J Pathol Transl Med.
2015 Jan;49(1):52-60. 10.4132/jptm.2014.10.26.
Diagnostic Accuracy of Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Pancreatic Lesions
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. iapark@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2381353
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2014.10.26
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration cytology (EUS-FNAC) is currently the most commonly used procedure for obtaining cytologic specimens of the pancreas. It is accurate, minimally invasive, safe and cost-effective. However, there is discrepancy between cytological and surgical diagnoses. This study was aimed at evaluating the diagnostic accuracy of EUS-FNAC of the pancreas.
METHODS
We performed a retrospective review of 191 cases of pancreatic lesions initially diagnosed by EUS-FNAC with subsequent histological diagnosis between 2010 and 2012 in the Department of Pathology, Seoul National University Hospital. Cytologic and surgical diagnoses were categorized into five groups: negative, benign, atypical, malignant, and insufficient for diagnosis. Subsequently, 167 cases with satisfactory yield in both surgical and cytology specimens were statistically analyzed to determine correlations with diagnosis.
RESULTS
In comparison to surgical diagnoses, cytologic diagnoses were true-positive in 103 cases (61.7%), true-negative in 28 cases (16.8%), false-positive in 9 cases (5.4%), and false-negative in 27 cases (16.1%). The diagnostic accuracy was 78.4%, sensitivity was 79.2%, and specificity was 75.7%. The positive predictive value was 92.0%, and negative predictive value was 50.9%.
CONCLUSIONS
EUS-FNAC has high accuracy, sensitivity, specificity and positive predictive value. Overcoming the limitations of EUS-FNAC will make it a useful and reliable diagnostic tool for accurate evaluation of pancreatic lesions.
MeSH Terms
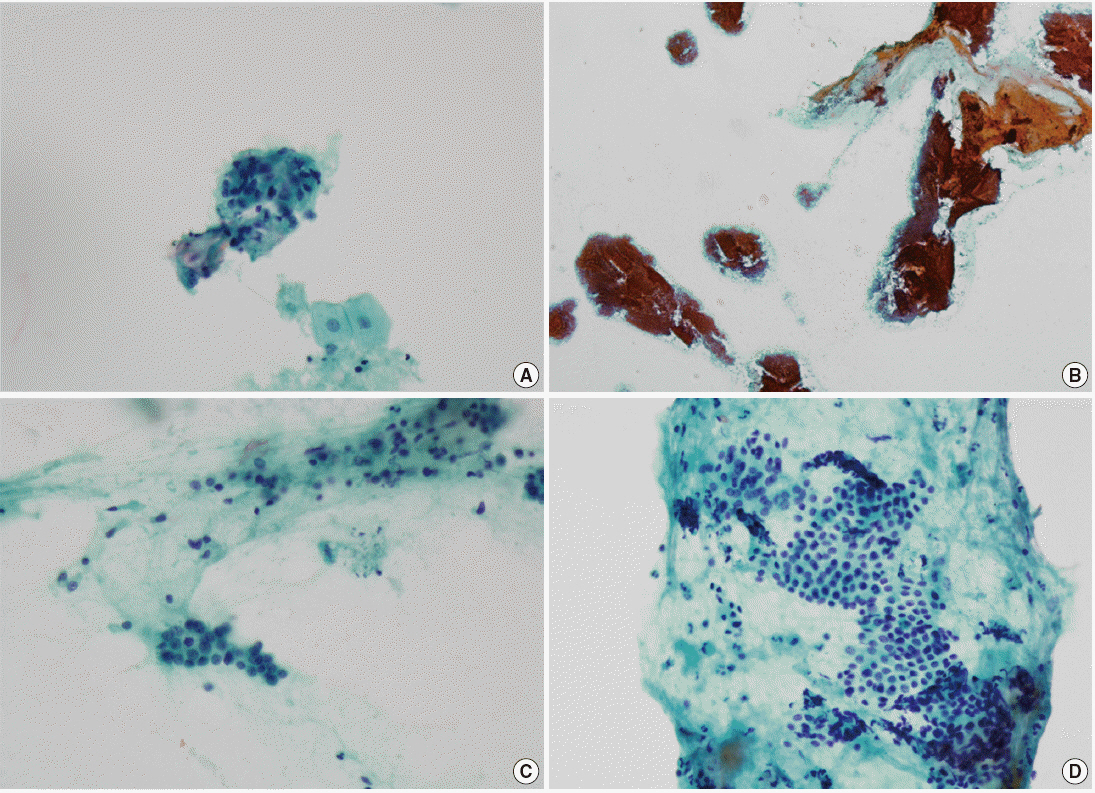
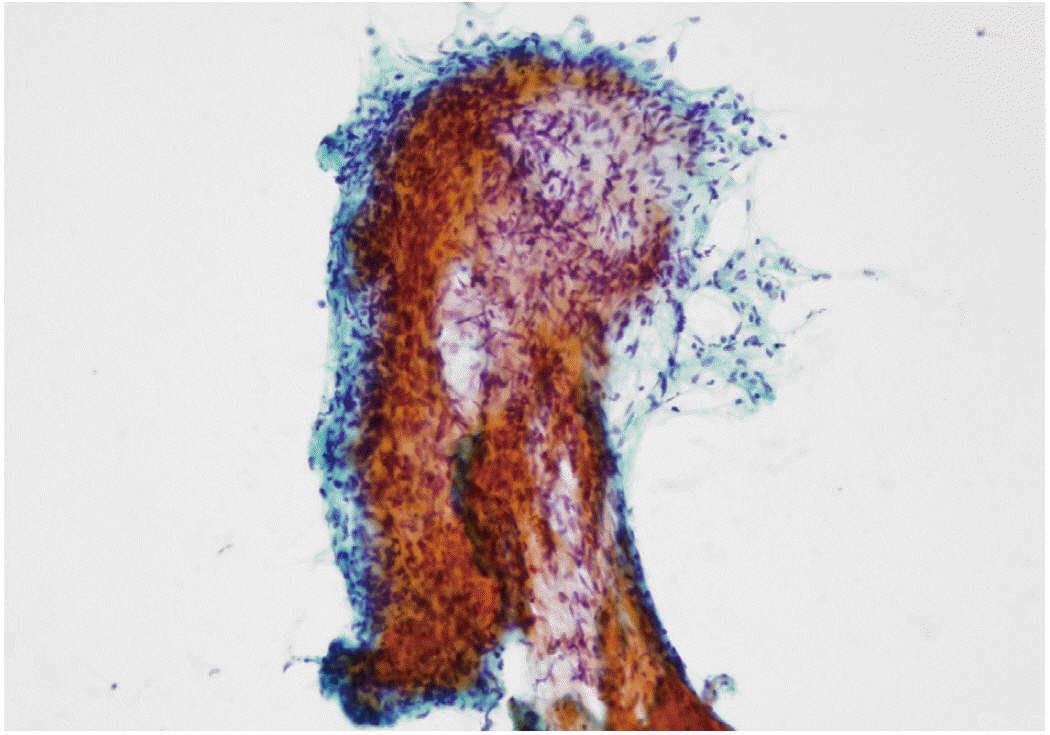
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jung KW, Won YJ, Kong HJ, Oh CM, Lee DH, Lee JS. Cancer statistics in Korea: incidence, mortality, survival, and prevalence in 2011. Cancer Res Treat. 2014; 46:109–23.
Article2. Matsumoto K, Takeda Y, Harada K, Horie Y, Yashima K, Murawaki Y. Effect of pancreatic juice cytology and/or endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy for pancreatic tumor. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014; 29:223–7.
Article3. Bluen BE, Lachter J, Khamaysi I, et al. Accuracy and quality assessment of EUS-FNA: a single-center large cohort of biopsies. Diagn Ther Endosc. 2012; 2012:139563.
Article4. Hewitt MJ, McPhail MJ, Possamai L, Dhar A, Vlavianos P, Monahan KJ. EUS-guided FNA for diagnosis of solid pancreatic neoplasms: a meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012; 75:319–31.
Article5. Yoshinaga S, Suzuki H, Oda I, Saito Y. Role of endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration (EUS-FNA) for diagnosis of solid pancreatic masses. Dig Endosc. 2011; 23 Suppl 1:29–33.
