J Korean Med Assoc.
2016 Mar;59(3):205-212. 10.5124/jkma.2016.59.3.205.
Usefulness of musculoskeletal ultrasonography for treatment of shoulder pain
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. drshoulder@korea.ac.kr
- KMID: 2382725
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5124/jkma.2016.59.3.205
Abstract
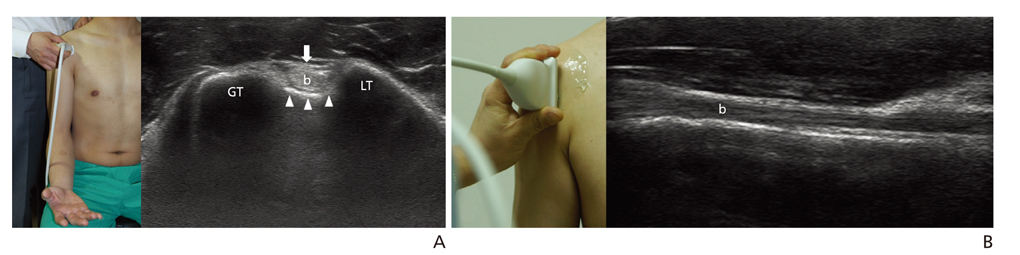
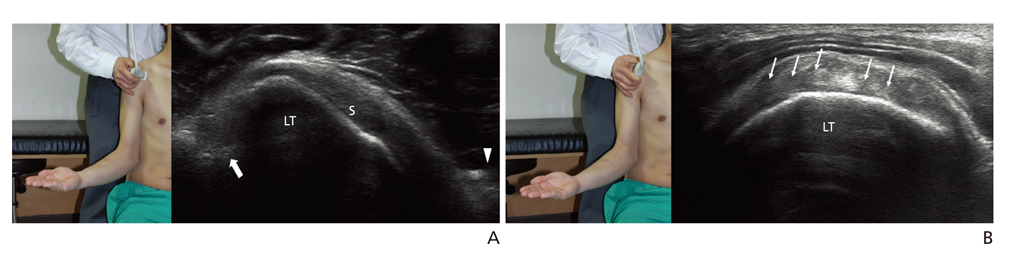
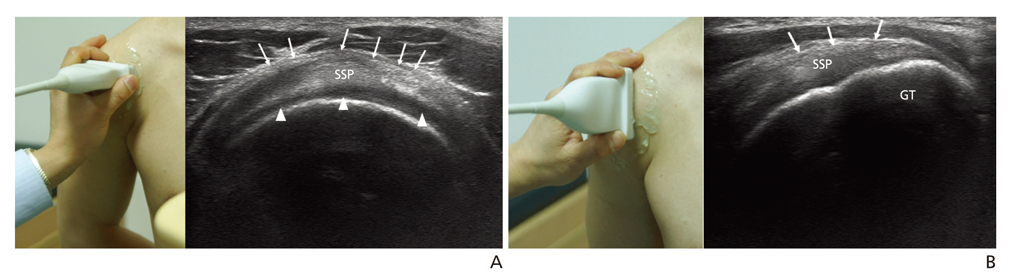
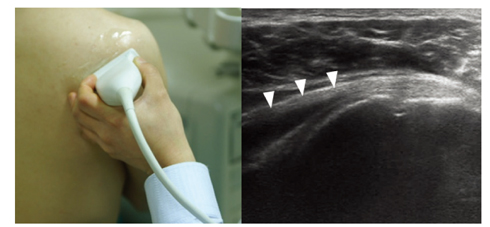
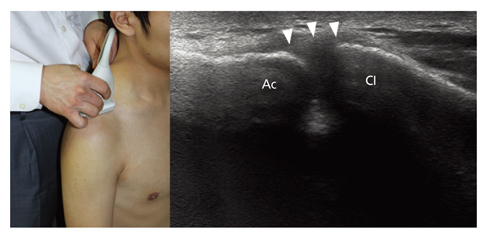
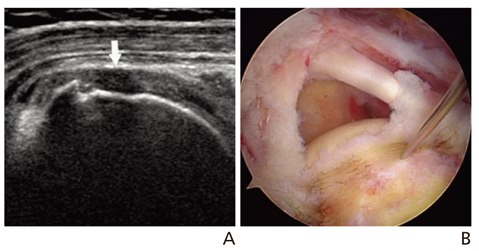
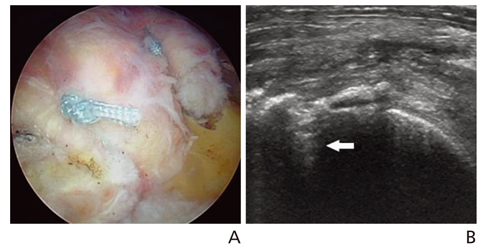
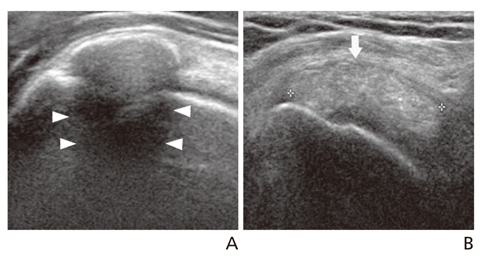
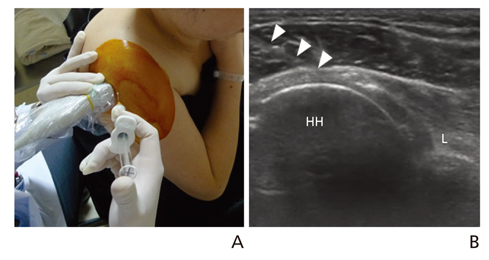
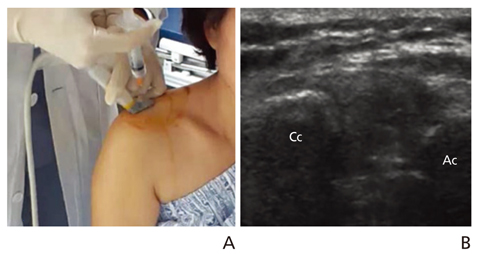
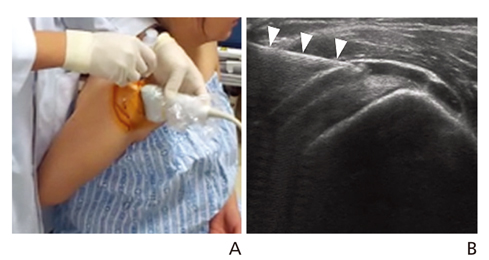
- Ultrasonography is a powerful and useful method for the examination of the various shoulder diseases. The use of high-resolution transducer and technical evolution allowed the improvement of the accuracy of detection of the rotator cuff disease. In addition to diagnostic tool, ultrasonography can be applied as an optimal guidance in many intervention therapy around shoulder. However, its limitation is that there is marked disparity between the operators' experience levels. This article describes stepwise methods for evaluating shoulder conditions, ultrasonographic findings of various shoulder pathology, and guidance techniques for intervention therapy.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Seltzer SE, Finberg HJ, Weissman BN, Kido DK, Collier BD. Arthrosonography: gray-scale ultrasound evaluation of the shoulder. Radiology. 1979; 132:467–468.
