Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr.
2017 Jun;20(2):114-123. 10.5223/pghn.2017.20.2.114.
Early Diagnosis of ABCB11 Spectrum Liver Disorders by Next Generation Sequencing
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. neurobaby79@gmail.com
- 2Department of Pathology, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2384825
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2017.20.2.114
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The goal of this study was the early diagnosis of ABCB11 spectrum liver disorders, especially those focused on benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis and progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis.
METHODS
Fifty patients presenting neonatal cholestasis were evaluated to identify underlying etiologies. Genetic analysis was performed on patients suspected to have syndromic diseases or ABCB11 spectrum liver disorders. Two families with proven ABCB11 spectrum liver disorders were subjected to genetic analyses to confirm the diagnosis and were provided genetic counseling. Whole exome sequencing and Sanger sequencing were performed on the patients and the family members.
RESULTS
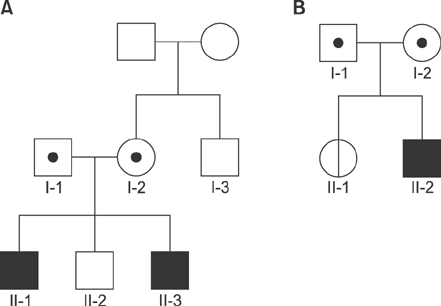
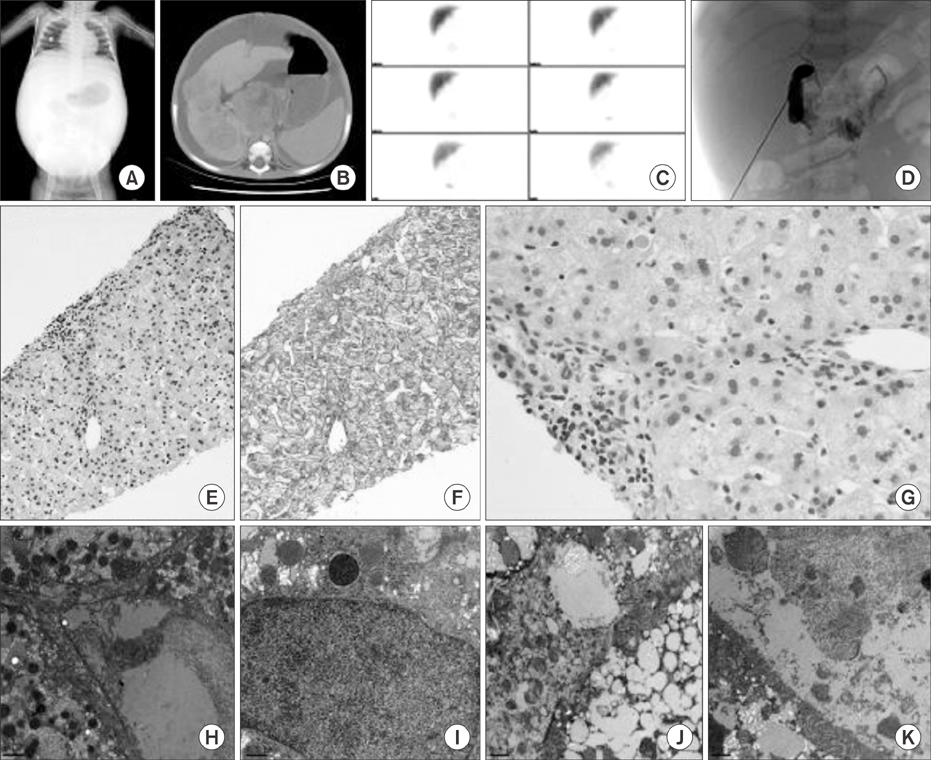
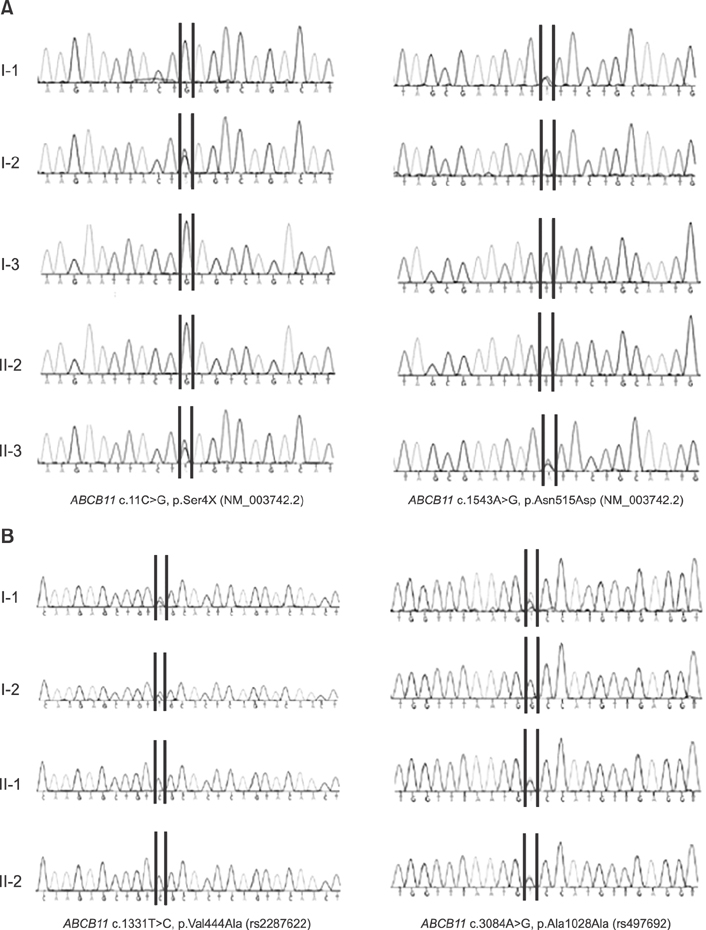
Idiopathic or viral hepatitis was diagnosed in 34%, metabolic disease in 20%, total parenteral nutrition induced cholestasis in 16%, extrahepatic biliary atresia in 14%, genetic disease in 10%, neonatal lupus in 2%, congenital syphilis in 2%, and choledochal cyst in 2% of the patients. The patient with progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis had novel heterozygous mutations of ABCB11 c.11C>G (p.Ser4*) and c.1543A>G (p.Asn515Asp). The patient with benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis had homozygous mutations of ABCB11 c.1331T>C (p.Val444Ala) and heterozygous, c.3084A>G (p.Ala1028Ala). Genetic confirmation of ABCB11 spectrum liver disorder led to early liver transplantation in the progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis patient. In addition, the atypically severe benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis patient was able to avoid unnecessary liver transplantation after genetic analysis.
CONCLUSION
ABCB11 spectrum liver disorders can be clinically indistinguishable as they share similar characteristics related to acute episodes. A comprehensive genetic analysis will facilitate optimal diagnosis and treatment.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Benign Recurrent Intrahepatic Cholestasis Type 2 in Siblings with Novel ABCB11 Mutations
Min Ji Sohn, Min Hyung Woo, Moon-Woo Seong, Sung Sup Park, Gyeong Hoon Kang, Jin Soo Moon, Jae Sung Ko
Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2019;22(2):201-206. doi: 10.5223/pghn.2019.22.2.201.
Reference
-
1. Kubitz R, Keitel V, Häussinger D. Inborn errors of biliary canalicular transport systems. Methods Enzymol. 2005; 400:558–569.
Article2. Feldman AG, Sokol RJ. Neonatal cholestasis. Neoreviews. 2013; 14.
Article3. van der Woerd WL, van Mil SW, Stapelbroek JM, Klomp LW, van de Graaf SF, Houwen RH. Familial cholestasis: progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis, benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis and intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2010; 24:541–553.
Article4. Ryeom HK, Choe BH, Kim JY, Kwon S, Ko CW, Kim HM, et al. Biliary atresia: feasibility of mangafodipir trisodium-enhanced MR cholangiography for evaluation. Radiology. 2005; 235:250–258.
Article5. Lee SY, Kim GC, Choe BH, Ryeom HK, Jang YJ, Kim HJ, et al. Efficacy of US-guided percutaneous cholecystocholangiography for the early exclusion and type determination of biliary atresia. Radiology. 2011; 261:916–922.
Article6. Saxena AK, Mittal V, Sodhi KS. Triangular cord sign in biliary atresia: does it have prognostic and medicolegal significance. Radiology. 2012; 263:621. author reply 621-2.
Article7. Luketic VA, Shiffman ML. Benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis. Clin Liver Dis. 2004; 8:133–149. vii
Article8. Hu G, He P, Liu Z, Chen Q, Zheng B, Zhang Q. Diagnosis of ABCB11 gene mutations in children with intrahepatic cholestasis using high resolution melting analysis and direct sequencing. Mol Med Rep. 2014; 10:1264–1274.
