J Pathol Transl Med.
2015 Nov;49(6):497-510. 10.4132/jptm.2015.09.17.
Tongue Growth during Prenatal Development in Korean Fetuses and Embryos
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral Pathology, College of Dentistry, Gangnueng-Wonju National University, Gangneung, Korea. sukkeunlee@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Orthodontics, College of Dentistry, Gangnueng-Wonju National University, Gangneung, Korea.
- 3Department of Dental Hygiene, College of Health Sciences, Cheongju University, Cheongju, Korea.
- 4Department of Pathology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2381409
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.09.17
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Prenatal tongue development may affect oral-craniofacial structures, but this muscular organ has rarely been investigated.
METHODS
In order to document the physiology of prenatal tongue growth, we histologically examined the facial and cranial base structures of 56 embryos and 106 fetuses.
RESULTS
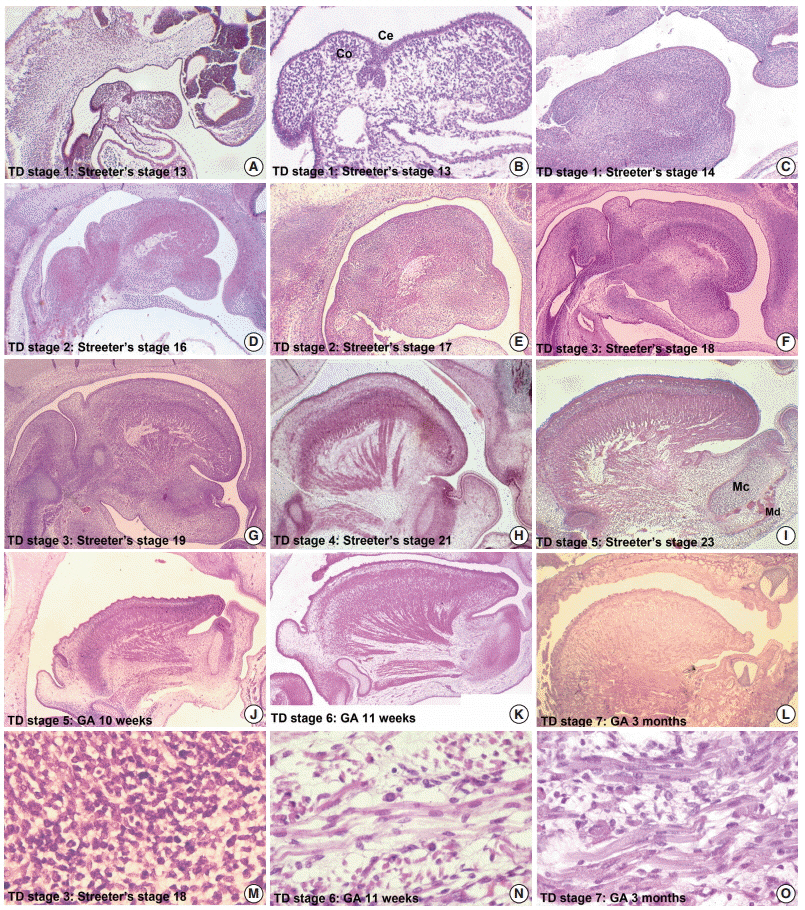
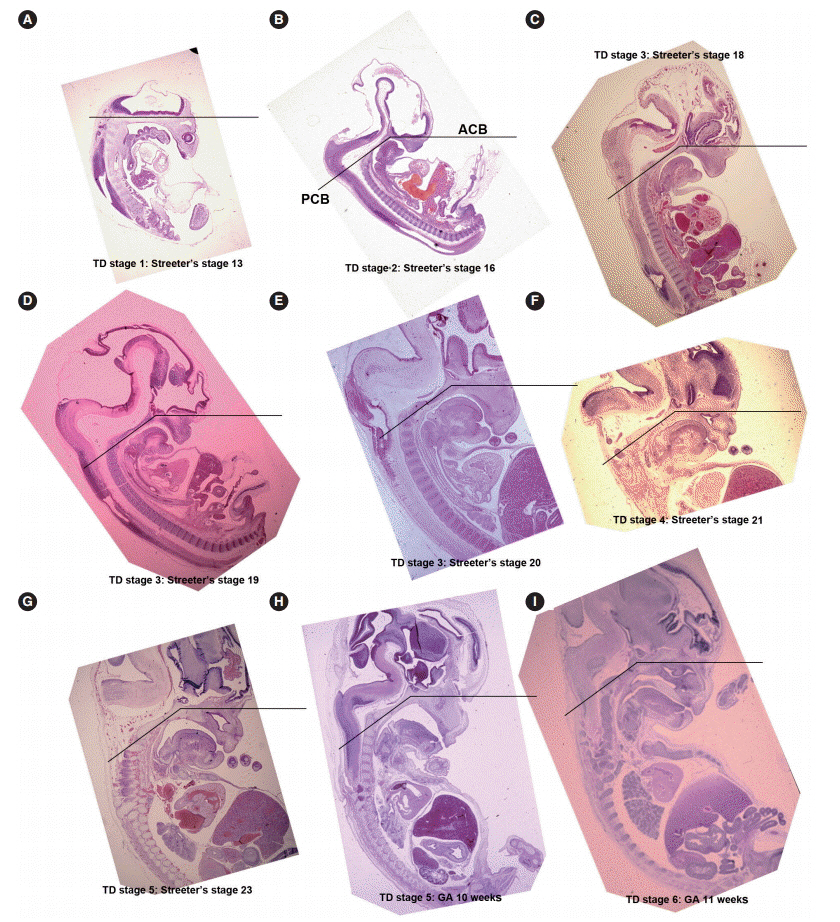
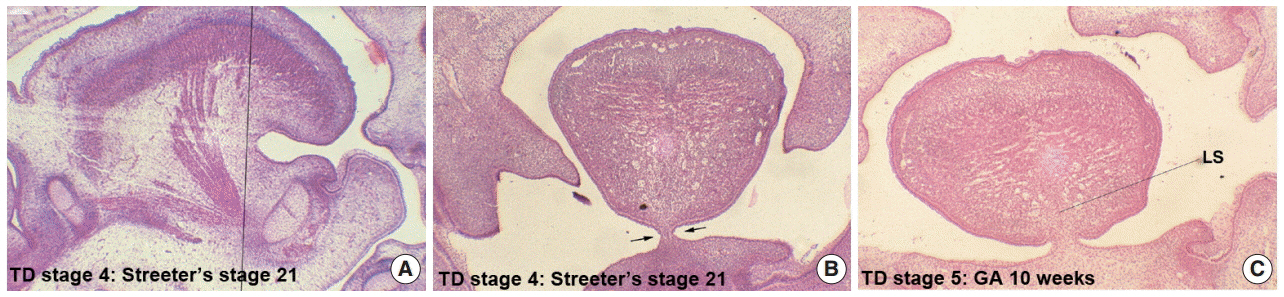
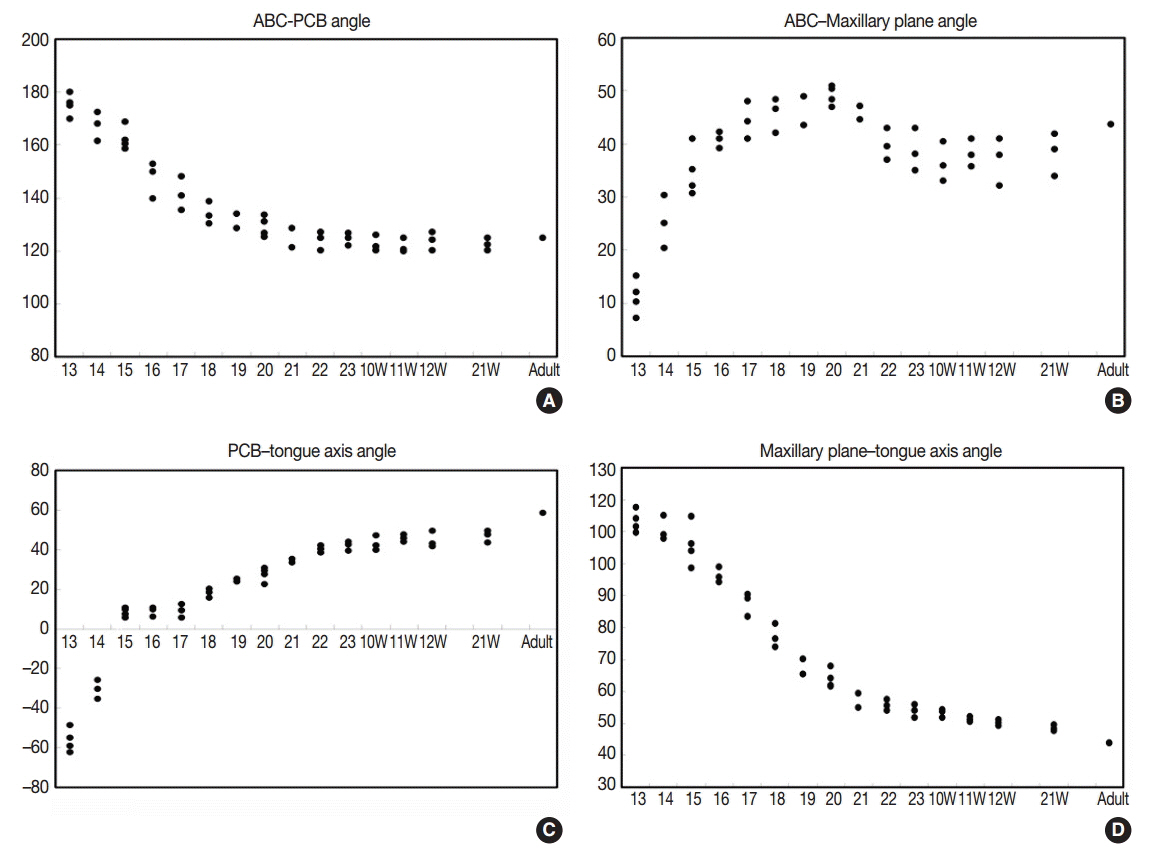
