Prog Med Phys.
2016 Dec;27(4):250-257. 10.14316/pmp.2016.27.4.250.
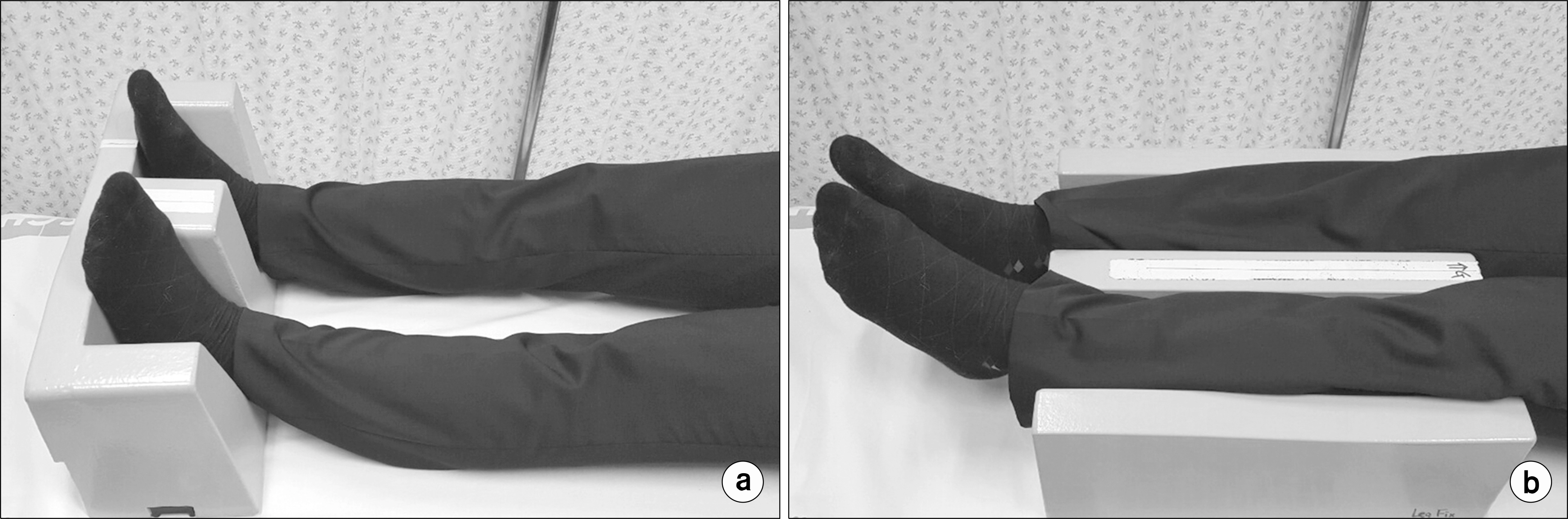
Comparison of Two Different Immobilization Devices for Pelvic Region Radiotherapy in Tomotherapy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, College of Medicine, Soonchunhyang University, Bucheon, Korea. rtjung@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Florida, Gainesville, Florida, USA.
- 3Department of Biomedical Engineering and Research Institute of Biomedical Engineering, The Catholic University, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Healthcare Convergence of Medical Informatics, Soonchunhyang University, Asan, Korea.
- KMID: 2376560
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2016.27.4.250
Abstract
- The purpose of this study was to compare the patient setup errors of two different immobilization devices (Feet Fix: FF and Leg Fix: LF) for pelvic region radiotherapy in Tomotherapy. Thirty six-patients previously treated with IMRT technique were selected, and divided into two groups based on applied immobilization devices (FF versus LF). We performed a retrospective clinical analysis including the mean, systematic, random variation, 3D-error, and calculated the planning target volume (PTV) margin. In addition, a rotational error (angles, °) for each patient was analyzed using the automatic image registration. The 3D-errors for the FF and the LF groups were 3.70 mm and 4.26 mm, respectively; the LF group value was 15.1% higher than in the FF group. The treatment margin in the ML, SI, and AP directions were 5.23 mm (6.08 mm), 4.64 mm (6.29 mm), 5.83 mm (8.69 mm) in the FF group (and the LF group), respectively, that the FF group was lower than in the LF group. The percentage in treatment fractions for the FF group (ant the LF group) in greater than 5 mm at ML, SI, and AP direction was 1.7% (3.6%), 3.3% (10.7%), and 5.0% (16.1%), respectively. Two different immobilization devices were affected the patient setup errors due to different fixed location in low extremity. The radiotherapy for the pelvic region by Tomotherapy should be considering variation for the rotational angles including Yaw and Pitch direction that incorrect setup error during the treatment. In addition the choice of an appropriate immobilization device is important because an unalterable rotation angle affects the setup error.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Yartsev S, Kron T, Van Dyk J. Tomotherapy as a tool in image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT): current clinical experience and outcomes. Biomed Imaging Interv J. 3:e17. 2007.
Article2. Schubert LK, Westerly DC, Tome WA, et al. A comprehensive assessment by tumor site of patient setup using daily MVCT imaging from more than 3,800 helical tomotherapy treatments. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 73:1260–1269. 2009.
Article3. Van Gestel D, Verellen D, Van DE voorde L, et al. The pothetial of helical tomotherapy in the treatment of head neck cancer. Oncologist. 18:697–706. 2013.4. Forrest LJ, Mackie TR, Ruchala K, et al. The utility of megavoltage computed tomograpy images from a helical tomotherapy system for setup verification purposes. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 60:1639–1644. 2004.5. Boswell SA, Jeraj R, Ruchala KJ, et al. A novel method to correct for pitch and yaw patient setup errors in helical tomotherapy. Med Phys. 32:1630–1639. 2005.
Article6. Jung JH, Cho KH, Moon SK, et al. Rotation error of breast cancer on 3D-CRT in TomoDirect. Prog Med Phys. 26:6–11. 2015.7. Li JG, Xing L. Inverse Planning incorporating organ motion. Med Phys. 27:1573–1578. 2000.
Article8. Chen J, Lee RJ, Handrahn D, Sause WT. intensity-modulated radiotherapy using implanted fiducial markers with daily portal imaging: assessment of prostate organ motion. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 68:912–919. 2007.
Article9. Rabinowitz I, Broomberg J, Goitein M, Mc Carthy K, Leong J. Accuracy of radiation field alignment in clinical practies. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 11:1857–1867. 1985.10. Li XA, Qi XS, Pitterle M, Kalakota K, Mueller K, Erickson BA, et al. Interfractional variations in patient setup and anatomic change assessed by daily computed tomography. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 68:581–591. 2007.
Article11. Lee JA, Kim CY, Park YJ, Yoon WS, Lee NK, Yang DS. Interfractional variability in intensity-modulated radiotherapy of prostate cancer with or without thermoplastic pelvic immo bilization. Strahlenther Onkol. 190:94–99. 2014.12. Mitine C, Hoornaert MT, Dutreix A, Beauduin M. Radiotherapy of pelvic malignancies: impact of two types of rigid immobilisation devices on localisation errors. Radiother Oncol. 52:19–27. 1999.
Article13. Malone S, Szanto J, Perry G, et al. A prospective comparison of three systems of patient immobilization for prostate radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 48:657–665. 2000.
Article14. White P, Yee CK, Shan LC, Chung LW, Man NH, Cheung YS. A comparison of two systems of patient immobilization for prostate radiotherapy. Radiat Oncol. 9:1–12. 2014.
Article15. Melancon AD, Kudchadker RJ, Amos R, et al. Patient- specific and generic immobilization devices for prostate radiotherapy. International Journal of Medical Physics, Clinical Engineering and Radiation Oncology. 2:125–132. 2013.16. Saini G, Aqqarwal A, Jafri SA, et al. A comparison between four immobilization systems for pelvic radiation therapy using CBCT and paires kilovoltage portals based image-guided radiotherapy. J Cancer Res Ther. 10:932–936. 2014.17. Kim YL, Cho KH, Jung JH, et al. Analysis of automatic rigid image-registration on tomotherapy. Journal of Radiological Science and Technology. 37:27–47. 2014.18. van Herk M. Errors and margins in radiotherapy. Semin Radiat Oncol. 14:52–64. 2004.19. Haslam JJ, Lujan AE, Mundt AJ, Bonta DV, Roeske JC. Setup errors in patinets treated with intensity-modulated whole pelvic radiation therapy for gynecological malignancies. Med Dosim. 30:36–42. 2005.20. Alongi F, Fiorino C, Cozzarini C, et al. IMRT significantly reduces acute toxicity of whole-pelvis irradiation in patient treated with postoperative adjuvant or salvage radiotherapy after radical proststectomy. Radiother Oncol. 93:207–212. 2009.21. Saw CB, Yakoob R, Enke CA, Lau TP, Ayyangar KM. Immobilization devices for intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT). Med Dosim. 26:71–77. 2001.
Article22. Fiorino C, Reni M, Boloqnesi A, Bonini A, Cattaneo GM, Calandrino R. Setup error in supine-positioned patients immobilized with two different modalities during conformal tadiotherapy of prostate cancer. Radiother Oncol. 49:133–141. 1998.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Development of Immobilization Devices for Patients with Pelvic Malignancies and a Feasibility Evaluation during Radiotherapy
- Dosimetric evaluation of Tomotherapy and four-box field conformal radiotherapy in locally advanced rectal cancer
- Comparison of survival rates between patients treated with conventional radiotherapy and helical tomotherapy for head and neck cancer
- Comparison of Helical TomoTherapy with Linear Accelerator Base Intensity-modulated Radiotherapy for Head & Neck Cases
- Application of Helical Tomotherapy for Two Cases of Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma