Cancer Res Treat.
2014 Oct;46(4):383-392. 10.4143/crt.2013.102.
p27 Loss Is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Pathology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. woohokim@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2380376
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2013.102
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (GEP-NETs) represent a heterogeneous disease group originating from the neuroendocrine cells. Identification of prognostic markers, related to neuroendocrine tissue-selective tumorigenesis, is necessary to find therapeutic targets.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A total of 327 patients with GEP-NETs were included in this study; there were 49 gastric, 29 duodenal, 49 pancreatic, 12 hepatobiliary, 33 appendiceal, 5 proximal colon, and 150 distal colon cases. We performed immunostaining with the tissue microarray method for menin, p27, and p18.
RESULTS
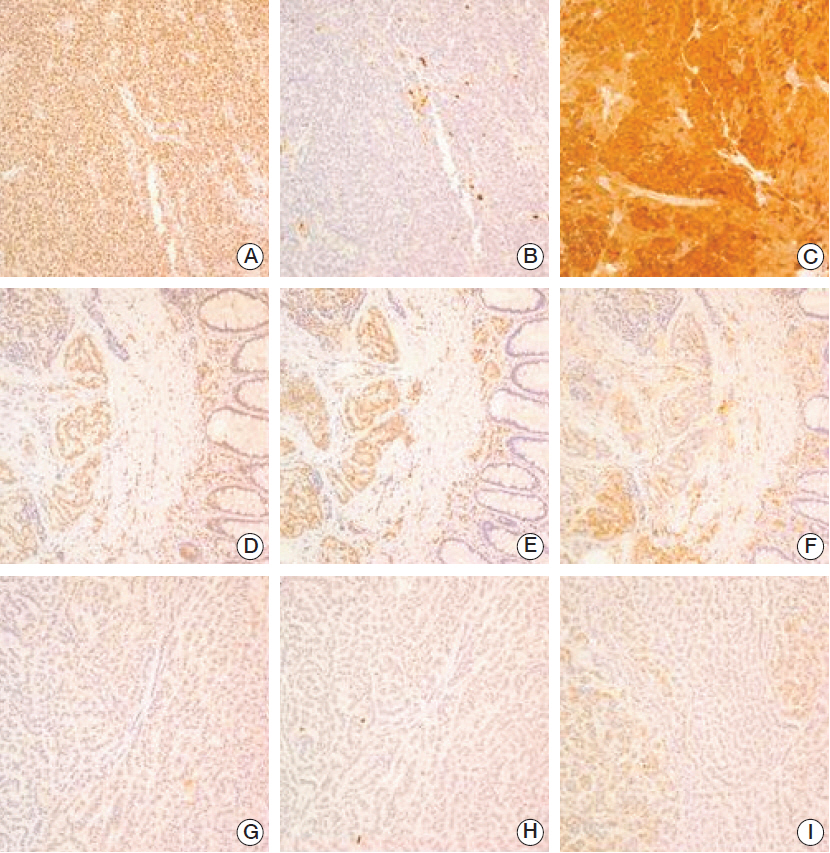
We observed negative staining for menin, p27, and p18 in 34%, 21%, and 56% of GEP-NETs, respectively. The loss of p27, but not menin, was positively correlated with the grade of Ki-67. Menin-/p27-, menin-/p27+, menin+/p27-, and menin+/p27+ phenotype groups included 13%, 22%, 8%, and 57% of patients, respectively. A dichotomized comparison showed that menin- or p27- tumors were significantly associated with foregut and midgut localizations, high World Health Organization (WHO) grade, lymph node metastasis, and more advanced stage as compared to menin+/p27+ patients. Kaplan-Meier analysis for the overall survival showed that p27 loss was significantly associated with decreased survival. Multivariate analysis showed that p27 loss is an independent factor for poor overall survival.
CONCLUSION
Our results revealed that the loss of p27 is associated with poor prognosis and the menin-p27 pathway is important in the tumorigenesis of GEP-NETs.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Carcinogenesis
Colon
Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitor p27
Gastrointestinal Neoplasms
Humans
Kaplan-Meier Estimate
Lymph Nodes
Multivariate Analysis
Negative Staining
Neoplasm Metastasis
Neuroendocrine Cells
Neuroendocrine Tumors*
Pancreatic Neoplasms
Phenotype
Prognosis*
Biomarkers, Tumor
World Health Organization
Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitor p27
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Gastrointestinal Pathology Study Group of Korean Society of Pathologists, Cho MY, Sohn JH, Jin SY, Kim H, Jung ES, et al. Proposal for a standardized pathology report of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: prognostic significance of pathological parameters. Korean J Pathol. 2013; 47:227–37.
Article2. Yao JC, Hassan M, Phan A, Dagohoy C, Leary C, Mares JE, et al. One hundred years after "carcinoid": epidemiology of and prognostic factors for neuroendocrine tumors in 35,825 cases in the United States. J Clin Oncol. 2008; 26:3063–72.
Article3. Chandrasekharappa SC, Guru SC, Manickam P, Olufemi SE, Collins FS, Emmert-Buck MR, et al. Positional cloning of the gene for multiple endocrine neoplasia-type 1. Science. 1997; 276:404–7.
Article4. Lemos MC, Thakker RV. Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1): analysis of 1336 mutations reported in the first decade following identification of the gene. Hum Mutat. 2008; 29:22–32.
Article5. Bhuiyan MM, Sato M, Murao K, Imachi H, Namihira H, Takahara J. Expression of menin in parathyroid tumors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000; 85:2615–9.
Article6. Yang Y, Hua X. In search of tumor suppressing functions of menin. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2007; 265-266:34–41.
Article7. Milne TA, Hughes CM, Lloyd R, Yang Z, Rozenblatt-Rosen O, Dou Y, et al. Menin and MLL cooperatively regulate expression of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005; 102:749–54.
Article8. Karnik SK, Hughes CM, Gu X, Rozenblatt-Rosen O, McLean GW, Xiong Y, et al. Menin regulates pancreatic islet growth by promoting histone methylation and expression of genes encoding p27Kip1 and p18INK4c. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005; 102:14659–64.
Article9. Marinoni I, Pellegata NS. p27kip1: a new multiple endocrine neoplasia gene? Neuroendocrinology. 2011; 93:19–28.
Article10. Duncan TJ, Al-Attar A, Rolland P, Harper S, Spendlove I, Durrant LG. Cytoplasmic p27 expression is an independent prognostic factor in ovarian cancer. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 2010; 29:8–18.
Article11. Psyrri A, Bamias A, Yu Z, Weinberger PM, Kassar M, Markakis S, et al. Subcellular localization and protein levels of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27 independently predict for survival in epithelial ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2005; 11:8384–90.
Article12. Lloyd RV, Erickson LA, Jin L, Kulig E, Qian X, Cheville JC, et al. p27kip1: a multifunctional cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor with prognostic significance in human cancers. Am J Pathol. 1999; 154:313–23.
Article13. Pellegata NS, Quintanilla-Martinez L, Keller G, Liyanarachchi S, Hofler H, Atkinson MJ, et al. Human pheochromocytomas show reduced p27Kip1 expression that is not associated with somatic gene mutations and rarely with deletions. Virchows Arch. 2007; 451:37–46.
Article14. Grabowski P, Schrader J, Wagner J, Horsch D, Arnold R, Arnold CN, et al. Loss of nuclear p27 expression and its prognostic role in relation to cyclin E and p53 mutation in gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2008; 14:7378–84.
Article15. Pellegata NS, Quintanilla-Martinez L, Siggelkow H, Samson E, Bink K, Hofler H, et al. Germ-line mutations in p27Kip1 cause a multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome in rats and humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006; 103:15558–63.
Article16. Franklin DS, Godfrey VL, O'Brien DA, Deng C, Xiong Y. Functional collaboration between different cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors suppresses tumor growth with distinct tissue specificity. Mol Cell Biol. 2000; 20:6147–58.
Article17. Franklin DS, Godfrey VL, Lee H, Kovalev GI, Schoonhoven R, Chen-Kiang S, et al. CDK inhibitors p18(INK4c) and p27(Kip1) mediate two separate pathways to collaboratively suppress pituitary tumorigenesis. Genes Dev. 1998; 12:2899–911.
Article18. Rahman A, Maitra A, Ashfaq R, Yeo CJ, Cameron JL, Hansel DE. Loss of p27 nuclear expression in a prognostically favorable subset of well-differentiated pancreatic endocrine neoplasms. Am J Clin Pathol. 2003; 120:685–90.
Article19. Cavallari I, D'Agostino DM, Ferro T, Rosato A, Barzon L, Pasquali C, et al. In situ analysis of human menin in normal and neoplastic pancreatic tissues: evidence for differential expression in exocrine and endocrine cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003; 88:3893–901.20. Edge S, Byrd DR, Compton CC, Fritz AG, Greene FL, Trotti A. AJCC cancer staging manual. 7th ed. New York: Springer-Verlag;2009. p. 181–9.21. Bosman FT, Carneiro F, Hruban RH, Theise ND. WHO classification of tumours of the digestive system. Lyon: IARC Press;2010. p. 13–4.22. Corbo V, Dalai I, Scardoni M, Barbi S, Beghelli S, Bersani S, et al. MEN1 in pancreatic endocrine tumors: analysis of gene and protein status in 169 sporadic neoplasms reveals alterations in the vast majority of cases. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2010; 17:771–83.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Antitumor Effects of Somatostatin Analogs in Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors
- Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor with Hepatic Metastasis Misdiagnosed as Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Endoscopic Ultrasound in Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors
- Duodenal Neuroendocrine Tumor: a Diagnostic Surprise during Workup for Anemia
- The Expression of p27 Protein in Gastri c Adenocarcinoma