In Streeter's stages 13-14 (fertilization age [FA], 28 to 32 days), the tongue protruded into the stomodeal cavity from the retrohyoid space to the cartilaginous mesenchyme of the primitive cranial base, and in Streeter's stage 15 (FA, 33 to 36 days), the tongue rapidly swelled and compressed the cranial base to initiate spheno-occipital synchondrosis and continued to swell laterally to occupy most of the stomodeal cavity in Streeter's stage 16-17 (FA, 37 to 43 days). In Streeter's stage 18-20 (FA, 44 to 51 days), the tongue was vertically positioned and filled the posterior nasopharyngeal space. As the growth of the mandible and maxilla advanced, the tongue was pulled down and protruded anteriorly to form the linguomandibular complex. Angulation between the anterior cranial base (ACB) and the posterior cranial base (PCB) was formed by the emerging tongue at FA 4 weeks and became constant at approximately 124degrees-126degrees from FA 6 weeks until birth, which was consistent with angulations measured on adult cephalograms.
CONCLUSIONS
The early clockwise growth of the ACB to the maxillary plane became harmonious with the counter-clockwise growth of the PCB to the tongue axis during the early prenatal period. These observations suggest that human embryonic tongue growth affects ACB and PCB angulation, stimulates maxillary growth, and induces mandibular movement to achieve the essential functions of oral and maxillofacial structures.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Achtel LW, Cole LJ, Bailey JS. X-irradiation of defined areas of the heads of weanling rats: effect on body growth and incisor development. Radiat Res. 1967; 31:430–40.2. Siebert JR. Prenatal growth of the median face. Am J Med Genet. 1986; 25:369–79.
Article3. Yamane A, Bringas P Jr, Mayo ML, et al. Transforming growth factor alpha up-regulates desmin expression during embryonic mouse tongue myogenesis. Dev Dyn. 1998; 213:71–81.
Article4. Uchiyama K, Ishikawa A, Hanaoka K. Expression of lbx1 involved in the hypaxial musculature formation of the mouse embryo. J Exp Zool. 2000; 286:270–9.5. Nagata J, Yamane A. Progress of cell proliferation in striated muscle tissues during development of the mouse tongue. J Dent Res. 2004; 83:926–9.
Article6. Wozniak W. The peripheral part of the hypoglossal nerve in human embryos at stage 14 (32 days). Folia Morphol (Warsz). 1995; 54:227–30.7. O’Rahilly R, Muller F. The early development of the hypoglossal nerve and occipital somites in staged human embryos. Am J Anat. 1984; 169:237–57.8. Vasyutina E, Stebler J, Brand-Saberi B, Schulz S, Raz E, Birchmeier C. CXCR4 and Gab1 cooperate to control the development of migrating muscle progenitor cells. Genes Dev. 2005; 19:2187–98.
