J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2012 Dec;52(6):551-554. 10.3340/jkns.2012.52.6.551.
Superficial Temporal Artery-Middle Cerebral Artery Anastomosis for Internal Carotid Artery Occlusion by Subacute In-Stent Thrombosis after Carotid Artery Stenting
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Busan Paik Hospital, School of Medicine, Inje University, Busan, Korea. kimst015@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Busan Paik Hospital, School of Medicine, Inje University, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 1426266
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2012.52.6.551
Abstract
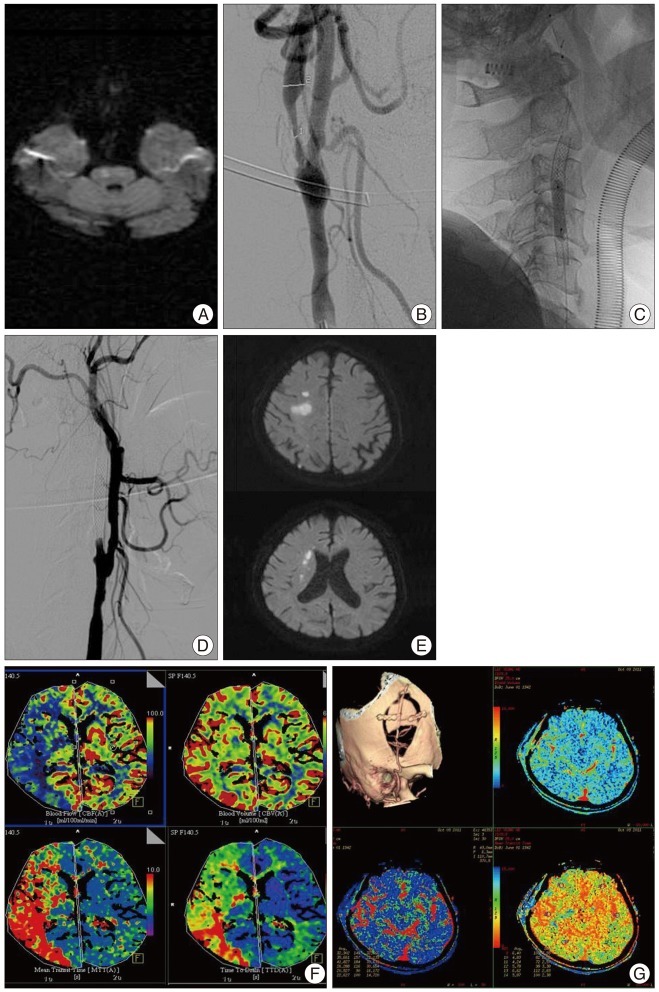
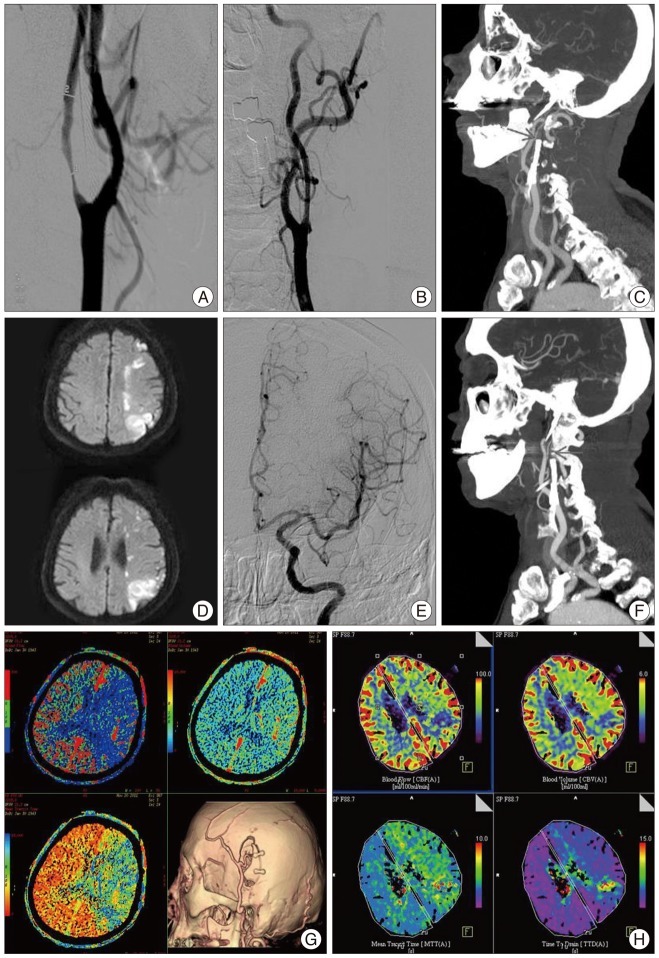
- Alternative to carotid endarterectomy, carotid artery stenting (CAS) can be performed for symptomatic severe stenosis of internal carotid artery, especially for high-risk patients. Among several complications after CAS, subacute in-stent thrombosis is rare but important, because patient's condition can deteriorate rapidly. Subacute in-stent thrombosis with carotid artery occlusion can be managed by superficial temporal artery-middle cerebral artery (STA-MCA) anastomosis. We report two cases of STA-MCA anastomosis for internal carotid artery occlusion by subacute in-stent thrombosis after CAS.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Adams HP Jr, del Zoppo G, Alberts MJ, Bhatt DL, Brass L, Furlan A, et al. Guidelines for the early management of adults with ischemic stroke : a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Stroke Council, Clinical Cardiology Council, Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention Council, and the Atherosclerotic Peripheral Vascular Disease and Quality of Care Outcomes in Research Interdisciplinary Working Groups : the American Academy of Neurology affirms the value of this guideline as an educational tool for neurologists. Stroke. 2007; 38:1655–1711. PMID: 17431204.
Article2. Brott TG, Hobson RW 2nd, Howard G, Roubin GS, Clark WM, Brooks W, et al. Stenting versus endarterectomy for treatment of carotid-artery stenosis. N Engl J Med. 2010; 363:11–23. PMID: 20505173.
Article3. Ederle J, Dobson J, Featherstone RL, Bonati LH, van der Worp HB, de Borst GJ, et al. Carotid artery stenting compared with endarterectomy in patients with symptomatic carotid stenosis (International Carotid Stenting Study) : an interim analysis of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2010; 375:985–997. PMID: 20189239.4. Feher G, Feher A, Pusch G, Koltai K, Tibold A, Gasztonyi B, et al. Clinical importance of aspirin and clopidogrel resistance. World J Cardiol. 2010; 2:171–186. PMID: 21160749.
Article5. Hwang G, Oh CW, Bang JS, Jung CK, Kwon OK, Kim JE, et al. Superficial temporal artery to middle cerebral artery bypass in acute ischemic stroke and stroke in progress. Neurosurgery. 2011; 68:723–729. discussion 729-730. PMID: 21311299.
Article6. Iancu A, Grosz C, Lazar A. Acute carotid stent thrombosis : review of the literature and long-term follow-up. Cardiovasc Revasc Med. 2010; 11:110–113. PMID: 20347802.
Article7. Jeffree RL, Stoodley MA. STA-MCA bypass for symptomatic carotid occlusion and haemodynamic impairment. J Clin Neurosci. 2009; 16:226–235. PMID: 19097907.
Article8. JET Study Group. [Japanese EC-IC Bypass Trial (JET study) : study design and interim analysis]. Surg Cereb Stroke. 2002; 30:97–100.9. Kakinuma K, Ezuka I, Takai N, Yamamoto K, Sasaki O. The simple indicator for revascularization of acute middle cerebral artery occlusion using angiogram and ultra-early embolectomy. Surg Neurol. 1999; 51:332–341. PMID: 10086500.
Article10. Lee CY, Ryu CW, Koh JS, Kim EJ. Total occlusion of the internal carotid artery by subacute in-stent thrombosis and subsequent spontaneous recanalization after stent-assisted coil embolization. Neurointervention. 2011; 6:38–41. PMID: 22125748.
Article11. Rho GJ, Shin WR, Kong TS, Kim MS, Lee CJ, Lee BH. Significance of clopidogrel resistance related to the stent-assisted angioplasty in patients with atherosclerotic cerebrovascular disease. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2011; 50:40–44. PMID: 21892403.
Article12. Riedel CH, Tietke M, Alfke K, Stingele R, Jansen O. Subacute stent thrombosis in intracranial stenting. Stroke. 2009; 40:1310–1314. PMID: 19213948.
Article13. Van Laanen J, Hendriks JM, Van Sambeek MR. Factors influencing restenosis after carotid artery stenting. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 2008; 49:743–747.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Subacute In-stent Thrombosis after Carotid Artery Stenting: A Case Report
- External Carotid Artery Angioplasty and Stenting Followed by Superficial Temporal Artery to Middle Cerebral Artery Anastomosis
- How to Escape Stentriever Wedging in an Open-cell Carotid Stent during Mechanical Thrombectomy for Tandem Cervical Internal Carotid Artery and Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion
- Aspiration Clot Removal by Mannual Compression of Common Carotid Artery for Acute Internal Carotid Occlusion: a Case Report
- Ophthalmic Artery Occlusion After Carotid Revascularization