Article2. Iannotti JP, Ciccone J, Buss DD, Visotsky JL, Mascha E, Cotman K, Rawool NM. Accuracy of office-based ultrasonography of the shoulder for the diagnosis of rotator cuff tears. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005; 87:1305–1311.
Article3. Farin PU, Jaroma H, Harju A, Soimakallio S. Medial displace-ment of the biceps brachii tendon: evaluation with dynamic sonography during maximal external shoulder rotation. Radiology. 1995; 195:845–848.
Article4. Pujol N, Hargunani R, Gadikoppula S, Holloway B, Ahrens PM. Dynamic ultrasound assessment in the diagnosis of intra-articular entrapment of the biceps tendon (hourglass biceps): a preliminary investigation. Int J Shoulder Surg. 2009; 3:80–84.
Article5. Crass JR, Craig EV, Feinberg SB. The hyperextended internal rotation view in rotator cuff ultrasonography. J Clin Ultrasound. 1987; 15:416–420.
Article6. Crass JR, Craig EV, Feinberg SB. Ultrasonography of rotator cuff tears: a review of 500 diagnostic studies. J Clin Ultrasound. 1988; 16:313–327.
Article7. Smith J, Dahm DL, Newcomer-Aney KL. Role of sonography in the evaluation of unstable os acromiale. J Ultrasound Med. 2008; 27:1521–1526.
Article8. Mack LA, Matsen FA 3rd, Kilcoyne RF, Davies PK, Sickler ME. US evaluation of the rotator cuff. Radiology. 1985; 157:205–209.
Article9. Soble MG, Kaye AD, Guay RC. Rotator cuff tear: clinical expe-rience with sonographic detection. Radiology. 1989; 173:319–321.
Article10. Farin PU, Jaroma H, Harju A, Soimakallio S. Shoulder impinge-ment syndrome: sonographic evaluation. Radiology. 1990; 176:845–849.
Article11. Teefey SA, Hasan SA, Middleton WD, Patel M, Wright RW, Yamaguchi K. Ultrasonography of the rotator cuff: a compa-rison of ultrasonographic and arthroscopic findings in one hun-dred consecutive cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000; 82:498–504.12. Middleton WD, Edelstein G, Reinus WR, Melson GL, Totty WG, Murphy WA. Sonographic detection of rotator cuff tears. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1985; 144:349–353.
Article13. Van Holsbeeck MT, Kolowich PA, Eyler WR, Craig JG, Shirazi KK, Habra GK, Vanderschueren GM, Bouffard JA. US depiction of partial-thickness tear of the rotator cuff. Radiology. 1995; 197:443–446.
Article14. Teefey SA, Rubin DA, Middleton WD, Hildebolt CF, Leibold RA, Yamaguchi K. Detection and quantification of rotator cuff tears: comparison of ultrasonographic, magnetic resonance imaging, and arthroscopic findings in seventy-one consecutive cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004; 86:708–716.15. Oh CH, Oh JH, Jo KH, Kim SH, Bin SW, Gong HS. Discre-pancy of ultrasound-MR arthrography-arthroscopy for the diagnosis of rotator cuff tear: case report. J Korean Orthop Ultrasound Soc. 2008; 1:23–26.16. El-Dalati G, Castellarin G, Martone E, Ricci M, Vecchini E, Caffarri S, Fusaro M, Pozzi Mucelli R. Standard sonography and arthrosonography in the study of rotator cuff tears. Radiol Med. 2005; 110:616–622.17. Lee HS, Joo KB, Park CK, Kim YS, Jeong WK, Kim YS, Park DW, Kim SI, Park TS. Sonography of the shoulder after arth-rography (arthrosonography): preliminary results. J Clin Ultrasound. 2002; 30:23–32.
Article18. Middleton WD, Payne WT, Teefey SA, Hildebolt CF, Rubin DA, Yamaguchi K. Sonography and MRI of the shoulder: com-parison of patient satisfaction. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004; 183:1449–1452.19. Uhthoff HK, Sarkar K, Maynard JA. Calcifying tendinitis: a new concept of its pathogenesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976; (118):164–168.20. Chiou HJ, Chou YH, Wu JJ, Hsu CC, Huang DY, Chang CY. Evaluation of calcific tendonitis of the rotator cuff: role of color Doppler ultrasonography. J Ultrasound Med. 2002; 21:289–295.21. Codman EA. The shoulder: rupture of the supraspinatus tendon and other lesions in or about the subacromial bursa. Boston: Thomas Todd;1934.22. Neviaser JS. Adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder: a study of the pathological findings in periarthritis of the shoulder. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1945; 27:211–222.23. Lee MH, Ahn JM, Muhle C, Kim SH, Park JS, Kim SH, Kim SM, Kang HS. Adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder: diagnosis using magnetic resonance arthrography, with arthroscopic findings as the standard. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2003; 27:901–906.24. Jung JY, Jee WH, Chun HJ, Kim YS, Chung YG, Kim JM. Adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder: evaluation with MR arthro-graphy. Eur Radiol. 2006; 16:791–796.
Article25. Lee JC, Sykes C, Saifuddin A, Connell D. Adhesive capsulitis: sonographic changes in the rotator cuff interval with arthro-scopic correlation. Skeletal Radiol. 2005; 34:522–527.
Article26. Moore DC. Block of the suprascapular nerve. In: Moore DC, editor. Regional block: a handbook for use in the clinical practice of medicine and surgery. Springfield: Charles C Thomas;1979. p. 300–303.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ultrasound-Guided Injection in the Management of Shoulder Pain
- Shoulder Ultrasonography: Common Findings
- Erratum: Usefulness of musculoskeletal ultrasonography for treatment of shoulder pain
- Ultrasonography for Diagnosing Sports-Related Shoulder Pain
- Musculoskeletal Problems in Upper Extremity after Stroke