Article9. Abu-Elteen KH, Abu-Alteen RM. The prevalence of Candida albicans populations in the mouths of complete denture wearers. New Microbiol. 1998; 21:41–8.10. Aduss H, Pruzansky S. Postnatal craniofacial development in children with the oral-facial-digital syndrome. Arch Oral Biol. 1964; 9:193–203.
Article11. Achiron R, Ben Arie A, Gabbay U, Mashiach S, Rotstein Z, Lipitz S. Development of the fetal tongue between 14 and 26 weeks of gestation: in utero ultrasonographic measurements. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 1997; 9:39–41.12. Slavkin HC. Regulatory issues during early craniofacial development: a summary. Cleft Palate J. 1990; 27:101–9.
Article13. Dalrymple KR, Prigozy TI, Shuler CF. Embryonic, fetal, and neonatal tongue myoblasts exhibit molecular heterogeneity in vitro. Differentiation. 2000; 66:218–26.14. Moore KL. The developing human: clinically oriented embryology. Philadelphia: W. B. Saunders;1982.15. Egerbacher M, Bock P. Lingual papillae. Am J Surg Pathol. 1997; 21:360.
Article16. Kim CH, Park HW, Kim K, Yoon JH. Early development of the nose in human embryos: a stereomicroscopic and histologic analysis. Laryngoscope. 2004; 114:1791–800.
Article17. Yamane A. Embryonic and postnatal development of masticatory and tongue muscles. Cell Tissue Res. 2005; 322:183–9.
Article18. Nie X. Apoptosis, proliferation and gene expression patterns in mouse developing tongue. Anat Embryol (Berl). 2005; 210:125–32.
Article19. Streeter GL. Developmental horizons in human embryos: description of age groups XV, XVI, XVII, and XVIII, being the third issue of a survey of the Carnegie Collection. Carnegie Institution of Washington Publication 575. Contrib Embryol. 1948; 32:133–203.20. Streeter GL, Heuser CH, Corner GW. Developmental horizons in human embryos: description of age groups XIX, XX, XXI, XXII, and XXIII, being the fifth issue of a survey of the Carnegie collection. Carnegie Institution of Washington Publication 592. Contrib Embryol. 1951; 34:165–96.21. O’Rahilly R. Guide to the staging of human embryos. Anat Anz. 1972; 130:556–9.22. Barlow LA, Northcutt RG. The role of innervation in the development of taste buds: insights from studies of amphibian embryos. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998; 855:58–69.23. Swanson JJ, Kuehl-Kovarik MC, Elmquist JK, Sakaguchi DS, Jacobson CD. Development of the facial and hypoglossal motor nuclei in the neonatal Brazilian opossum brain. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1999; 112:159–72.
Article24. Lee SK, Kim YS, Lim CY, Chi JG. Prenatal growth pattern of the human maxilla. Acta Anat (Basel). 1992; 145:1–10.
Article25. Lee SK, Kim YS, Jo YA, Seo JW, Chi JG. Prenatal development of cranial base in normal Korean fetuses. Anat Rec. 1996; 246:524–34.
Article26. Lee SK, Kim YS, Oh HS, Yang KH, Kim EC, Chi JG. Prenatal development of the human mandible. Anat Rec. 2001; 263:314–25.
Article27. Chi JG, Suh YL, Lee SK, et al. Atlas of human embryo and fetus: embryonic, anatomic, histologic and ultrasonographic observations. Seoul: Academya;2001.28. Lee SK, Lim CY, Chi JG. Development and growth of tongue in Korean fetuses. Korean J Pathol. 1990; 24:358–74.29. Hong SJ. Study on the prenatal growth and development of tongue in Korean fetuses. Gangneung: Department of Oral Pathology, College of Dentistry Graduate School, Gangneung-Wonju National University;2006.30. Tamatsu Y, Gasser RF. Development of the sensory nerves to the dorsum of the tongue in staged human embryos. Clin Anat. 2004; 17:99–106.
Article31. Shuler CF, Dalrymple KR. Molecular regulation of tongue and craniofacial muscle differentiation. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2001; 12:3–17.
Article32. Sato M, Sato T. Fine structure of developed human tongue muscle. Okajimas Folia Anat Jpn. 1992; 69:115–30.
Article33. Langdon H, Klueber K, Barnwell Y. The anatomy of M. genioglossus in the 15-week human fetus. Anat Embryol (Berl). 1978; 155:107–13.
Article34. Diewert VM. A morphometric analysis of craniofacial growth and changes in spatial relations during secondary palatal development in human embryos and fetuses. Am J Anat. 1983; 167:495–522.
Article35. Humphrey T. Development of oral and facial motor mechanisms in human fetuses and their relation to craniofacial growth. J Dent Res. 1971; 50:1428–41.
Article36. Diewert VM. Differential changes in cartilage cell proliferation and cell density in the rat craniofacial complex during secondary palate development. Anat Rec. 1980; 198:219–28.
Article37. Diewert VM, Pratt RM. Selective inhibition of mandibular growth and induction of cleft palate by diazo-oxo-norleucine (DON) in the rat. Teratology. 1979; 20:37–51.
Article38. Greene RM, Pratt RM. Developmental aspects of secondary palate formation. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1976; 36:225–45.
Article39. Trenouth MJ. Angular changes in cephalometric and centroid planes during foetal growth. Br J Orthod. 1981; 8:77–81.
Article40. Trenouth MJ. Changes in the jaw relationships during human foetal cranio-facial growth. Br J Orthod. 1985; 12:33–9.
Article41. Humphrey T. The relation between human fetal mouth opening reflexes and closure of the palate. Am J Anat. 1969; 125:317–44.
Article42. Humphrey T. Palatopharyngeal fusion in a human fetus and its relation to cleft palate formation. Ala J Med Sci. 1970; 7:398–426.43. Niikuni N, Nakajima I, Akasaka M. The relationship between tongue-base position and craniofacial morphology in preschool children. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2004; 28:131–4.
Article44. Friede H, Figueroa AA. The Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome: a longitudinal study of the macroglossia and dentofacial complex. J Craniofac Genet Dev Biol Suppl. 1985; 1:179–87.45. Laroche C, Testelin S, Devauchelle B. Cleft palate and Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2005; 42:212–7.
Article46. Wang J, Goodger NM, Pogrel MA. The role of tongue reduction. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2003; 95:269–73.
Article47. Ardran GM, Harker P, Kemp FH. Tongue size in Down’s syndrome. J Ment Defic Res. 1972; 16:160–6.
Article48. Skrinjaric T, Glavina D, Jukic J. Palatal and dental arch morphology in Down syndrome. Coll Antropol. 2004; 28:841–7.49. Bradley RM, Mistretta CM, Nagai T. Demonstration of sensory innervation of rat tongue with anterogradely transported horseradish peroxidase. Brain Res. 1986; 367:364–7.
Article50. Matsushima TA, Satou M, Ueda K. Glossopharyngeal and tectal influences on tongue-muscle motoneurons in the Japanese toad. Brain Res. 1986; 365:198–203.
Article51. Mbiene JP, Mistretta CM. Initial innervation of embryonic rat tongue and developing taste papillae: nerves follow distinctive and spatially restricted pathways. Acta Anat (Basel). 1997; 160:139–58.
Article52. Berger AJ, Bayliss DA, Viana F. Development of hypoglossal motoneurons. J Appl Physiol (1985). 1996; 81:1039–48.
Article53. Vij S, Kanagasuntheram R. Development of the nerve supply to the human tongue. Acta Anat (Basel). 1972; 81:466–77.
Article54. Lee SK, Kim YS, Lim CY. A pathological consideration of ankyloglossia and lingual myoplasty. J Korean Dent Assoc. 1989; 27:287–308.55. Yoon JY, Lee I, Lee SS, et al. Cephalometric changes after lingual myoplasty for ankyloglossia associated malocclusions. Port Ortod. 2005; 10:1–17.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Development and Growth of Tongue in Korean Fetuses
- A study on the craniofacial growth and development in Korean embryos and fetuses
- Morphological Observation on the Prenatal Development of Human Femur: Analysis of 146 embryos and fetuses
- Sonoembryology
- The Effect of Bovine Serum Albumin on in Vitro Growth and Development of Mouse Two-Cell Stage Embryos