J Periodontal Implant Sci.
2016 Jun;46(3):152-165. 10.5051/jpis.2016.46.3.152.
The effects of bone density and crestal cortical bone thickness on micromotion and peri-implant bone strain distribution in an immediately loaded implant: a nonlinear finite element analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Nara Medical University, Nara, Japan. sugiurat@naramed-u.ac.jp
- 2Applied Electronics Laboratory, Kanazawa Institute of Technology, Tokyo, Japan.
- KMID: 2382980
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2016.46.3.152
Abstract
- PURPOSE
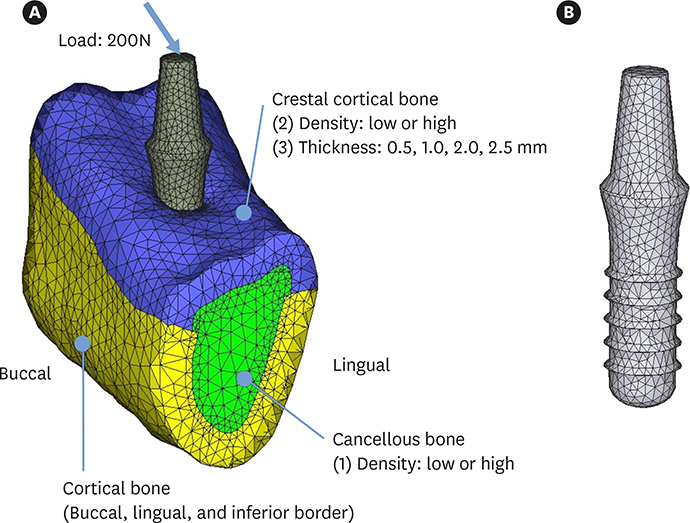
This study investigated the effects of bone density and crestal cortical bone thickness at the implant-placement site on micromotion (relative displacement between the implant and bone) and the peri-implant bone strain distribution under immediate-loading conditions.
METHODS
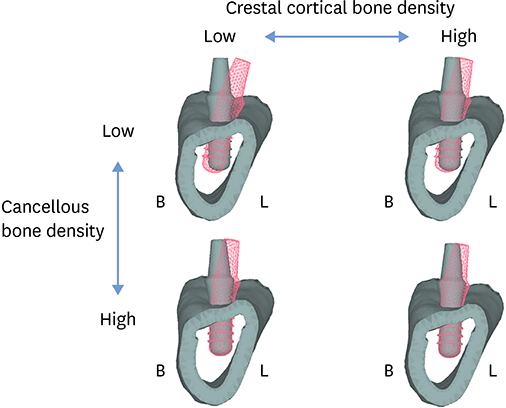
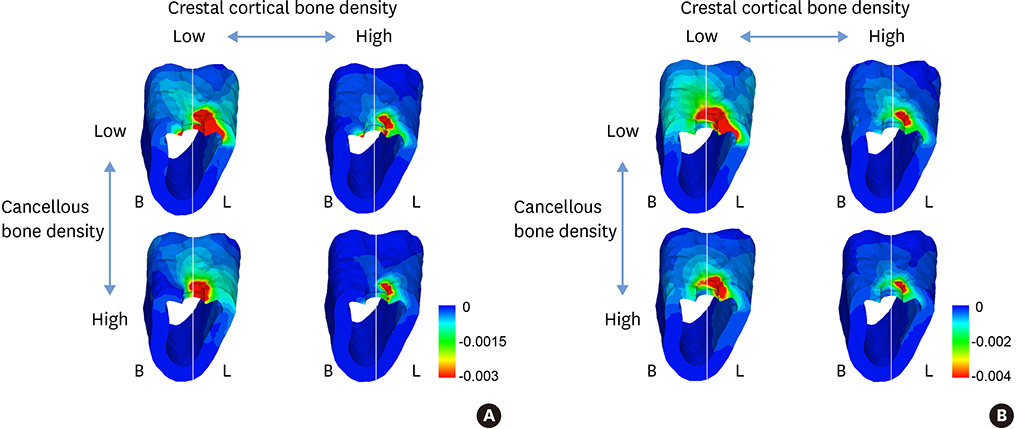
A three-dimensional finite element model of the posterior mandible with an implant was constructed. Various bone parameters were simulated, including low or high cancellous bone density, low or high crestal cortical bone density, and crestal cortical bone thicknesses ranging from 0.5 to 2.5 mm. Delayed- and immediate-loading conditions were simulated. A buccolingual oblique load of 200 N was applied to the top of the abutment.
RESULTS
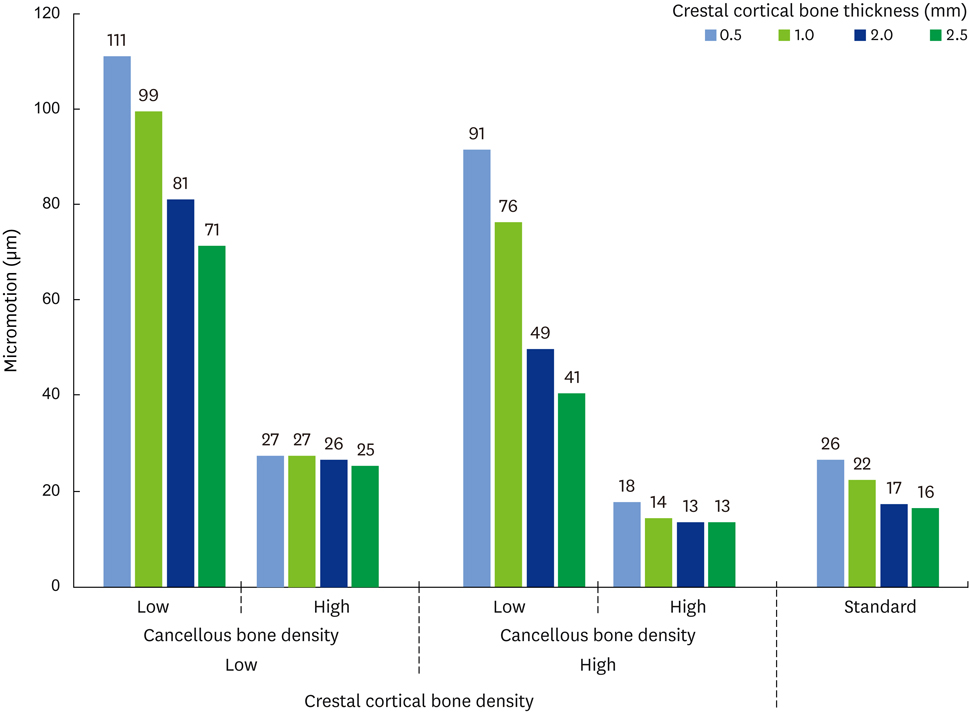
The maximum extent of micromotion was approximately 100 μm in the low-density cancellous bone models, whereas it was under 30 μm in the high-density cancellous bone models. Crestal cortical bone thickness significantly affected the maximum micromotion in the low-density cancellous bone models. The minimum principal strain in the peri-implant cortical bone was affected by the density of the crestal cortical bone and cancellous bone to the same degree for both delayed and immediate loading. In the low-density cancellous bone models under immediate loading, the minimum principal strain in the peri-implant cortical bone decreased with an increase in crestal cortical bone thickness.
CONCLUSIONS
Cancellous bone density may be a critical factor for avoiding excessive micromotion in immediately loaded implants. Crestal cortical bone thickness significantly affected the maximum extent of micromotion and peri-implant bone strain in simulations of low-density cancellous bone under immediate loading.
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Three-dimensional finite element analysis according to the insertion depth of an immediately loaded implant in the anterior maxilla
Cheol-Woo Park, Sung-Hun Kim, In-Sung Yeo, Hyung-In Yoon, Jung-Suk Han
J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2018;56(2):105-113. doi: 10.4047/jkap.2018.56.2.105.Effects of implant tilting and the loading direction on the displacement and micromotion of immediately loaded implants: an in vitro experiment and finite element analysis
Tsutomu Sugiura, Kazuhiko Yamamoto, Satoshi Horita, Kazuhiro Murakami, Sadami Tsutsumi, Tadaaki Kirita
J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2017;47(4):251-262. doi: 10.5051/jpis.2017.47.4.251.
Reference
-
1. Misch CE, Wang HL, Misch CM, Sharawy M, Lemons J, Judy KW. Rationale for the application of immediate load in implant dentistry: Part I. Implant Dent. 2004; 13:207–217.
Article2. Laviv A, Levin L, Usiel Y, Schwartz-Arad D. Survival of immediately provisionalized dental implants: a case-control study with up to 5 years follow-up. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2010; 12:Suppl 1. e23–7.
Article3. Pessoa RS, Coelho PG, Muraru L, Marcantonio E Jr, Vaz LG, Vander Sloten J, et al. Influence of implant design on the biomechanical environment of immediately placed implants: computed tomography-based nonlinear three-dimensional finite element analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2011; 26:1279–1287.4. Brunski JB, Puleo DA, Nanci A. Biomaterials and biomechanics of oral and maxillofacial implants: current status and future developments. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2000; 15:15–46.5. Duyck J, Rønold HJ, Van Oosterwyck H, Naert I, Vander Sloten J, Ellingsen JE. The influence of static and dynamic loading on marginal bone reactions around osseointegrated implants: an animal experimental study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2001; 12:207–218.
Article6. Pilliar RM, Lee JM, Maniatopoulos C. Observations on the effect of movement on bone ingrowth into porous-surfaced implants. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986; (208):108–113.
Article7. Tabassum A, Meijer GJ, Wolke JG, Jansen JA. Influence of surgical technique and surface roughness on the primary stability of an implant in artificial bone with different cortical thickness: a laboratory study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2010; 21:213–220.
Article8. Bayarchimeg D, Namgoong H, Kim BK, Kim MD, Kim S, Kim TI, et al. Evaluation of the correlation between insertion torque and primary stability of dental implants using a block bone test. J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2013; 43:30–36.
Article9. Ikumi N, Tsutsumi S. Assessment of correlation between computerized tomography values of the bone and cutting torque values at implant placement: a clinical study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2005; 20:253–260.10. Rozé J, Babu S, Saffarzadeh A, Gayet-Delacroix M, Hoornaert A, Layrolle P. Correlating implant stability to bone structure. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2009; 20:1140–1145.
Article11. Hsu JT, Fuh LJ, Tu MG, Li YF, Chen KT, Huang HL. The effects of cortical bone thickness and trabecular bone strength on noninvasive measures of the implant primary stability using synthetic bone models. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2013; 15:251–261.
Article12. Miyamoto I, Tsuboi Y, Wada E, Suwa H, Iizuka T. Influence of cortical bone thickness and implant length on implant stability at the time of surgery--clinical, prospective, biomechanical, and imaging study. Bone. 2005; 37:776–780.
Article13. Bardyn T, Gédet P, Hallermann W, Büchler P. Quantifying the influence of bone density and thickness on resonance frequency analysis: an in vitro study of biomechanical test materials. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009; 24:1006–1014.14. Nkenke E, Hahn M, Weinzierl K, Radespiel-Tröger M, Neukam FW, Engelke K. Implant stability and histomorphometry: a correlation study in human cadavers using stepped cylinder implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2003; 14:601–609.
Article15. Marquezan M, Lima I, Lopes RT, Sant’Anna EF, de Souza MM. Is trabecular bone related to primary stability of miniscrews? Angle Orthod. 2014; 84:500–507.
Article16. Palma-Carrió C, Maestre-Ferrín L, Peñarrocha-Oltra D, Peñarrocha-Diago MA, Peñarrocha-Diago M. Risk factors associated with early failure of dental implants. A literature review. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2011; 16:e514–7.17. Petrie CS, Williams JL. Probabilistic analysis of peri-implant strain predictions as influenced by uncertainties in bone properties and occlusal forces. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2007; 18:611–619.
Article18. Guan H, van Staden R, Loo YC, Johnson N, Ivanovski S, Meredith N. Influence of bone and dental implant parameters on stress distribution in the mandible: a finite element study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009; 24:866–876.19. Sugiura T, Yamamoto K, Kawakami M, Horita S, Murakami K, Kirita T. Influence of bone parameters on peri-implant bone strain distribution in the posterior mandible. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2015; 20:e66–73.
Article20. Morton D, Jaffin R, Weber HP. Immediate restoration and loading of dental implants: clinical considerations and protocols. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2004; 19:Suppl. 103–108.21. Lekholm U, Zarb GA. Patient selection and preparation. In : Brånemark PI, Zarb GA, Albrektsson T, editors. Tissue-integrated prostheses: osseointegration in clinical dentistry. Chicago (IL): Quintessence;1985. p. 199–209.22. Kurniawan D, Nor FM, Lee HY, Lim JY. Finite element analysis of bone-implant biomechanics: refinement through featuring various osseointegration conditions. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012; 41:1090–1096.
Article23. Keyak JH, Rossi SA, Jones KA, Skinner HB. Prediction of femoral fracture load using automated finite element modeling. J Biomech. 1998; 31:125–133.
Article24. Ding X, Liao SH, Zhu XH, Zhang XH, Zhang L. Effect of diameter and length on stress distribution of the alveolar crest around immediate loading implants. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2009; 11:279–287.
Article25. Mericske-Stern R, Assal P, Mericske E, Bürgin W. Occlusal force and oral tactile sensibility measured in partially edentulous patients with ITI implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1995; 10:345–353.
Article26. Hudieb M, Wakabayashi N, Suzuki T, Kasugai S. Morphologic classification and stress analysis of the mandibular bone in the premolar region for implant placement. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2010; 25:482–490.27. Gonda T, Yasuda D, Ikebe K, Maeda Y. Biomechanical factors associated with mandibular cantilevers: analysis with three-dimensional finite element models. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2014; 29:e275–82.
Article28. Vandamme K, Naert I, Geris L, Vander Sloten J, Puers R, Duyck J. The effect of micro-motion on the tissue response around immediately loaded roughened titanium implants in the rabbit. Eur J Oral Sci. 2007; 115:21–29.
Article29. Trisi P, Perfetti G, Baldoni E, Berardi D, Colagiovanni M, Scogna G. Implant micromotion is related to peak insertion torque and bone density. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2009; 20:467–471.
Article30. Cha JY, Kil JK, Yoon TM, Hwang CJ. Miniscrew stability evaluated with computerized tomography scanning. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2010; 137:73–79.
Article31. Shen WL, Chen CS, Hsu ML. Influence of implant collar design on stress and strain distribution in the crestal compact bone: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2010; 25:901–910.32. Frost HM. Skeletal structural adaptations to mechanical usage (SATMU): 2. Redefining Wolff’s law: the remodeling problem. Anat Rec. 1990; 226:414–422.
Article33. Pattin CA, Caler WE, Carter DR. Cyclic mechanical property degradation during fatigue loading of cortical bone. J Biomech. 1996; 29:69–79.
Article34. Mellal A, Wiskott HW, Botsis J, Scherrer SS, Belser UC. Stimulating effect of implant loading on surrounding bone. Comparison of three numerical models and validation by in vivo data. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2004; 15:239–248.35. Huang HL, Fuh LJ, Hsu JT, Tu MG, Shen YW, Wu CL. Effects of implant surface roughness and stiffness of grafted bone on an immediately loaded maxillary implant: a 3D numerical analysis. J Oral Rehabil. 2008; 35:283–290.
Article36. Ferreira MB, Barão VA, Delben JA, Faverani LP, Hipólito AC, Assunção WG. Non-linear 3D finite element analysis of full-arch implant-supported fixed dentures. Mater Sci Eng C. 2014; 38:306–314.
Article37. Duaibis R, Kusnoto B, Natarajan R, Zhao L, Evans C. Factors affecting stresses in cortical bone around miniscrew implants: a three-dimensional finite element study. Angle Orthod. 2012; 82:875–880.38. Chiapasco M. Early and immediate restoration and loading of implants in completely edentulous patients. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2004; 19:Suppl. 76–91.39. Seker E, Ulusoy M, Ozan O, Doğan DÖ, Seker BK. Biomechanical effects of different fixed partial denture designs planned on bicortically anchored short, graft-supported long, or 45-degree-inclined long implants in the posterior maxilla: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2014; 29:e1–9.
Article40. Chang PK, Chen YC, Huang CC, Lu WH, Chen YC, Tsai HH. Distribution of micromotion in implants and alveolar bone with different thread profiles in immediate loading: a finite element study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2012; 27:e96–101.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- THREE-DIMENSIONAL FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF THE EFFECT OF CORTICAL ENGAGEMENT ON IMPLANT LOAD TRANSFER IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE
- Effects of implant tilting and the loading direction on the displacement and micromotion of immediately loaded implants: an in vitro experiment and finite element analysis
- Three-dimensional finite element analysis according to the insertion depth of an immediately loaded implant in the anterior maxilla
- EFFECTS OF BONE ENGAGEMENT TYPE&IMPLANT LENGTH ON STRESS DISTRIBUTION: A THREE DIMENSIONAL FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS
- Contact non-linear finite element model analysis of initial stability of mini implant