Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr.
2015 Dec;18(4):261-267. 10.5223/pghn.2015.18.4.261.
The Importance of Esophageal and Gastric Diseases as Causes of Chest Pain
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kyjoo@hanyang.ac.kr
- KMID: 2383304
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2015.18.4.261
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Pediatric chest pain is considered to be idiopathic or caused by benign diseases. This study was to find out how much upper gastrointestinal (UGI) diseases are major causes of chest pain in pediatric patients.
METHODS
The records of 75 children (42 boys and 33 girls, aged 3-17 years old) who have presented with mainly chest pain from January 1995 to March 2015 were retrospectively reviewed. Chest X-ray and electrocardiography (ECG) were performed in all aptients. Further cardiologic and gastrointestinal (GI) evaluations were performed in indicated patients.
RESULTS
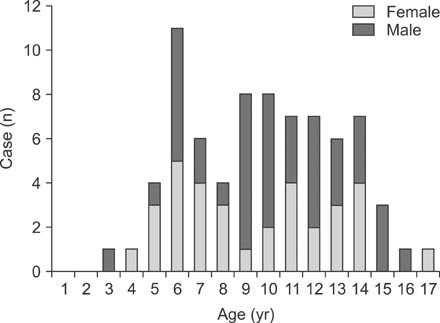
Chest pain was most common in the children of 6 and 9 to 14 years old. Esopha-gogastric diseases were unexpectedly the most common direct causes of the chest pain, the next are idiopathic, cardiac diseases, chest trauma, respiratory disease, and psychosomatic disease. Even though 21 showed abnormal ECG findings and 7 showed abnormalities on echocardiography, cardiac diseases were determined to be the direct causes only in 9. UGI endoscopy was performed in 57 cases, and esophago-gastric diseases which thereafter were thought to be causative diseases were 48 cases. The mean age of the children with esophago-gastric diseases were different with marginal significance from that of the other children with chest pain not related with esophago-gastric diseases. All the 48 children diagnosed with treated with GI medicines based on the diagnosis, and 37 cases (77.1%) subsequently showed clinical improvement.
CONCLUSION
Diagnostic approaches to find out esophageal and gastric diseases in children with chest pain are important as well as cardiac and respiratory investigations.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Driscoll DJ, Glicklich LB, Gallen WJ. Chest pain in children: a prospective study. Pediatrics. 1976; 57:648–651.
Article2. Fyfe DA, Moodie DS. Chest pain in pediatric patients presenting to a cardiac clinic. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 1984; 23:321–324.
Article3. Pantell RH, Goodman BW Jr. Adolescent chest pain: a prospective study. Pediatrics. 1983; 71:881–887.
Article4. Bernstein D. History and physical examination. In : Kliegman RM, Stanton BF, St Geme JW, Schor NF, editors. Nelson textbook of pediatrics. 20th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders;2015. p. 2163–2170.5. Yoon KL. Chest pain in children and adolescents. J Korean Med Assoc. 2010; 53:407–414.
Article6. Sabri MR, Ghavanini AA, Haghighat M, Imanieh MH. Chest pain in children and adolescents: epigastric tenderness as a guide to reduce unnecessary work-up. Pediatr Cardiol. 2003; 24:3–5.
Article7. Jang KM, Choe BH, Choe JY, Hong SJ, Park HJ, Chu MA, et al. Changing prevalence of helicobacter pylori infections in korean children with recurrent abdominal pain. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2015; 18:10–16.
Article8. Asnes RS, Santulli R, Bemporad JR. Psychogenic chest pain in children. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 1981; 20:788–791.
Article9. Raiola G, Galati MC, De Sanctis V, Salerno D, Arcuri VM, Mussari A. Chest pain in adolescents. Minerva Pediatr. 2002; 54:623–630.10. Selbst SM. Chest pain in children. Pediatrics. 1985; 75:1068–1070.
Article11. Swenson JM, Fischer DR, Miller SA, Boyle GJ, Ettedgui JA, Beerman LB. Are chest radiographs and electrocardiograms still valuable in evaluating new pediatric patients with heart murmurs or chest pain? Pediatrics. 1997; 99:1–3.
Article12. Kim JH, Moon HK, Jun JG. Clinical study of chest pain in children. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1990; 33:1526–1532.13. Leung AK, Robson WL, Cho H. Chest pain in children. Can Fam Physician. 1996; 42:1156–1160. 1163–1164.14. Selbst SM. Consultation with the specialist. Chest pain in children. Pediatr Rev. 1997; 18:169–173.
Article15. Evangelista JA, Parsons M, Renneburg AK. Chest pain in children: diagnosis through history and physical examination. J Pediatr Health Care. 2000; 14:3–8.
Article16. Selbst SM, Ruddy RM, Clark BJ, Henretig FM, Santulli T Jr. Pediatric chest pain: a prospective study. Pediatrics. 1988; 82:319–323.
Article17. Rowe BH, Dulberg CS, Peterson RG, Vlad P, Li MM. Characteristics of children presenting with chest pain to a pediatric emergency department. CMAJ. 1990; 143:388–394.18. Kocis KC. Chest pain in pediatrics. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1999; 46:189–203.
Article19. Woolf PK, Gewitz MH, Berezin S, Medow MS, Stewart JM, Fish BG, et al. Noncardiac chest pain in adolescents and children with mitral valve prolapse. J Adolesc Health. 1991; 12:247–250.
Article20. Berezin S, Medow MS, Glassman MS, Newman LJ. Esophageal chest pain in children with asthma. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1991; 12:52–55.
Article21. Hsia PC, Maher KA, Lewis JH, Cattau EL Jr, Fleischer DE, Benjamin SB. Utility of upper endoscopy in the evaluation of noncardiac chest pain. Gastrointest Endosc. 1991; 37:22–26.
Article22. Berezin S, Medow MS, Glassman MS, Newman LJ. Chest pain of gastrointestinal origin. Arch Dis Child. 1988; 63:1457–1460.
Article23. Katz PO. Approach to the patient with unexplained chest pain. Semin Gastrointest Dis. 2001; 12:38–45.
Article24. Lipsitz JD, Masia C, Apfel H, Marans Z, Gur M, Dent H, et al. Noncardiac chest pain and psychopathology in children and adolescents. J Psychosom Res. 2005; 59:185–188.
Article25. Shin SA, Kim YJ, Lee JW, Kim NS, Moon SJ. Clinical evaluation and diagnosis of children with chest pain. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 2003; 46:1248–1252.26. Cheung TK, Lim PW, Wong BC. Noncardiac chest pain--an Asia-Pacific survey on the views of primary care physicians. Dig Dis Sci. 2007; 52:3043–3048.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Diagnosis and Management of Esophageal Chest Pain
- Esophageal Motility and Reflux Diseases in Patients with Noncardiac Chest Pain
- Noncardiac Chest Pain: Epidemiology, Natural Course and Pathogenesis
- Guidelines of Esophageal Stent Insertion for Benign and Malignant Diseases
- The Role of High Resolution Manometry in Non-Cardiac Chest Pain