Cancer Res Treat.
2015 Jan;47(1):18-25. 10.4143/crt.2013.202.
A Phase I/II Trial to Evaluate the Technical Feasibility of Partial Breast Irradiation with Three-Dimensional Conformal Radiation Therapy in Korean Women with Stage I Breast Carcinoma: An Initial Report of the Korean Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (KROG) Study 0804
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. ahnsja@chonnam.ac.kr
- 2Department of Surgery, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiation Oncology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2380386
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2013.202
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This prospective study was designed to verify the technical feasibility of partial breast irradiation in breast cancer patients with small breasts, which are commonly encountered in Korean women.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
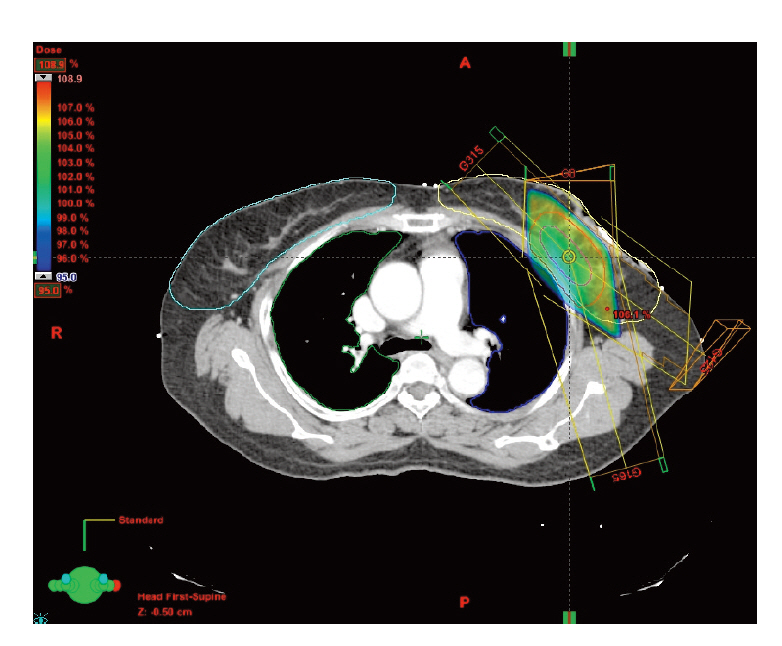
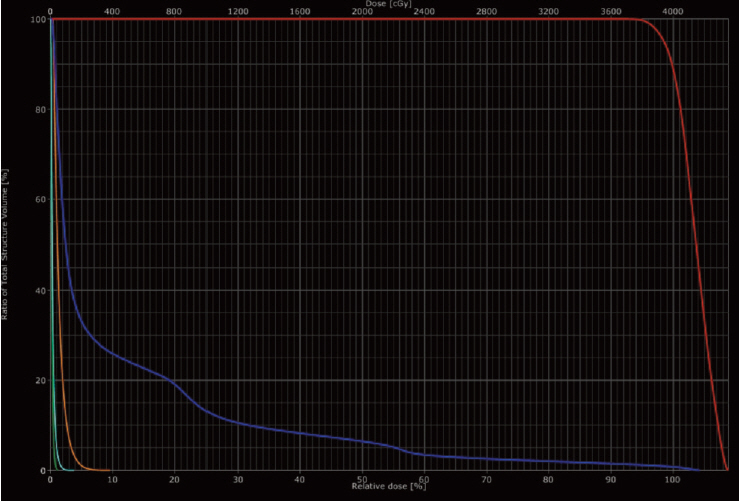
A total of 40 Gy, administered in 10 fractions on consecutive days (one fraction per day), was prescribed to the isocenters of the fields using three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy (3-DCRT). For all patients, treatment planning and dose parameters strictly adhered to the constraints set forth in the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) 0319 protocol. This study was designed such that if fewer than five of the first 42 evaluable patients received unacceptable scores, the treatment would be considered reproducible.
RESULTS
Ten treatment plans (23.8%) were determined to have major variations. There was no major variation in planning target volume (PTV) coverage. The ipsilateral and contralateral breast dose limitations were not met in four (9.5%) and four cases (9.5%), respectively. Major variations in ipsilateral and contralateral lung dose limitations were observed in two cases (4.8%). Major variations in the heart and thyroid dose limitations were observed in one (2.4%) and one case (2.4%), respectively. In multivariate analysis, a ratio of PTV to ipsilateral breast volume (PTV/IB) > 0.16 was the only significant factor that statistically affected major variations.
CONCLUSION
We concluded that partial breast irradiation using 3-DCRT could not be reproduced in Korean breast cancer patients, particularly small-volumed breast surrogated as PTV/IB > 0.16. The dominant cause was the major variation in surrounding normal breast tissues.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Assessment of Eligibility and Utilization of Accelerated Partial Breast Irradiation in Korean Breast Cancer Patients (KROG 22-15)
Seok-Joo Chun, Ji Hwan Jo, Yong Bae Kim, Sangjoon Park, Sung-Ja Ahn, Su Ssan Kim, Kyubo Kim, Kyung Hwan Shin
Cancer Res Treat. 2024;56(2):549-556. doi: 10.4143/crt.2023.1109.
Reference
-
References
1. Polgar C, Fodor J, Major T, Nemeth G, Lovey K, Orosz Z, et al. Breast-conserving treatment with partial or whole breast irradiation for low-risk invasive breast carcinoma: 5-year results of a randomized trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007; 69:694–702.2. Smith BD, Arthur DW, Buchholz TA, Haffty BG, Hahn CA, Hardenbergh PH, et al. Accelerated partial breast irradiation consensus statement from the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2019; 74:987–1001.
Article3. Valachis A, Mauri D, Polyzos NP, Mavroudis D, Georgoulias V, Casazza G. Partial breast irradiation or whole breast radiotherapy for early breast cancer: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Breast J. 2010; 16:245–51.
Article4. Fowble B, Solin LJ, Schultz DJ, Rubenstein J, Goodman RL. Breast recurrence following conservative surgery and radiation: patterns of failure, prognosis, and pathologic findings from mastectomy specimens with implications for treatment. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1990; 19:833–42.
Article5. Smith TE, Lee D, Turner BC, Carter D, Haffty BG. True recurrence vs. new primary ipsilateral breast tumor relapse: an analysis of clinical and pathologic differences and their implications in natural history, prognoses, and therapeutic management. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2000; 48:1281–9.
Article6. Morrow M. Rational local therapy for breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2002; 347:1270–1.
Article7. Ribeiro GG, Magee B, Swindell R, Harris M, Banerjee SS. The Christie Hospital breast conservation trial: an update at 8 years from inception. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 1993; 5:278–83.
Article8. Chang JH, Lee NK, Kim JY, Kim YJ, Moon SH, Kim TH, et al. Phase II trial of proton beam accelerated partial breast irradiation in breast cancer. Radiother Oncol. 2013; 108:209–14.
Article9. Vicini F, Winter K, Straube W, Wong J, Pass H, Rabinovitch R, et al. A phase I/II trial to evaluate three-dimensional confor-mal radiation therapy confined to the region of the lumpectomy cavity for Stage I/II breast carcinoma: initial report of feasibility and reproducibility of Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) Study 0319. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005; 63:1531–7.
Article10. Vicini F, Winter K, Wong J, Pass H, Rabinovitch R, Chafe S, et al. Initial efficacy results of RTOG 0319: three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy (3D-CRT) confined to the region of the lumpectomy cavity for stage I/II breast carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010; 77:1120–7.11. Harris JR, Levene MB, Svensson G, Hellman S. Analysis of cosmetic results following primary radiation therapy for stages I and II carcinoma of the breast. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1979; 5:257–61.
Article12. Landis DM, Luo W, Song J, Bellon JR, Punglia RS, Wong JS, et al. Variability among breast radiation oncologists in delineation of the postsurgical lumpectomy cavity. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007; 67:1299–308.
Article13. Smitt MC, Nowels KW, Zdeblick MJ, Jeffrey S, Carlson RW, Stockdale FE, et al. The importance of the lumpectomy surgical margin status in long-term results of breast conservation. Cancer. 1995; 76:259–67.14. Dzhugashvili M, Pichenot C, Dunant A, Balleyguier C, Delaloge S, Mathieu MC, et al. Surgical clips assist in the visualization of the lumpectomy cavity in three-dimensional conformal accelerated partial-breast irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010; 76:1320–4.
Article15. Petersen RP, Truong PT, Kader HA, Berthelet E, Lee JC, Hilts ML, et al. Target volume delineation for partial breast radiotherapy planning: clinical characteristics associated with low interobserver concordance. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007; 69:41–8.
Article16. Vicini FA, Beitsch PD, Quiet CA, Keleher A, Garcia D, Snider HC, et al. First analysis of patient demographics, technical reproducibility, cosmesis, and early toxicity: results of the American Society of Breast Surgeons MammoSite breast brachytherapy trial. Cancer. 2005; 104:1138–48.17. Hepel JT, Tokita M, MacAusland SG, Evans SB, Hiatt JR, Price LL, et al. Toxicity of three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy for accelerated partial breast irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009; 75:1290–6.
Article18. Leonard KL, Hepel JT, Hiatt JR, Dipetrillo TA, Price LL, Wazer DE. The effect of dose-volume parameters and interfraction interval on cosmetic outcome and toxicity after 3-dimensional conformal accelerated partial breast irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013; 85:623–9.
Article19. Bergom C, Prior P, Kainz K, Morrow NV, Ahunbay EE, Walker A, et al. A phase I/II study piloting accelerated partial breast irradiation using CT-guided intensity modulated radiation therapy in the prone position. Radiother Oncol. 2013; 108:215–9.
Article20. Moon SH, Shin KH, Kim TH, Yoon M, Park S, Lee DH, et al. Dosimetric comparison of four different external beam partial breast irradiation techniques: three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy, intensity-modulated radiotherapy, helical tomotherapy, and proton beam therapy. Radiother Oncol. 2009; 90:66–73.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Recent Development of Radiation Therapy for Breast Cancer
- Partial Breast Irradiation (PBI)
- Intensity-modulated radiation therapy: a review with a physics perspective
- Radiation Therapy for Patiens with Early-Stage Breast Carcinoma Treated with Breast-Conserving Surgery
- Assessment of Eligibility and Utilization of Accelerated Partial Breast Irradiation in Korean Breast Cancer Patients (KROG 22-15)