J Korean Soc Radiol.
2017 Jun;76(6):375-385. 10.3348/jksr.2017.76.6.375.
Clinicopathological and Imaging Features of Breast Cancer in Korean Women under 40 Years of Age
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. mjjang74@gmail.com
- 2Department of Surgery, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 2379319
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2017.76.6.375
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the clinicopathological and imaging features of mammography, ultrasonography, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for breast cancer in Korean women under 40 years of age according to molecular subtypes.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We included 183 breast cancers in 176 consecutive women under 40 years old who had been diagnosed with breast cancer between January 2012 and November 2014. The patients' clinical and pathologic records were available as electronic medical records. A retrospective review of the pre-operative imaging studies was performed with 177 mammographies, 183 ultrasonographies, and 178 MRIs.
RESULTS
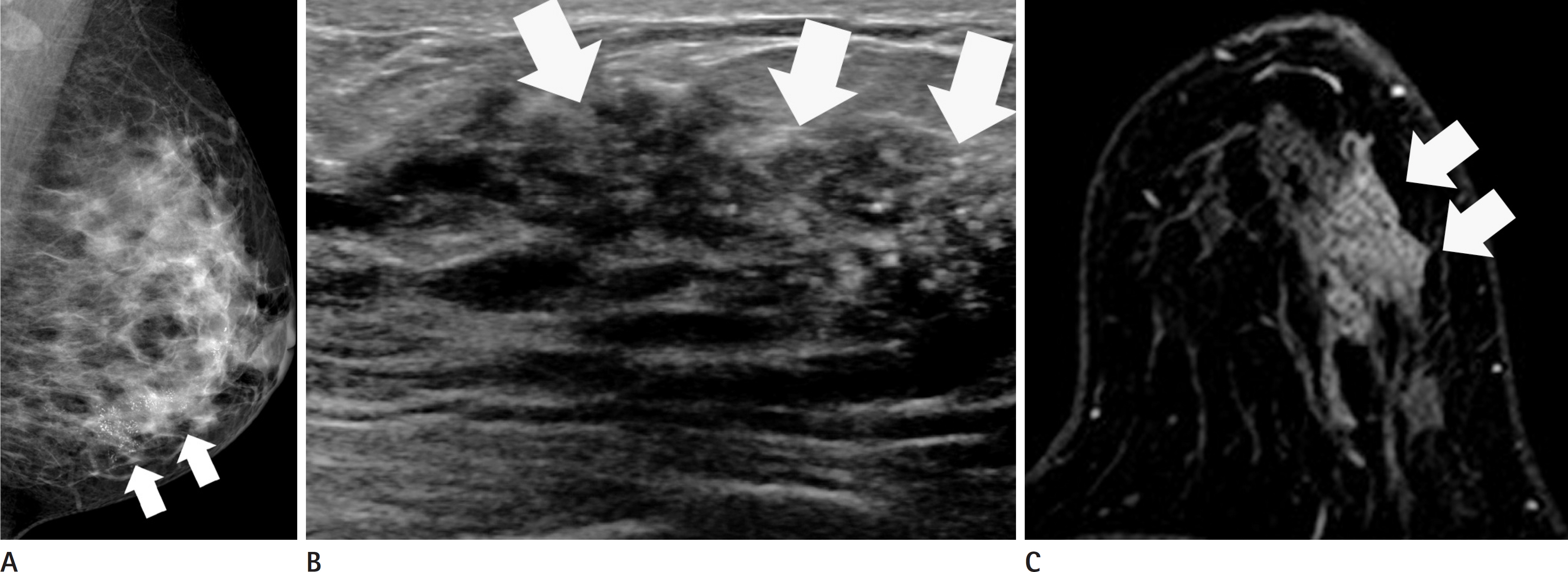
Eighty-six percent (158/183) of lesions were symptomatic, with masses (147/183) as the most common presentation. Eighty percent (22/25) of the asymptomatic lesions were diagnosed via screening ultrasonography. The luminal A subtype was the most common (n = 79, 43%), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-enriched subtype showed indistinct margins on mammography (p = 0.006), the triple negative subtype depicted a posterior enhancement on ultrasonography (p < 0.001) and rim enhancement on MRI (p < 0.001).
CONCLUSION
Breast cancers in Korean women under 40 years of age are commonly presented with a palpable mass, and luminal A is the most common molecular subtype. In our study, the imaging and pathologic characteristics of breast cancer in younger women were similar to those previously reported for older patients.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Breast Cancer in Women Younger than 35-Years-Old: Correlation of MRI Findings with Clinicopathological Features and Immunohistochemical Subtypes
Sae Hyung Lee, Bong Joo Kang, Yeong Yi An
J Korean Soc Radiol. 2018;79(4):196-203. doi: 10.3348/jksr.2018.79.4.196.
Reference
-
1. Jemal A, Clegg LX, Ward E, Ries LA, Wu X, Jamison PM, et al. Annual report to the nation on the status of cancer, 1975-2001, with a special feature regarding survival. Cancer. 2004; 101:3–27.
Article2. Ko SS. Korean Breast Cancer Society. Chronological chang-ing patterns of clinical characteristics of Korean breast cancer patients during 10 years (1996-2006) using nationwide breast cancer registration on-line program: biannual up-date. J Surg Oncol. 2008; 98:318–323.