Article9. Meier Y, Zodan T, Lang C, Zimmermann R, Kullak-Ublick GA, Meier PJ, et al. Increased susceptibility for intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy and contraceptive-induced cholestasis in carriers of the 1331T>C polymorphism in the bile salt export pump. World J Gastroenterol. 2008; 14:38–45.
Article10. Lang C, Meier Y, Stieger B, Beuers U, Lang T, Kerb R, et al. Mutations and polymorphisms in the bile salt export pump and the multidrug resistance protein 3 associated with drug-induced liver injury. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2007; 17:47–60.
Article11. Kubitz R, Keitel V, Scheuring S, Köhrer K, Häussinger D. Benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis associated with mutations of the bile salt export pump. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2006; 40:171–175.
Article12. Keitel V, Vogt C, Häussinger D, Kubitz R. Combined mutations of canalicular transporter proteins cause severe intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. Gastroenterology. 2006; 131:624–629.
Article13. Byrne JA, Strautnieks SS, Ihrke G, Pagani F, Knisely AS, Linton KJ, et al. Missense mutations and single nucleotide polymorphisms in ABCB11 impair bile salt export pump processing and function or disrupt pre-messenger RNA splicing. Hepatology. 2009; 49:553–567.
Article14. Pauli-Magnus C, Kerb R, Fattinger K, Lang T, Anwald B, Kullak-Ublick GA, et al. BSEP and MDR3 haplotype structure in healthy Caucasians, primary biliary cirrhosis and primary sclerosing cholangitis. Hepatology. 2004; 39:779–791.
Article15. van Mil SW, van der Woerd WL, van der Brugge G, Sturm E, Jansen PL, Bull LN, et al. Benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis type 2 is caused by mutations in ABCB11. Gastroenterology. 2004; 127:379–384.
Article16. Folvik G, Hilde O, Helge GO. Benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis: review and long-term follow-up of five cases. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2012; 47:482–488.
Article17. Whitington PF, Freese DK, Alonso EM, Schwarzenberg SJ, Sharp HL. Clinical and biochemical findings in progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1994; 18:134–141.18. Herbst SM, Schirmer S, Posovszky C, Jochum F, Rödl T, Schroeder JA, et al. Taking the next step forward-diagnosing inherited infantile cholestatic disorders with next generation sequencing. Mol Cell Probes. 2015; 29:291–298.
Article19. Mieli-Vergani G, Howard ER, Mowat AP. Liver disease in infancy: a 20 year perspective. Gut. 1991; Suppl. S123–S128.
Article20. van der Velden LM, Stapelbroek JM, Krieger E, van den Berghe PV, Berger R, Verhulst PM, et al. Folding defects in P-type ATP 8B1 associated with hereditary cholestasis are ameliorated by 4-phenylbutyrate. Hepatology. 2010; 51:286–296.
Article21. Hayashi H, Sugiyama Y. 4-phenylbutyrate enhances the cell surface expression and the transport capacity of wild-type and mutated bile salt export pumps. Hepatology. 2007; 45:1506–1516.
Article22. Misawa T, Hayashi H, Sugiyama Y, Hashimoto Y. Discovery and structural development of small molecules that enhance transport activity of bile salt export pump mutant associated with progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 2. Bioorg Med Chem. 2012; 20:2940–2949.
Article23. Stormon MO, Dorney SF, Kamath KR, O'Loughlin EV, Gaskin KJ. The changing pattern of diagnosis of infantile cholestasis. J Paediatr Child Health. 2001; 37:47–50.
Article24. Srivastava A. Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2014; 4:25–36.
Article25. Jung C, Driancourt C, Baussan C, Zater M, Hadchouel M, Meunier-Rotival M, et al. Prenatal molecular diagnosis of inherited cholestatic diseases. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2007; 44:453–458.
Article26. Chen ST, Chen HL, Su YN, Liu YJ, Ni YH, Hsu HY, et al. Prenatal diagnosis of progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 2. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008; 23:1390–1393.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Recent Advances in Autism Spectrum Disorders: Applications of Whole Exome Sequencing Technology
- Recent Advances in the Clinical Application of Next-Generation Sequencing
- Exome Sequencing in Mendelian Disorders
- Application of Next Generation Sequencing in Laboratory Medicine
- Benign Recurrent Intrahepatic Cholestasis Type 2 in Siblings with Novel ABCB11 Mutations