Ann Lab Med.
2017 Sep;37(5):462-464. 10.3343/alm.2017.37.5.462.
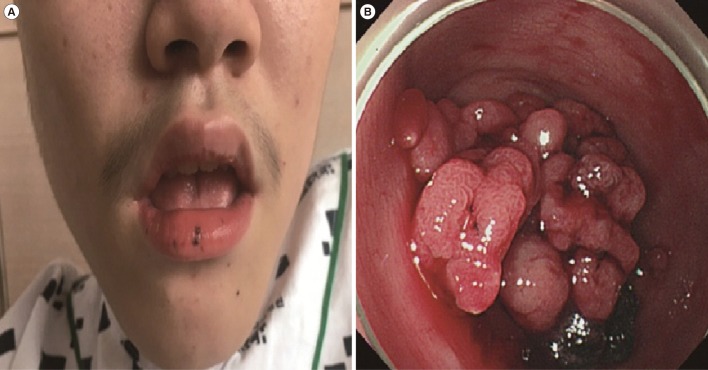
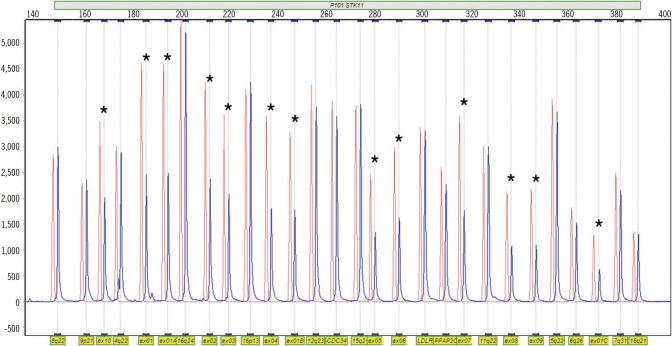
Complete STK11 Deletion and Atypical Symptoms in Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Bucheon, Korea. dr4baby@naver.com
- 2Digestive Disease Center and Research Institute, Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Bucheon, Korea.
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Mokpo Hankook Hospital, Mokpo, Korea.
- 4Department of Laboratory Medicine and Clinical Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2383928
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2017.37.5.462
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hemminki A, Markie D, Tomlinson I, Avizienyte E, Roth S, Loukola A, et al. A serine/threonine kinase gene defective in Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. Nature. 1998; 391:184–187. PMID: 9428765.2. Hemminki A, Tomlinson I, Markie D, Järvinen H, Sistonen P, Björkqvist AM, et al. Localization of a susceptibility locus for Peutz-Jeghers syndrome to 19p using comparative genomic hybridization and targeted linkage analysis. Nat Genet. 1997; 15:87–90. PMID: 8988175.3. Tiainen M, Ylikorkala A, Mäkelä TP. Growth suppression by Lkb1 is mediated by a G(1) cell cycle arrest. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999; 96:9248–9251. PMID: 10430928.4. Le Meur N, Martin C, Saugier-Veber P, Joly G, Lemoine F, Moirot H, et al. Complete germline deletion of the STK11 gene in a family with Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet. 2004; 12:415–418. PMID: 14970844.5. Hearle NC, Rudd MF, Lim W, Murday V, Lim AG, Phillips RK, et al. Exonic STK11 deletions are not a rare cause of Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. J Med Genet. 2006; 43:e15. PMID: 16582077.6. Schouten JP, McElgunn CJ, Waaijer R, Zwijnenburg D, Diepvens F, Pals G. Relative quantification of 40 nucleic acid sequences by multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002; 30:e57. PMID: 12060695.7. Souza J, Faucz F, Sotomaior V, Filho AB, Rosenfeld J, Raskin S. Chromosome 19p13.3 deletion in a child with Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, congenital heart defect, high myopia, learning difficulties and dysmorphic features: Clinical and molecular characterization of a new contiguous gene syndrome. Genet Mol Biol. 2011; 34:557–561. PMID: 22215957.8. Amos CI, Keitheri-Cheteri MB, Sabripour M, Wei C, McGarrity TJ, Seldin MF, et al. Genotype-phenotype correlations in Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. J Med Genet. 2004; 41:327–333. PMID: 15121768.