J Rheum Dis.
2017 Apr;24(2):85-92. 10.4078/jrd.2017.24.2.85.
Urinary Tumor Necrosis Factor-like Weak Inducer of Apoptosis as a Biomarker for Lupus Nephritis: A Meta-analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Medical Center, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. lyhcgh@korea.ac.kr
- KMID: 2378086
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2017.24.2.85
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
This study evaluates serum or urinary tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) as a biomarker for lupus nephritis (LN).
METHODS
We conducted a meta-analysis examining serum or urinary TWEAK levels in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), patients with LN (active or inactive), and healthy controls. We tabulated correlation coefficients between urinary TWEAK level and total or renal SLE Disease Activity Index (tSLEDAI or rSLEDAI).
RESULTS
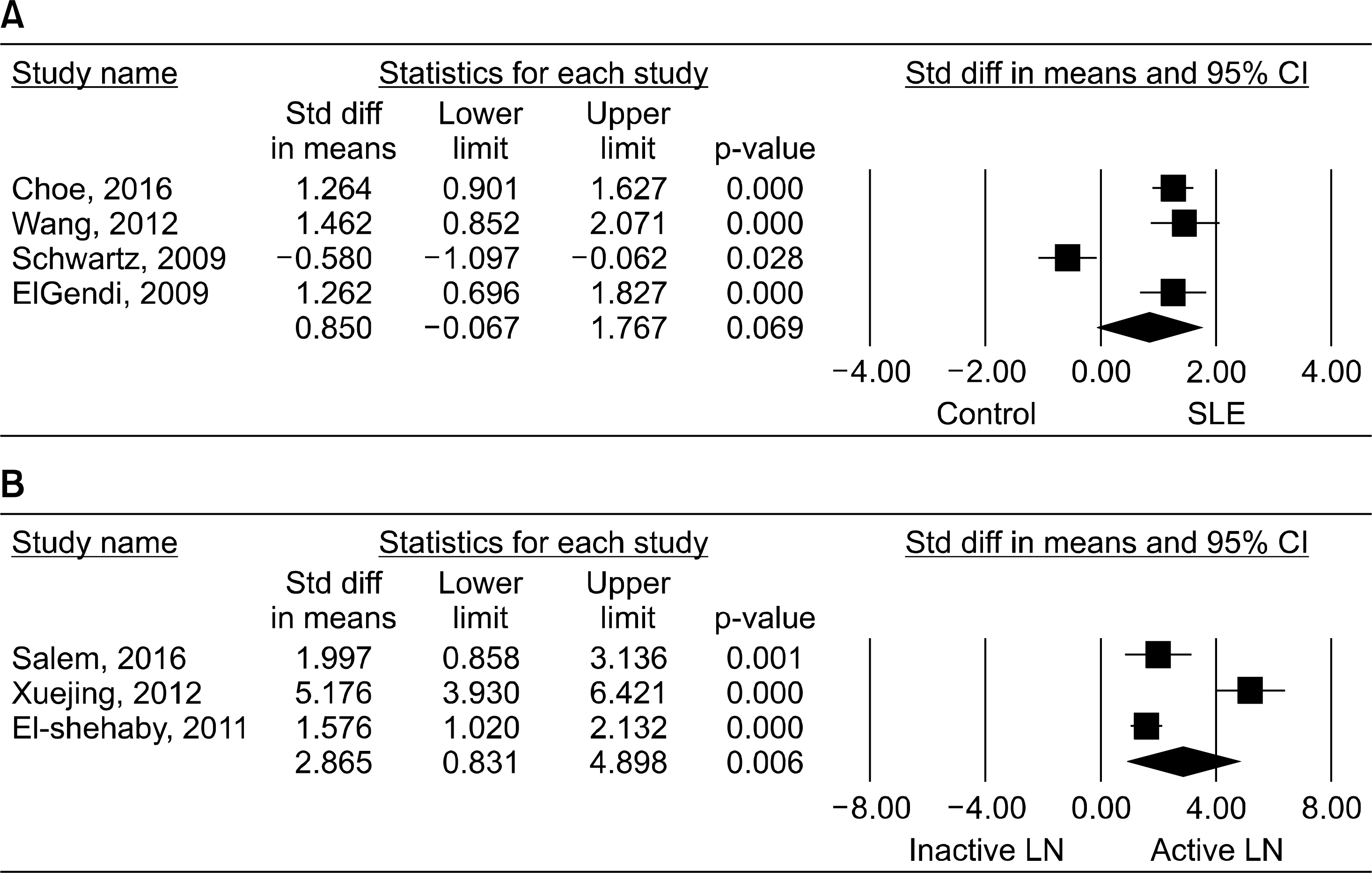
Eight studies were included in this meta-analysis. The meta-analysis revealed that serum TWEAK levels tended to be higher in patients with SLE than in controls (standard mean difference [SMD]=0.850, 95% confidence interval [CI]=−0.067∼1.767, p=0.069). Urinary TWEAK was significantly higher in patients with active LN than in those with inactive LN (SMD=2.865, 95% CI= −0.831∼4.898, p=0.006). In addition, urinary TWEAK was positively associated with tSLEDAI and rSLEDAI (correlation coefficient= 0.436, 95% CI=0.204∼0.622, p=4.3×10â»â´; correlation coefficient=0.483, 95% CI=0.108∼0.738, p=0.014). Pooled sensitivity and specificity of urinary TWEAK for diagnosis of LN were 81.3% (95% CI, 73.3∼87.8) and 76.0% (95% CI, 66.3∼84.2), indicating good diagnostic accuracy.
CONCLUSION
The meta-analysis demonstrated that urinary TWEAK was significantly higher in patients with active LN than in those with inactive LN, and that urinary TWEAK levels were positively correlated with renal disease activity.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Is Urinary Tumor Necrosis Factor-like Weak Inducer of Apoptosis a Biomarker of Lupus Nephritis?
