Clin Endosc.
2015 Nov;48(6):579-582. 10.5946/ce.2015.48.6.579.
Endoscopic Extraction of Biliary Fascioliasis Diagnosed Using Intraductal Ultrasonography in a Patient with Acute Cholangitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Digestive Disease Center and Research Institute, Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University School of Medicine, Bucheon and Seoul, Korea. joseph@schmc.ac.kr
- KMID: 2380421
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2015.48.6.579
Abstract
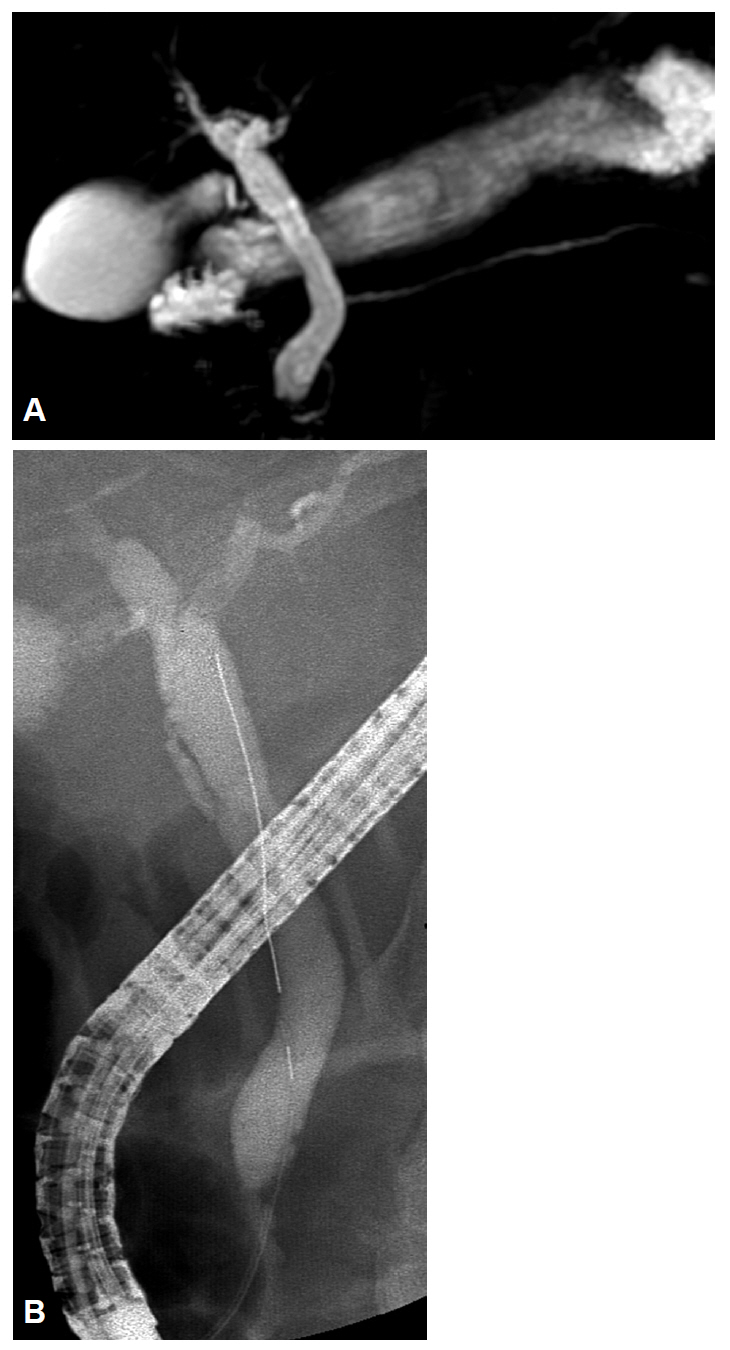
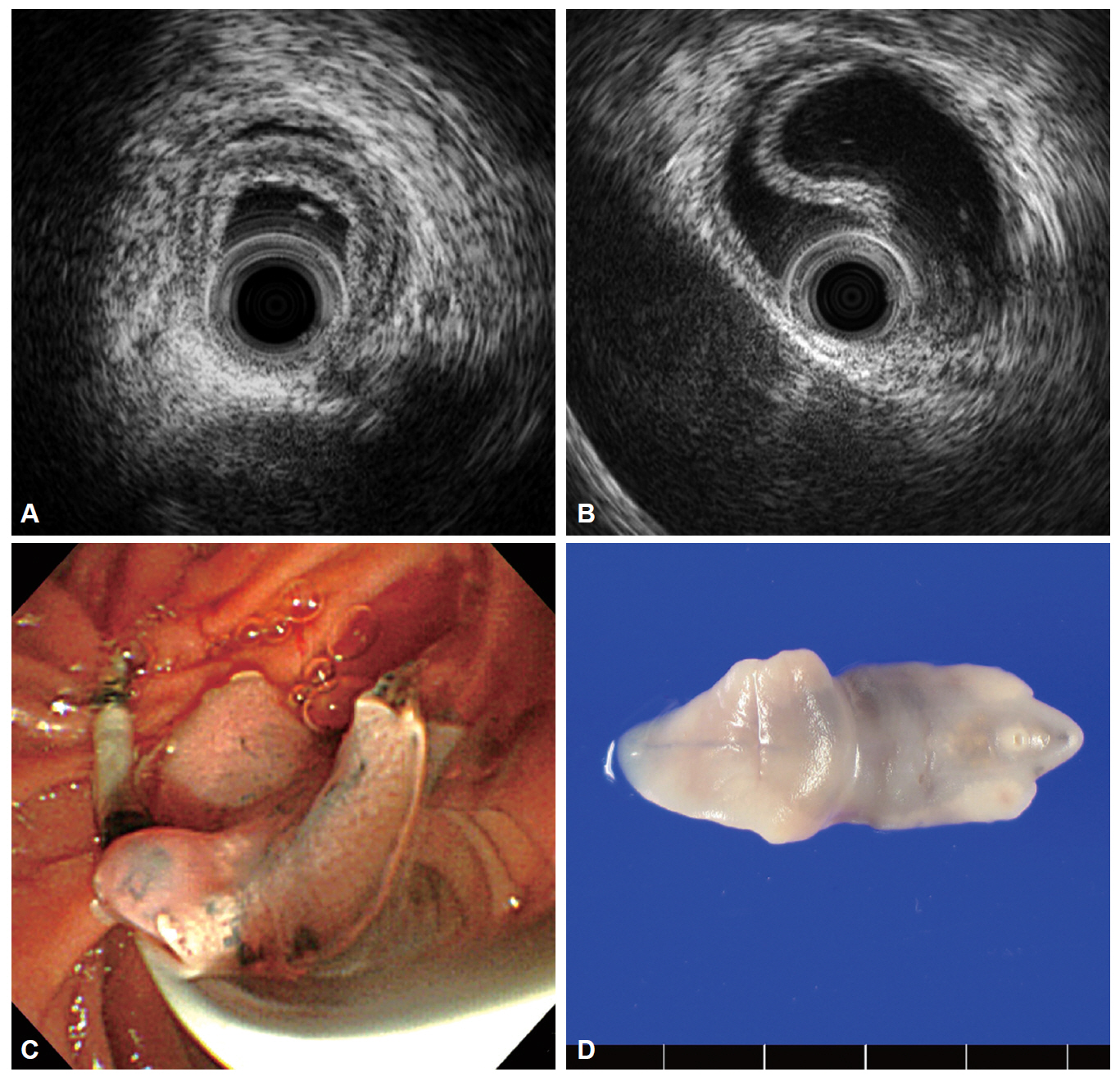
- Fasciola hepatica infection may result in biliary obstruction with or without cholangitis in the chronic biliary phase. Because clinical symptoms and signs of F. hepatica are similar to other biliary diseases that cause bile duct obstruction, such as stones or bile duct malignancies, that are, in fact, more common, this condition may not be suspected and diagnosis may be overlooked and delayed. Patients undergoing endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography or endoscopic ultrasonography for the evaluation of bile duct obstruction may be incidentally detected with the worm, and diagnosis can be confirmed by extraction of the leaf-like trematode from the bile duct. Intraductal ultrasonography (IDUS) can provide high-resolution cross-sectional images of the bile duct, and is useful in evaluating indeterminate biliary diseases. We present a case of biliary fascioliasis that was diagnosed using IDUS and managed endoscopically in a patient with acute cholangitis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
트리클라벤다졸로 치료한 간질에 의한 간농양
Hyun Joon Park, Gil-Soon Choi, Minjung Jung, Sang Uk Lee
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2021;77(1):39-44. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2020.152.
Reference
-
1. Rana SS, Bhasin DK, Nanda M, Singh K. Parasitic infestations of the biliary tract. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2007; 9:156–164.
Article2. Kaya M, Beştaş R, Cetin S. Clinical presentation and management of Fasciola hepatica infection: single-center experience. World J Gastroenterol. 2011; 17:4899–4904.
Article3. el-Newihi HM, Waked IA, Mihas AA. Biliary complications of Fasciola hepatica: the role of endoscopic retrograde cholangiography in management. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1995; 21:309–311.4. Dias LM, Silva R, Viana HL, Palhinhas M, Viana RL. Biliary fascioliasis: diagnosis, treatment and follow-up by ERCP. Gastrointest Endosc. 1996; 43:616–620.
Article5. Tamada K, Inui K, Menzel J. Intraductal ultrasonography of the bile duct system. Endoscopy. 2001; 33:878–885.
Article6. Badalov NL, Anklesaria A, Torok A, et al. Fasciola hepatica causing acute pancreatitis complicated by biliary sepsis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 70:386–387.
Article7. Goenka MK, Majumder S, Sethy PK, Kumar S, Goenka U. Hepatobiliary fascioliasis treated at endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. Endoscopy. 2010; 42 Suppl 2:E103.
Article8. Sotoudehmanesh R, Yoonessi A. Diagnosis of Fasciola hepatica by endoscopic ultrasound. Endoscopy. 2003; 35:1088.
Article9. Woo SY, Jung HJ, Kim WT, et al. A case of acute pancreatitis associated with Fasciola hepatica. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 2006; 33:183–186.10. Ha KH, Kim KY, Park KW, et al. Fasciola hepatica infection with sphincter of Oddi dysfunction. Korean J Pancreas Biliary Tract. 2011; 16:165–168.11. Kang BK, Jung BK, Lee YS, et al. A case of Fasciola hepatica infection mimicking cholangiocarcinoma and ITS-1 sequencing of the worm. Korean J Parasitol. 2014; 52:193–196.
Article12. Kim YH, Kang KJ, Kwon JH. Four cases of hepatic fascioliasis mimicking cholangiocarcinoma. Korean J Hepatol. 2005; 11:169–175.13. Na SY, Cha SW, Lee BH, et al. Biliary fascioliasis mimicking focal Cholangiocarcinoma on PET/CT. Korean J Pancreas Biliary Tract. 2012; 17:37–41.14. Kim DC, Moon JH, Choi HJ, et al. Usefulness of intraductal ultrasonography in icteric patients with highly suspected choledocholithiasis showing normal endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. Dig Dis Sci. 2014; 59:1902–1908.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Biliary Fascioliasis Mimicking Neoplasia of the Common Hepatic Duct
- Intraductal ultrasonography for biliary strictures
- A Case of Fascioliasis Diagnosed by ERCP
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Cholangitis
- Usefulness of Intraductal Ultrasonography in the Diagnosis of Cholangiocarcinoma and IgG4-Related Sclerosing Cholangitis