Article3. Ahn SH, Son BH, Kim SW, Kim SI, Jeong J, Ko SS, et al. Poor outcome of hormone receptor-positive breast cancer at very young age is due to tamoxifen resistance: nationwide survival data in Korea–a report from the Korean Breast Cancer Society. J Clin Oncol. 2007; 25:2360–2368.
Article4. Fredholm H, Eaker S, Frisell J, Holmberg L, Fredriksson I, Lindman H. Breast cancer in young women: poor survival despite intensive treatment. PLoS One. 2009; 4:e7695.
Article5. Prevalence and penetrance of BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations in a population-based series of breast cancer cases. Anglian Breast Cancer Study Group. Br J Cancer. 2000; 83:1301–1308.6. Zhou P, Recht A. Young age and outcome for women with early-stage invasive breast carcinoma. Cancer. 2004; 101:1264–1274.
Article7. Neal RD, Allgar VL. Sociodemographic factors and delays in the diagnosis of six cancers: analysis of data from the “National Survey of NHS Patients: Cancer”. Br J Cancer. 2005; 92:1971–1975.
Article8. Partridge AH, Hughes ME, Ottesen RA, Wong YN, Edge SB, Theriault RL, et al. The effect of age on delay in diagnosis and stage of breast cancer. Oncologist. 2012; 17:775–782.
Article9. Ruddy KJ, Gelber S, Tamimi RM, Schapira L, Come SE, Meyer ME, et al. Breast cancer presentation and diagnos-tic delays in young women. Cancer. 2014; 120:20–25.
Article10. Keegan TH, DeRouen MC, Press DJ, Kurian AW, Clarke CA. Occurrence of breast cancer subtypes in adolescent and young adult women. Breast Cancer Res. 2012; 14:R55.
Article11. Park YH, Lee SJ, Jung HA, Kim SM, Kim MJ, Kil WH, et al. Prevalence and clinical outcomes of young breast cancer (YBC) patients according to intrinsic breast cancer subtypes: single institutional experience in Korea. Breast. 2015; 24:213–217.
Article12. Hammond ME, Hayes DF, Dowsett M, Allred DC, Hagerty KL, Badve S, et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology/College Of American Pathologists guideline recommendations for immunohistochemical testing of estrogen and proges-terone receptors in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010; 28:2784–2795.
Article13. Cheang MC, Chia SK, Voduc D, Gao D, Leung S, Snider J, et al. Ki67 index, HER2 status, and prognosis of patients with luminal B breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2009; 101:736–750.
Article14. American College of Radiology. ACR BI-RADS® Atlas, Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System. Reston: American College of Radiology;2013.15. Collins LC, Marotti JD, Gelber S, Cole K, Ruddy K, Kereako-glow S, et al. Pathologic features and molecular phenotype by patient age in a large cohort of young women with breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012; 131:1061–1066.
Article16. Tang J, Wu CC, Xie ZM, Luo RZ, Yang MT. Comparison of clinical features and treatment outcome of breast cancers in young and elderly chinese patients. Breast Care (Basel). 2011; 6:435–440.
Article17. Kim EK, Noh WC, Han W, Noh DY. Prognostic significance of young age (<35 years) by subtype based on ER, PR, and HER2 status in breast cancer: a nationwide registry-based study. World J Surg. 2011; 35:1244–1253.18. Bassett LW, Ysrael M, Gold RH, Ysrael C. Usefulness of mammography and sonography in women less than 35 years of age. Radiology. 1991; 180:831–835.
Article19. Taneja S, Evans AJ, Rakha EA, Green AR, Ball G, Ellis IO. The mammographic correlations of a new immunohistochemical classification of invasive breast cancer. Clin Radiol. 2008; 63:1228–1235.
Article20. Bullier B, MacGrogan G, Bonnefoi H, Hurtevent-Labrot G, Lhomme E, Brouste V, et al. Imaging features of sporadic breast cancer in women under 40 years old: 97 cases. Eur Radiol. 2013; 23:3237–3245.21. Lehman CD, Lee CI, Loving VA, Portillo MS, Peacock S, DeMartini WB. Accuracy and value of breast ultrasound for primary imaging evaluation of symptomatic women 30-39 years of age. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2012; 199:1169–1177.
Article22. Au-Yong IT, Evans AJ, Taneja S, Rakha EA, Green AR, Paish C, et al. Sonographic correlations with the new molecular classification of invasive breast cancer. Eur Radiol. 2009; 19:2342–2348.
Article23. Kojima Y, Tsunoda H. Mammography and ultrasound features of triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer. 2011; 18:146–151.
Article24. Kim JY, Lee SH, Lee JW, Kim S, Choo KS. Magnetic resonance imaging characteristics of invasive breast cancer in women aged less than 35 years. Acta Radiol. 2015; 56:924–932.
Article25. Uematsu T, Kasami M, Yuen S. Triple-negative breast cancer: correlation between MR imaging and pathologic findings. Radiology. 2009; 250:638–647.
Article26. Thapa B, Singh Y, Sayami P, Shrestha UK, Sapkota R, Sayami G. Breast cancer in young women from a low risk popula-tion in Nepal. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013; 14:5095–5099.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Imaging and Clinicopathologic Characteristics of Breast Cancers in Younger Group Compared to in Old Group
- New Trends in Breast Imaging
- Comparison of hormonal receptor and HER2 status between ultrasound-guided 14-gauge core needle biopsy and surgery in breast cancer patients
- Comparison of health literacy and health behaviors between Korean women with and without breast cancer
- Risk Factors for Breast Cancer: A Case-Control Study