Jun-Ki Min
J Rheum Dis. 2017;24(3):125-126. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2017.24.3.125.
Reference
-
1. Waldman M, Appel GB. Update on the treatment of lupus nephritis. Kidney Int. 2006; 70:1403–12.
Article2. Lech M, Anders HJ. The pathogenesis of lupus nephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013; 24:1357–66.
Article3. Ogura Y, Mishra V, Hindi SM, Kuang S, Kumar A. Proinflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-like weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) suppresses satellite cell self-renewal through inversely modulating Notch and NF-κ B signaling pathways. J Biol Chem. 2013; 288:35159–69.4. Winkles JA. The TWEAK-Fn14 cytokine-receptor axis: discovery, biology and therapeutic targeting. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008; 7:411–25.
Article5. Campbell S, Burkly LC, Gao HX, Berman JW, Su L, Browning B, et al. Proinflammatory effects of TWEAK/ Fn14 interactions in glomerular mesangial cells. J Immunol. 2006; 176:1889–98.6. Zhao Z, Burkly LC, Campbell S, Schwartz N, Molano A, Choudhury A, et al. TWEAK/Fn14 interactions are instrumental in the pathogenesis of nephritis in the chronic graft-versus-host model of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 2007; 179:7949–58.
Article7. Michaelson JS, Wisniacki N, Burkly LC, Putterman C. Role of TWEAK in lupus nephritis: a bench-to-bedside review. J Autoimmun. 2012; 39:130–42.
Article8. Chicheportiche Y, Bourdon PR, Xu H, Hsu YM, Scott H, Hession C, et al. TWEAK, a new secreted ligand in the tumor necrosis factor family that weakly induces apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 1997; 272:32401–10.
Article9. Sanz AB, Sanchez-Niño MD, Ortiz A. TWEAK, a multifunctional cytokine in kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2011; 80:708–18.
Article10. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009; 6:e1000097.
Article11. Hozo SP, Djulbegovic B, Hozo I. Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2005; 5:13.
Article12. Ridout KK, Ridout SJ, Price LH, Sen S, Tyrka AR. Depression and telomere length: A meta-analysis. J Affect Disord. 2016; 191:237–47.
Article13. Egger M, Smith GD, Phillips AN. Meta-analysis: principles and procedures. BMJ. 1997; 315:1533–7.
Article14. DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 1986; 7:177–88.
Article15. Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. 2002; 21:1539–58.
Article16. Walter SD. Properties of the summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) curve for diagnostic test data. Stat Med. 2002; 21:1237–56.
Article17. Zamora J, Abraira V, Muriel A, Khan K, Coomarasamy A. Meta-DiSc: a software for meta-analysis of test accuracy data. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2006; 6:31.
Article18. Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997; 315:629–34.
Article19. Salem MN, Taha HA, Abd El-Fattah El-Feqi M, Eesa NN, Mohamed RA. Urinary TNF-like weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) as a biomarker of lupus nephritis. Z Rheumatol. 2016; Sep 12 [Epub].DOI: DOI:10.1007/s00393-016-0184-1.20. Choe JY, Kim SK. Serum TWEAK as a biomarker for disease activity of systemic lupus erythematosus. Inflamm Res. 2016; 65:479–88.
Article21. Xuejing Z, Jiazhen T, Jun L, Xiangqing X, Shuguang Y, Fuyou L. Urinary TWEAK level as a marker of lupus nephritis activity in 46 cases. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012; 2012; 359647.
Article22. Wang C, Chen LL, Pan HF, Leng RX, Qin WZ, Ye DQ. Expression of human tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol. 2012; 31:335–9.
Article23. El-Shehaby A, Darweesh H, El-Khatib M, Momtaz M, Marzouk S, El-Shaarawy N, et al. Correlations of urinary biomarkers, TNF-like weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK), osteoprotegerin (OPG), monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), and IL-8 with lupus nephritis. J Clin Immunol. 2011; 31:848–56.
Article24. Schwartz N, Rubinstein T, Burkly LC, Collins CE, Blanco I, Su L, et al. Urinary TWEAK as a biomarker of lupus nephritis: a multicenter cohort study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009; 11:R143.
Article25. ElGendi SS, El-Sherif WT. Anti-C1q antibodies, sCD40L, TWEAK and CD4/CD8 ratio in systemic lupus erythematosus and their relations to disease activity and renal involvement. Egypt J Immunol. 2009; 16:135–48.26. Schwartz N, Su L, Burkly LC, Mackay M, Aranow C, Kollaros M, et al. Urinary TWEAK and the activity of lupus nephritis. J Autoimmun. 2006; 27:242–50.
Article27. Lee YH, Song GG. Urinary MCP-1 as a biomarker for lupus nephritis: a meta-analysis. Z Rheumatol. 2016 Jun 9; [Epub].DOI: DOI:10.1007/s00393-016-0109-z.28. Mok CC. Biomarkers for lupus nephritis: a critical appraisal. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010; 2010; 638413.
Article29. Illei GG, Tackey E, Lapteva L, Lipsky PE. Biomarkers in systemic lupus erythematosus. I. General overview of biomarkers and their applicability. Arthritis Rheum. 2004; 50:1709–20.
Article30. Reyes-Thomas J, Blanco I, Putterman C. Urinary biomarkers in lupus nephritis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2011; 40:138–50.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Is Urinary Tumor Necrosis Factor-like Weak Inducer of Apoptosis a Biomarker of Lupus Nephritis?
- A case of Lupus Nephritis
- The Expression of Apoptosis in Lupus Nephritis
- Urinary Transforming Growth Factor-beta Induced Gene-h3 (betaig-h3)as a Marker of Lupus Activity in SLE with Nephritis
- Role of Clusterin and Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptors on the Apoptosis of Prostate Cancer Cells