J Korean Med Sci.
2017 Jul;32(7):1072-1076. 10.3346/jkms.2017.32.7.1072.
Statistical Data Editing in Scientific Articles
- Affiliations
-
- 1Past President, World Association of Medical Editors; Founder and Editor, The International Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine (The IJOEM); Adjunct Professor, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, Shiraz, Iran; Managing Director, R&D Head
- KMID: 2379599
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2017.32.7.1072
Abstract
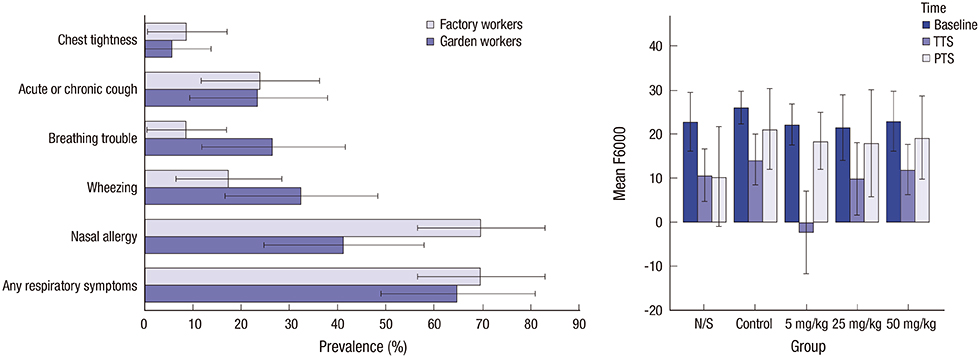
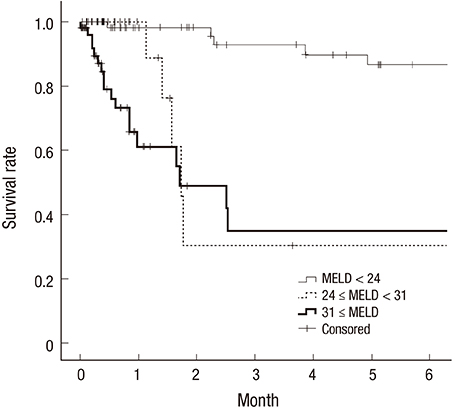
- Scientific journals are important scholarly forums for sharing research findings. Editors have important roles in safeguarding standards of scientific publication and should be familiar with correct presentation of results, among other core competencies. Editors do not have access to the raw data and should thus rely on clues in the submitted manuscripts. To identify probable errors, they should look for inconsistencies in presented results. Common statistical problems that can be picked up by a knowledgeable manuscript editor are discussed in this article. Manuscripts should contain a detailed section on statistical analyses of the data. Numbers should be reported with appropriate precisions. Standard error of the mean (SEM) should not be reported as an index of data dispersion. Mean (standard deviation [SD]) and median (interquartile range [IQR]) should be used for description of normally and non-normally distributed data, respectively. If possible, it is better to report 95% confidence interval (CI) for statistics, at least for main outcome variables. And, P values should be presented, and interpreted with caution, if there is a hypothesis. To advance knowledge and skills of their members, associations of journal editors are better to develop training courses on basic statistics and research methodology for non-experts. This would in turn improve research reporting and safeguard the body of scientific evidence.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
GPTZero Performance in Identifying Artificial Intelligence-Generated Medical Texts: A Preliminary Study
Farrokh Habibzadeh
J Korean Med Sci. 2023;38(38):e319. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e319.
Reference
-
1. Simi A, Yadollahie M, Habibzadeh F. Knowledge and attitudes of breast self examination in a group of women in Shiraz, southern Iran. Postgrad Med J. 2009; 85:283–287.2. Habibzadeh F, Habibzadeh P. How much precision in reporting statistics is enough? Croat Med J. 2015; 56:490–492.3. Lang TA, Secic M. How to Report Statistics in Medicine: Annotated Guidelines for Authors, Editors, and Reviewers. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Physicians;2006.4. Habibzadeh F. Common statistical mistakes in manuscripts submitted to biomedical journals. Eur Sci Ed. 2013; 39:92–94.5. Equator Network (GB). STARD 2015: an updated list of essential items for reporting diagnostic accuracy studies [Internet]. accessed on 29 March 2017. Available at http://www.stard-statement.org/.6. Habibzadeh F, Yadollahie M. Number needed to misdiagnose: a measure of diagnostic test effectiveness. Epidemiology. 2013; 24:170.7. Habibzadeh F, Habibzadeh P, Yadollahie M. On determining the most appropriate test cut-off value: the case of tests with continuous results. Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2016; 26:297–307.8. Habibzadeh F, Habibzadeh P, Yadollahie M. Criterion used for determination of test cut-off value. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. Forthcoming. 2017.9. Habibzadeh F, Habibzadeh P, Yadollahie M. Choice of criterion used in the ROC analysis. Indian J Med Res. Forthcoming. 2017.10. Moitra S, Thapa P, Das P, Das J, Debnath S, Singh M, Datta A, Sen S, Moitra S. Respiratory morbidity among Indian tea industry workers. Int J Occup Environ Med. 2016; 7:148–155.11. Jahani L, Mehrparvar AH, Esmailidehaj M, Rezvani ME, Moghbelolhossein B, Razmjooei Z. The effect of atorvastatin on preventing noise-induced hearing loss: an experimental study. Int J Occup Environ Med. 2016; 7:15–21.12. Baron DN, Clarke HM. Units, Symbols, and Abbreviations: a Guide for Authors and Editors in Medicine and Related Sciences. 6th ed. London: Royal Society of Medicine Press Ltd.;2008.13. Lang TA, Altman DG. Basic statistical reporting for articles published in clinical medical journals: the statistical analyses and methods in the published literature, or SAMPL guidelines. In : Smart P, Maisonneuve H, Polderman A, editors. The EASE Science Editors' Handbook. Redruth: European Association of Science Editors;2013. p. 175–182. .14. Goodman S. A dirty dozen: twelve p-value misconceptions. Semin Hematol. 2008; 45:135–140.15. Goodman SN. Toward evidence-based medical statistics. 1: the P value fallacy. Ann Intern Med. 1999; 130:995–1004.16. Goodman SN. Toward evidence-based medical statistics. 2: the Bayes factor. Ann Intern Med. 1999; 130:1005–1013.17. Hong G, Lee KW, Suh S, Yoo T, Kim H, Park MS, Choi Y, Yi NJ, Suh KS. The model for end-stage liver disease score-based system predicts short term mortality better than the current Child-Turcotte-Pugh score-based allocation system during waiting for deceased liver transplantation. J Korean Med Sci. 2013; 28:1207–1212.18. Li H, Han D, Hou Y, Chen H, Chen Z. Statistical inference methods for two crossing survival curves: a comparison of methods. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0116774.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Recommendations for Image and Video Articles in Scholarly Publishing
- Using ChatGPT for language editing in scientific articles
- Editing, Publishing and Aggregating Video Articles: Do We Need a Scholarly Approach?
- Improving Scientific Writing Skills and Publishing Capacity by Developing University-Based Editing System and Writing Programs
- Transparency considerations for describing statistical analyses in research