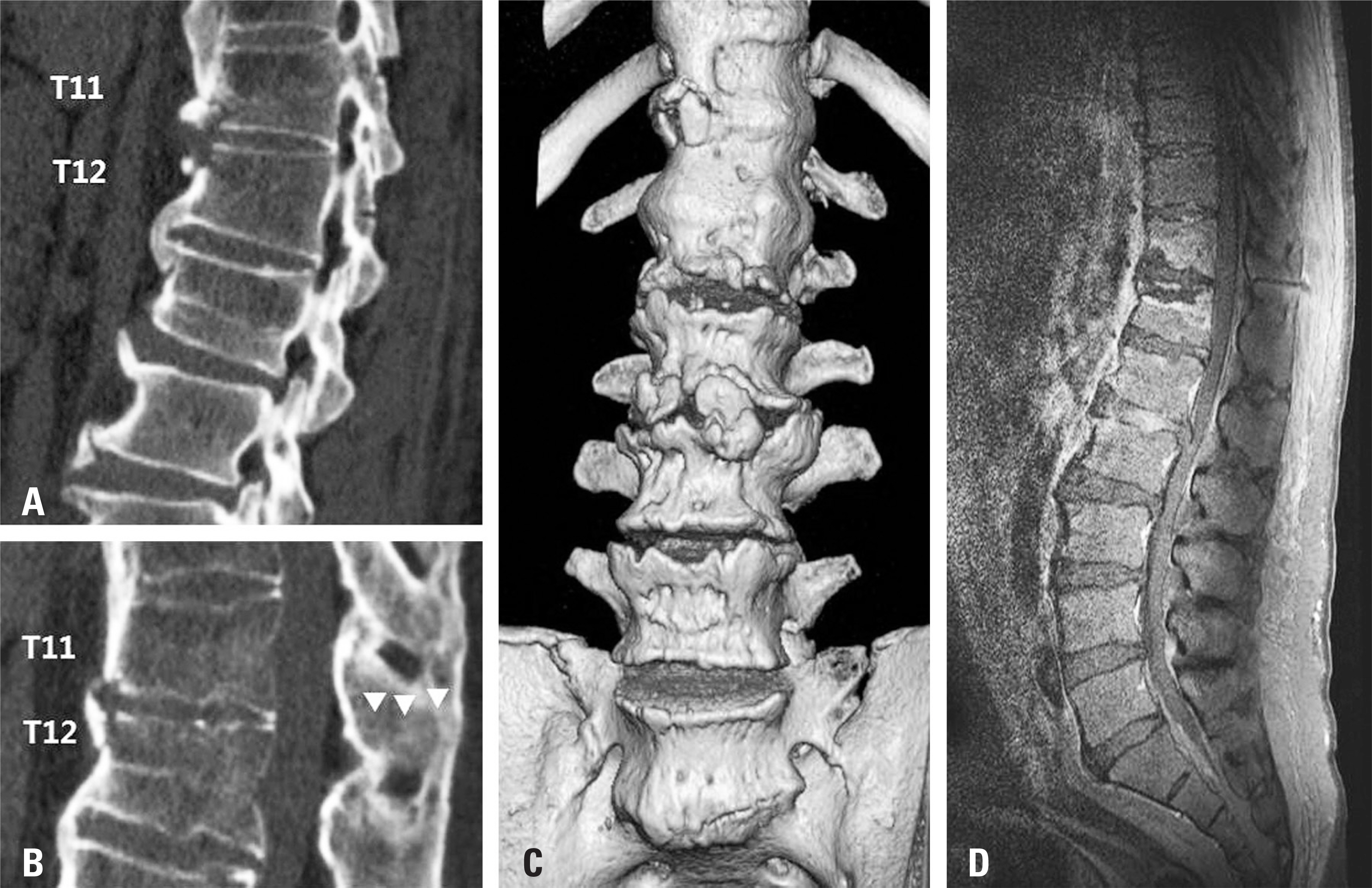
To report a case of progressive kyphotic deformity after spinal fusion in a patient with diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH). SUMMARY OF LITERATURE REVIEW: DISH is characterized by spinal and peripheral enthesopathy, and is a completely different disease from ankylosing spondylitis (AS). Though DISH can be associated with thoracic kyphosis, no reports have described a progressive thoracolumbar kyphotic deformity after spinal fusion surgery in a DISH patient.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A 47-year-old male presented with pain in the thoracolumbar region. After excluding the possibility of AS and confirming the diagnosis of DISH, we performed spinal fusion for the treatment of a T11-T12 flexion-distraction injury. The kyphotic deformity was found to be aggravated after the first operation, and we then performed corrective osteotomy and additional spinal fusion. Results: The kyphotic deformity of the patient was corrected after the second operation.
RESULTS
The kyphotic deformity of the patient was corrected after the second operation.
CONCLUSIONS
In DISH patients in whom AS must be excluded in the differential diagnosis, a kyphotic deformity can become aggravated despite spinal fusion surgery, so regular and continuous follow-up is required.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Resnick D, Niwayama G. Radiographic and pathologic features of spinal involvement in diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis. Radiology. 1976; 119:559–68.2. Olivieri I, D'Angelo S, Palazzi C, et al. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis: differentiation from ankylosing spondylitis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2009; 5:321–8.
Article3. Nardo L, Lane NE, Parimi N, et al. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis association with thoracic spine kyphosis: a cross-sectional study for the Health Aging and Body Com-position Study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014; 24:1418–24.4. Yamada K, Toyoda H, Terai H, et al. Spinopelvic alignment of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis in lumbar spinal stenosis. Eur Spine J. 2014; 6:1302–8.
Article5. Park YS, Kim HS, Baek SW, et al. Preoperative computer-based simulations for the correction of kyphotic deformities in ankylosing spondylitis patients. Spine J. 2014; 14:2420–4.
Article6. Kim SK, Choi BR, Kim CG, et al. The prevalence of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis in Korea. J Rheumatol. 2004; 10:2032–5.7. Mader R, Verlaan JJ, Buskila D. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis: clinical features and pathogenic mechanisms. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2013; 12:741–50.
Article8. Diederichs G, Engelken F, Marshall LM, et al. Osteoporotic fractures in men research group. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH): relation to vertebral fractures and bone density. Osteoporos Int. 2011; 6:1789–97.9. Westerveld LA, Verlaan JJ, Oner FC. Spinal fractures in patients with ankylosing spinal disorders: a systematic review of the literature on treatment, neurological status and complications. Eur Spine J. 2009; 2:145–56.
Article10. Otsuki B, Fujibayashi S, Takemoto M, et al. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis(DISH) is a risk factor for surgery in short segment lumbar interbody fusion. Eur Spine J. 2015; 11:2514–9.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis and Thoracic Myelopathy in Spondyloepiphyseal Dysplasia Congenita: A Case Report
- CT Findings of May–Thurner Syndrome in Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis: A Case Report
- Dysphagia Due to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis of The Cervical Spine: A Case Report
- A Case of Dysphagia due to Cricopharyngeal Dysfunction and Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis
- Compression Fractures in the Setting of Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis