Korean J Gastroenterol.
2017 May;69(5):298-307. 10.4166/kjg.2017.69.5.298.
The Performance of Serum Biomarkers for Predicting Fibrosis in Patients with Chronic Viral Hepatitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Dankook University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea. ihsong21@dankook.ac.kr
- 3Department of Pathology, Dankook University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea.
- KMID: 2383388
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2017.69.5.298
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/AIMS
The invasiveness of a liver biopsy and its inconsistent results have prompted efforts to develop noninvasive tools to evaluate the severity of chronic hepatitis. This study was intended to assess the performance of serum biomarkers for predicting liver fibrosis in patients with chronic viral hepatitis.
METHODS
A total of 302 patients with chronic hepatitis B or C, who had undergone liver biopsy, were retrospectively enrolled. We investigated the diagnostic accuracy of several clinical factors for predicting advanced fibrosis (F≥3).
RESULTS
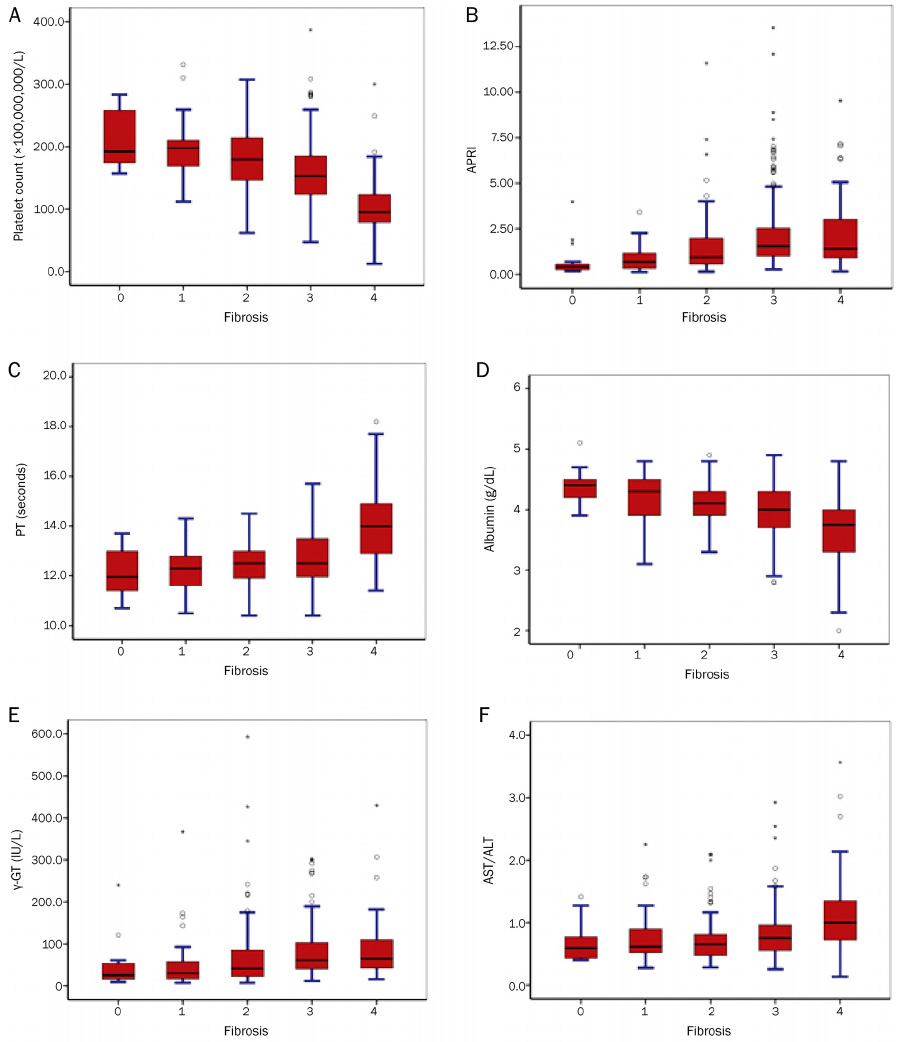
The study population included 227 patients with chronic hepatitis B, 73 patients with chronic hepatitis C, and 2 patients with co-infection (hepatitis B and C). Histological cirrhosis was identified in 16.2% of the study population. The grade of porto-periportal activity was more correlated with the stage of chronic hepatitis compared with that of lobular activity (r=0.640 vs. r=0.171). Fibrosis stage was correlated with platelet count (r=-0.520), aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index (APRI) (r=0.390), prothrombin time (r=0.376), and albumin (r=-0.357). For the diagnosis of advanced fibrosis, platelet count and APRI were the most predictive variables (AUROC=0.752, and 0.713, respectively).
CONCLUSIONS
In a hepatitis B endemic region, platelet count and APRI could be considered as reliable non-invasive markers for predicting fibrosis of chronic viral hepatitis. However, it is necessary to validate the diagnostic accuracy of these markers in another population.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bravo AA, Sheth SG, Chopra S. Liver biopsy. N Engl J Med. 2001; 344:495–500.2. Dienstag JL. The role of liver biopsy in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2002; 36:5 Suppl 1. S152–S160.3. Seeff LB, Everson GT, Morgan TR, et al. Complication rate of percutaneous liver biopsies among persons with advanced chronic liver disease in the HALT-C trial. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010; 8:877–883.4. McGill DB, Rakela J, Zinsmeister AR, Ott BJ. A 21-year experience with major hemorrhage after percutaneous liver biopsy. Gastroenterology. 1990; 99:1396–1400.5. Van Thiel DH, Gavaler JS, Wright H, Tzakis A. Liver biopsy. Its safety and complications as seen at a liver transplant center. Transplantation. 1993; 55:1087–1090.6. Manning DS, Afdhal NH. Diagnosis and quantitation of fibrosis. Gastroenterology. 2008; 134:1670–1681.7. Regev A, Berho M, Jeffers LJ, et al. Sampling error and intraobserver variation in liver biopsy in patients with chronic HCV infection. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002; 97:2614–2618.8. Maharaj B, Maharaj RJ, Leary WP, et al. Sampling variability and its influence on the diagnostic yield of percutaneous needle biopsy of the liver. Lancet. 1986; 1:523–525.9. Bedossa P, Dargère D, Paradis V. Sampling variability of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2003; 38:1449–1457.10. Colloredo G, Guido M, Sonzogni A, Leandro G. Impact of liver biopsy size on histological evaluation of chronic viral hepatitis: the smaller the sample, the milder the disease. J Hepatol. 2003; 39:239–244.11. Grønbaek K, Christensen PB, Hamilton‐Dutoit S, et al. Interobserver variation in interpretation of serial liver biopsies from patients with chronic hepatitis C. J Viral Hepat. 2002; 9:443–449.12. Friedrich-Rust M, Ong MF, Martens S, et al. Performance of transient elastography for the staging of liver fibrosis: a meta-analysis. Gastroenterology. 2008; 134:960–974.13. Rizzo L, Calvaruso V, Cacopardo B, et al. Comparison of transient elastography and acoustic radiation force impulse for non-invasive staging of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011; 106:2112–2120.14. Wang QB, Zhu H, Liu HL, Zhang B. Performance of magnetic resonance elastography and diffusion‐weighted imaging for the staging of hepatic fibrosis: a meta‐analysis. Hepatology. 2012; 56:239–247.15. Park YN, Chon CY, Park JB, et al. Histological grading and staging of chronic hepatitis standardized guideline proposed by the Korean Study Group for the Pathology of Digestive Diseases. Korean J Pathol. 1999; 33:337–346.16. Yu E. Korean Study Group for the Pathology of Digestive Diseases. Histologic grading and staging of chronic hepatitis: on the basis of standardized guideline proposed by the Korean Study Group for the Pathology of Digestive Diseases. Taehan Kan Hakhoe Chi. 2003; 9:42–46.17. Wai CT, Greenson JK, Fontana RJ, et al. A simple noninvasive index can predict both significant fibrosis and cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2003; 38:518–526.18. Lin ZH, Xin YN, Dong QJ, et al. Performance of the aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index for the staging of hepatitis C-related fibrosis: an updated meta-analysis. Hepatology. 2011; 53:726–736.19. Bataller R, Brenner DA. Liver fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 2005; 115:209–218.20. Benyon RC, Arthur MJ. Extracellular matrix degradation and the role of hepatic stellate cells. Semin Liver Dis. 2001; 21:373–384.21. Afdhal NH, Nunes D. Evaluation of liver fibrosis: a concise review. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004; 99:1160–1174.22. Castera L. Non-invasive diagnosis of steatosis and fibrosis. Diabetes metab. 2008; 34(6 Pt 2):674–679.23. Zhou K, Lu LG. Assessment of fibrosis in chronic liver diseases. J Dig Dis. 2009; 10:7–14.24. Rosenberg WM, Voelker M, Thiel R, et al. Serum markers detect the presence of liver fibrosis: a cohort study. Gastroenterology. 2004; 127:1704–1713.25. Shin WG, Park SH, Jang MK, et al. Aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index (APRI) can predict liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B. Dig Liver Dis. 2008; 40:267–274.26. Sim SJ, Cheong JY, Cho SW, et al. Efficacy of AST to platelet ratio index in predicting severe hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2005; 45:340–347.27. Wai CT, Cheng CL, Wee A, et al. Non‐invasive models for predicting histology in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Liver int. 2006; 26:666–672.28. Shaheen AA, Myers RP. Diagnostic accuracy of the aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index for the prediction of hepatitis C-related fibrosis: a systematic review. Hepatology. 2007; 46:912–921.29. Sheth SG, Flamm SL, Gordon FD, Chopra S. AST/ALT ratio predicts cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Am J Gastroenterol. 1998; 93:44–48.30. Guha IN, Myers RP, Patel K, Talwalkar JA. Biomarkers of liver fibrosis: what lies beneath the receiver operating characteristic curve? Hepatology. 2011; 54:1454–1462.31. Halfon P, Bourliere M, Deydier R, et al. Independent prospective multicenter validation of biochemical markers (fibrotest-actitest) for the prediction of liver fibrosis and activity in patients with chronic hepatitis C: the fibropaca study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006; 101:547–555.32. Poynard T, Imbert-Bismut F, Munteanu M, et al. Overview of the diagnostic value of biochemical markers of liver fibrosis (FibroTest, HCV FibroSure) and necrosis (ActiTest) in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Comp Hepatol. 2004; 3:8.33. Angulo P, Hui JM, Marchesini G, et al. The NAFLD fibrosis score: a noninvasive system that identifies liver fibrosis in patients with NAFLD. Hepatology. 2007; 45:846–854.34. Ratziu V. Serum fibrosis markers: death by validation or a leap of faith? J Hepatol. 2010; 53:222–224.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- New Biomarkers of Chronic Hepatitis B
- The role of different viral biomarkers on the management of chronic hepatitis B
- Clinical and Histologic Evaluation on HBeAg Positive and Negative Chronic Hepatitis B in Young Adults
- New perspectives of biomarkers for the management of chronic hepatitis B
- The Clinical Significance of Serum Hyaluronic Acid and Type IV Collagen Levels in Chronic Viral Hepatitis and Liver Cirrhosis