Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab.
2017 Jun;22(2):125-128. 10.6065/apem.2017.22.2.125.
Diabetes mellitus due to agenesis of the dorsal pancreas in a patient with heterotaxy syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Severance Children's Hospital, Endocrine Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kimho@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Sowha Children's Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2383908
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.6065/apem.2017.22.2.125
Abstract
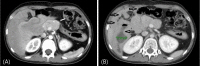
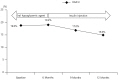
- Heterotaxy syndrome (HS) is a congenital disorder resulting from an abnormal arrangement of visceral organs across the normal left-right axis in the embryonic period. HS is usually associated with multiple anomalies, including defects of the major cardiovascular system and the extracardiovascular system such as intestinal malrotation, abnormal lung lobulation, bronchus anomalies, and pancreatic dysplasia. Although pancreatic dysplasia is occasionally accompanied with HS, the occurrence of diabetes mellitus (DM) due to pancreatic dysplasia in HS is rarely reported. We here report a case involving 13-year-old girl with DM caused by agenesis of the dorsal pancreas and HS diagnosed on the basis of the presence of a double-outlet right ventricle with bilateral pulmonary stenosis and intestinal malrotation with duodenal cyst. Timely diagnosis and treatment with insulin improved glycemic control.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Britz-Cunningham SH, Shah MM, Zuppan CW, Fletcher WH. Mutations of the Connexin43 gap-junction gene in patients with heart malformations and defects of laterality. N Engl J Med. 1995; 332:1323–1329. PMID: 7715640.
Article2. Shiraishi I, Ichikawa H. Human heterotaxy syndrome – from molecular genetics to clinical features, management, and prognosis –. Circ J. 2012; 76:2066–2075. PMID: 22864291.3. Williams GD, Feng A. Heterotaxy syndrome: implications for anesthesia management. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2010; 24:834–844. PMID: 20421166.
Article4. Stingl H, Schnedl WJ, Krssak M, Bernroider E, Bischof MG, Lahousen T, et al. Reduction of hepatic glycogen synthesis and breakdown in patients with agenesis of the dorsal pancreas. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002; 87:4678–4685. PMID: 12364458.
Article5. Schnedl WJ, Piswanger-Soelkner C, Wallner SJ, Reittner P, Krause R, Lipp RW, et al. Agenesis of the dorsal pancreas and associated diseases. Dig Dis Sci. 2009; 54:481–487. PMID: 18618254.
Article6. Joo YE, Kang HC, Kim HS, Choi SK, Rew JS, Chung MY, et al. Agenesis of the dorsal pancreas: a case report and review of the literature. Korean J Intern Med. 2006; 21:236–239. PMID: 17249505.
Article7. Kapa S, Gleeson FC, Vege SS. Dorsal pancreas agenesis and polysplenia/heterotaxy syndrome: a novel association with aortic coarctation and a review of the literature. JOP. 2007; 8:433–437. PMID: 17625295.8. Adeyemi SD. Combination of annular pancreas and partial situs inversus: a multiple organ malrotation syndrome associated with duodenal obstruction. J Pediatr Surg. 1988; 23:188–191. PMID: 3343656.
Article9. Ito H, Ohgi S, Kanno T, Ishibashi T. Heterotaxy syndrome with pancreatic malrotation: CT features. Abdom Imaging. 2003; 28:856–858. PMID: 14753606.
Article10. Mishra S. Cardiac and non-cardiac abnormalities in heterotaxy syndrome. Indian J Pediatr. 2015; 82:1135–1146. PMID: 26612104.
Article11. Barbarini DS, Haslinger V, Schmidt K, Patch AM, Müller G, Simma B. Neonatal diabetes mellitus due to pancreas agenesis: a new case report and review of the literature. Pediatr Diabetes. 2009; 10:487–491. PMID: 19496968.
Article12. Ashraf A, Abdullatif H, Hardin W, Moates JM. Unusual case of neonatal diabetes mellitus due to congenital pancreas agenesis. Pediatr Diabetes. 2005; 6:239–243. PMID: 16390394.
Article13. Chen R, Hussain K, Al-Ali M, Dattani MT, Hindmarsh P, Jones PM, et al. Neonatal and late-onset diabetes mellitus caused by failure of pancreatic development: report of 4 more cases and a review of the literature. Pediatrics. 2008; 121:e1541–e1547. PMID: 18519458.
Article14. Kamisawa T, Tu Y, Egawa N, Ishiwata J, Okamoto A. Hypoplasia of ventral pancreas shows a threadlike ventral pancreatic duct. Pancreas. 1999; 18:214–215. PMID: 10090421.
Article15. Lång K, Lasson A, Müller MF, Thorlacius H, Toth E, Olsson R. Dorsal agenesis of the pancreas - a rare cause of abdominal pain and insulin-dependent diabetes. Acta Radiol. 2012; 53:2–4. PMID: 22139719.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Complete Agenesis of Dorsal Pancreas
- A Case of Complete Agenesis of the Dorsal Pancreas in a Patient with Newly Diagnosed Diabetes Mellitus
- Agenesis of the Dorsal Pancreas: An autopsy case
- A Case of Partial Agenesis of Dorsal Panacreas
- A Case of Complete Agenesis of the Dorsal Pancreas with Left Renal Agenesis and Absence of the Left Vertebral Pedicle in T12