Korean J Neurotrauma.
2015 Oct;11(2):151-153. 10.13004/kjnt.2015.11.2.151.
Iatrogenic Dural Arteriovenous Fistula after Superficial Temporal Artery to Middle Cerebral Artery Anastomosis: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Bongseng Memorial Hospital, Busan, Korea. drkschae@gmail.com
- KMID: 2378276
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2015.11.2.151
Abstract
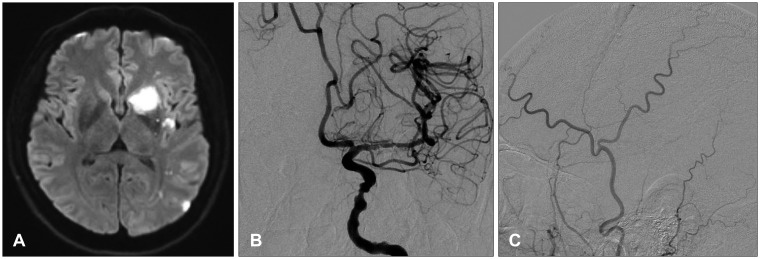
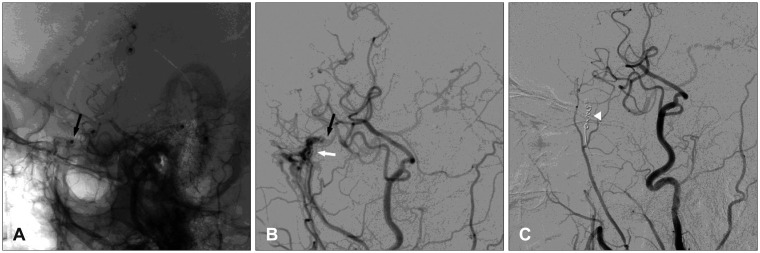
- Dural arteriovenous fistulas (AVFs) are uncommon, representing only 10% to 15% of all intracranial AVFs. Here we present the case of a patient with cerebral infarction who experienced a dural AVF after craniotomy for superficial temporal artery (STA) to middle cerebral artery (MCA) bypass surgery. A 48-year-old man presented with dysarthria and right side hemiparesis. A brain magnetic resonance imaging scan revealed multiple acute infarctions and severe stenosis of the left MCA. Therefore, STA-MCA bypass surgery was performed. A follow-up angiography performed 2 weeks after the surgery showed an abnormal vascular channel from the left middle meningeal artery (MMA) to the middle meningeal vein (MMV) just anterior to the border of the craniotomy margin. This fistula originated from a screw used for cranial fixation. The screw injured the MMA and MMV, and this resulted in the formation of a fistula. The fistula was successfully treated with transarterial embolization. Surgeons should be careful when fixing bones with screws and plates as fistulas can develop if vessels are injured.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ahn JY, Kim OJ, Joo YJ, Joo JY. Dural arteriovenous malformation occurring after craniotomy for pial arteriovenous malformation. J Clin Neurosci. 2003; 10:134–136. PMID: 12464548.
Article2. Chandrashekar HS, Nagarajan K, Srikanth SG, Jayakumar PN, Vasudev MK, Pandey P. Middle meningeal arteriovenous fistula and its spontaneous closure. A case report and review of the literature. Interv Neuroradiol. 2007; 13:173–178. PMID: 20566146.3. Hashimoto H, Iida J, Masui K, Nishi N, Yonezawa T, Sakaki T. Dural arteriovenous malformation of the anterior cranial fossa occurring after bifrontal craniotomy. Surg Neurol. 1998; 49:47–50. PMID: 9428894.4. Inagawa T, Takeda T, Taguchi H, Kamiya K, Yamada T. Traumatic middle meningeal arteriovenous fistula caused by three-point skull fixation. Case report. J Neurosurg. 1984; 60:853–855. PMID: 6707757.5. Nabors MW, Azzam CJ, Albanna FJ, Gulya AJ, Davis DO, Kobrine AI. Delayed postoperative dural arteriovenous malformations. Report of two cases. J Neurosurg. 1987; 66:768–772. PMID: 3572502.6. Pappas CT, Zabramski JM, Shetter AG. Iatrogenic arteriovenous fistula presenting as a recurrent subdural hematoma. Case report. J Neurosurg. 1992; 76:134–136. PMID: 1727151.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Traumatic Arteriovenous Fistula of the Superficial Temporal Artery
- Surgical Treatment of a Post-Traumatic Arteriovenous Fistula of the Superficial Temporal Artery and Vein
- A Middle Cerebral Artery AneurysmOriginating Near the Site of Anastomosis after Superficial Temporal Artery-Middle Cerebral Artery Bypass: Case Report
- Iatrogenic mixed pial and dural arteriovenous fistula after pterional approach for surgical clipping of aneurysm: A case report
- Superficial Temporal Artery-Middle Cerebral Artery Anastomosis for Internal Carotid Artery Occlusion by Subacute In-Stent Thrombosis after Carotid Artery Stenting