Article6. Kim TH, Choi KH, Song HS, Kim JW, Jeon BJ. Histology combined with cytology by endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration for the diagnosis of solid pancreatic mass and intra-abdominal lymphadenopathy. Gut Liver. 2013; 7:605–10.
Article7. Matsuyama M, Ishii H, Kuraoka K, et al. Ultrasound-guided vs endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration for pancreatic cancer diagnosis. World J Gastroenterol. 2013; 19:2368–73.8. Fisher L, Segarajasingam DS, Stewart C, Deboer WB, Yusoff IF. Endoscopic ultrasound guided fine needle aspiration of solid pancreatic lesions: performance and outcomes. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009; 24:90–6.
Article9. Ardengh JC, Lopes CV, de Lima LF, et al. Diagnosis of pancreatic tumors by endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration. World J Gastroenterol. 2007; 13:3112–6.
Article10. Varadarajulu S, Tamhane A, Eloubeidi MA. Yield of EUS-guided FNA of pancreatic masses in the presence or the absence of chronic pancreatitis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005; 62:728–36.
Article11. Mitsuhashi T, Ghafari S, Chang CY, Gu M. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration of the pancreas: cytomorphological evaluation with emphasis on adequacy assessment, diagnostic criteria and contamination from the gastrointestinal tract. Cytopathology. 2006; 17:34–41.12. Erickson RA, Sayage-Rabie L, Beissner RS. Factors predicting the number of EUS-guided fine-needle passes for diagnosis of pancreatic malignancies. Gastrointest Endosc. 2000; 51:184–90.
Article13. Kawamoto S, Siegelman SS, Hruban RH, Fishman EK. Lymphoplasmacytic sclerosing pancreatitis (autoimmune pancreatitis): evaluation with multidetector CT. Radiographics. 2008; 28:157–70.
Article14. Abraham SC, Leach S, Yeo CJ, et al. Eosinophilic pancreatitis and increased eosinophils in the pancreas. Am J Surg Pathol. 2003; 27:334–42.
Article15. Moriya T, Kimura W, Hirai I, et al. Pancreatic schwannoma: Case report and an updated 30-year review of the literature yielding 47 cases. World J Gastroenterol. 2012; 18:1538–44.
Article16. Navina S, McGrath K, Chennat J, et al. Adequacy assessment of endoscopic ultrasound-guided, fine-needle aspirations of pancreatic masses for theranostic studies: optimization of current practices is warranted. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2014; 138:923–8.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- How to optimize the diagnostic yield of endoscopic ultrasoundguided fine-needle sampling in solid pancreatic lesions from a technical perspective
- How Can We Get the Best Results with Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration?
- Role of Repeated Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration for Inconclusive Initial Cytology Result
- Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration in Cystic Pancreatic Lesions
- Technical Advances in Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)-Guided Tissue Acquisition for Pancreatic Cancers: How Can We Get the Best Results with EUS-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration?