Ann Dermatol.
2011 Nov;23(4):432-438.
Causality Assessment of Cutaneous Adverse Drug Reactions
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Gachon University of Medicine and Science, Gil Hospital, Incheon, Korea. jyroh1@gilhospital.com
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Cutaneous adverse drug reactions (ADRs) are the most common adverse reactions attributed to drugs. A systematic and effective approach to a patient with suspected drug eruption allows for prompt recognition, classification and treatment of cutaneous ADRs. A standardized and effective approach for objective causality assessment is necessary to make consistent and accurate identification of ADRs.
OBJECTIVE
Although the Naranjo algorithm is the most widely used assessment tool, it contains many components which are not suitable for clinical assessment of ADRs in Korea. The purpose of this study is to compare correlations of the Naranjo algorithm and the Korean algorithm to evaluate usefulness of both algorithms in order to make a causal link between drugs and cutaneous ADRs. In addition, this study classifies the clinical types and causative agents of cutaneous ADRs.
METHODS
The authors retrospectively reviewed the clinical types and laboratory findings of patients who were diagnosed with cutaneous ADRs in the dermatology clinic at Gil hospital. One hundred forty-one patients were enrolled in this evaluation. The causal relationship of ADRs was assessed by using the Naranjo algorithm and Korean algorithm (version 2.0).
RESULTS
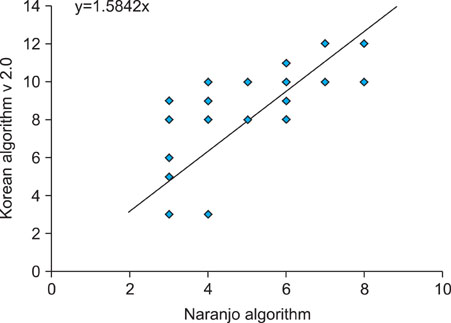
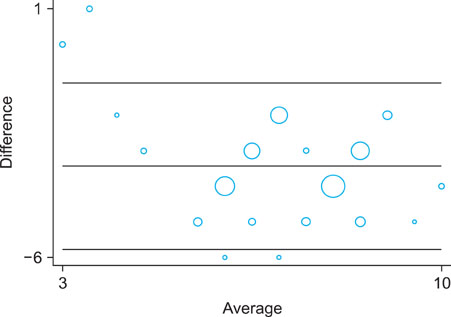
A cross-tabulation analysis was applied to the Naranjo algorithm and Korean algorithm (version 2.0). Simple correlation analysis and a Bland-Altman plot were used for statistical analysis. Correlation analysis confirmed that the two assessment algorithms were significantly correlated. Exanthematous eruptions (68.8%), Stevens- Johnson syndrome (10.6%), and urticaria (8.5%) were the most common types of cutaneoues ADRs. The most common causative agents were antibiotics/antimicrobials, antipyretics/non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and central nervous system depressants.
CONCLUSION
The Naranjo algorithm and Korean algorithm (version 2.0) were significantly correlated with each other, and thus reliable assessment methods to determine cutaneous ADRs.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Shear NH, Knowles SR, Shapiro L. Wolff K, Goldsmith LA, Katz SI, Gilchrest BA, Paller AS, Leffell DJ, editors. Cutaneous reactions to drugs. Fitzpatrick's dermatology in general medicine. 2008. 7th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill;355–362.2. James WD, Berger TG, Elston DM. Andrews' disease of the skin. 2006. 10th ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders;115–138.3. Knowles SR, Shear NH. Wolverton SE, editor. Cutaneous drug reactions with systemic features. Comprehensive dermatologic drug therapy. 2007. 2nd ed. Indianapolis: Saunders Elsevier;977–988.
Article4. Revuz J, Valeyrie-Allanore . Bolognia J, Jorizzo J, Rapini R, editors. Drug reaction. Dermatology. 2003. 1st ed. Philadelphia: Mosby;333–353.5. Kwon KS, Kim BS, Jang BS, Kim MB, Oh CK, Kwon YW, et al. Clinical study of drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) on drug eruption patients over the last 10 years (1995~2004). Korean J Dermatol. 2005. 43:1164–1169.6. Roujeau JC, Stern RS. Severe adverse cutaneous reactions to drugs. N Engl J Med. 1994. 331:1272–1285.
Article7. Bachot N, Roujeau JC. Differential diagnosis of severe cutaneous drug eruptions. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2003. 4:561–572.
Article8. Roujeau JC. Treatment of severe drug eruptions. J Dermatol. 1999. 26:718–722.
Article9. Johnson JA, Bootman JL. Drug-related morbidity and mortality. A cost-of-illness model. Arch Intern Med. 1995. 155:1949–1956.
Article10. Kim KJ, Jeong MC, Yoo JH. Clinical study and skin tests of patients with drug eruption. Korean J Dermatol. 1998. 36:887–896.11. Shin KS, Cho KH, Lee YS. Clinical study of hospitalized patients with drug eruption during a 10-year reriod (1975-1985). Korean J Dermatol. 1987. 25:176–182.12. Kim SN, Lee BH. Clinical study for drug eruptions. Korean J Dermatol. 1978. 16:377–381.13. Naranjo CA, Busto U, Sellers EM, Sandor P, Ruiz I, Roberts EA, et al. A method for estimating the probability of adverse drug reactions. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1981. 30:239–245.
Article14. Hong KS, Park BJ, Sin SG, Yang JS, Lee SM, Kim YN, et al. Development of a Korean algorithm for causality assessment of adverse drug reactions. J Korean Soc Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2002. 10:129–142.
Article15. Franceschi M, Scarcelli C, Niro V, Seripa D, Pazienza AM, Pepe G, et al. Prevalence, clinical features and avoidability of adverse drug reactions as cause of admission to a geriatric unit: a prospective study of 1756 patients. Drug Saf. 2008. 31:545–556.
Article16. Davies EC, Green CF, Mottram DR, Pirmohamed M. Adverse drug reactions in hospitals: a narrative review. Curr Drug Saf. 2007. 2:79–87.
Article17. Lazarou J, Pomeranz BH, Corey PN. Incidence of adverse drug reactions in hospitalized patients: a meta-analysis of prospective studies. JAMA. 1998. 279:1200–1205.
Article18. Bang DS, Cho CK, Lee SN. Statistical study of dermatoses during the last 5 years (1976~1980). Korean J Dermatol. 1983. 21:37–44.19. Hahm JH. A comparative study on clinical evaluation of inpatient dermatology consultation between 1976 and 1991. Korean J Dermatol. 1992. 30:651–658.20. Becquemont L. Pharmacogenomics of adverse drug reactions: practical applications and perspectives. Pharmacogenomics. 2009. 10:961–969.
Article21. Lee SM, Hahn SK, Park BJ. Signal detection and causality evaluation for pharmacovigilance. J Korean Soc Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2005. 13:121–133.
Article22. Moore N, Biour M, Paux G, Loupi E, Begaud B, Boismare F, et al. Adverse drug reaction monitoring: doing it the French way. Lancet. 1985. 2:1056–1058.
Article23. Danan G, Benichou C. Causality assessment of adverse reactions to drugs--I. A novel method based on the conclusions of international consensus meetings: application to drug-induced liver injuries. J Clin Epidemiol. 1993. 46:1323–1330.
Article24. Classen DC, Pestotnik SL, Evans RS, Burke JP. Computerized surveillance of adverse drug events in hospital patients. JAMA. 1991. 266:2847–2851.
Article25. Dormann H, Muth-Selbach U, Krebs S, Criegee-Rieck M, Tegeder I, Schneider HT, et al. Incidence and costs of adverse drug reactions during hospitalisation: computerised monitoring versus stimulated spontaneous reporting. Drug Saf. 2000. 22:161–168.26. Hogan DJ. Morbilliform drug eruptions. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009. 61:152.
Article27. Gerson D, Sriganeshan V, Alexis JB. Cutaneous drug eruptions: a 5-year experience. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008. 59:995–999.
Article28. Gendernalik SB, Galeckas KJ. Fixed drug eruptions: a case report and review of the literature. Cutis. 2009. 84:215–219.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cutaneous adverse drug reactions
- Hyperprolactinemia after taking Levosulpiride and its Causality Assessment: An Adverse Event Reported by a Community Pharmacy
- Comparison of the Naranjo and WHO-Uppsala Monitoring Centre criteria for causality assessment of adverse drug reactions
- The frequency of adverse drug reactions in a tertiary care hostpital in Korea
- Adverse drug reactions