Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr.
2017 Mar;20(1):65-70. 10.5223/pghn.2017.20.1.65.
Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba Syndrome in a Patient with a PTEN Mutation Identified by Chromosomal Microarray Analysis: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea. ryoo518@gilhospital.com
- KMID: 2375281
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2017.20.1.65
Abstract
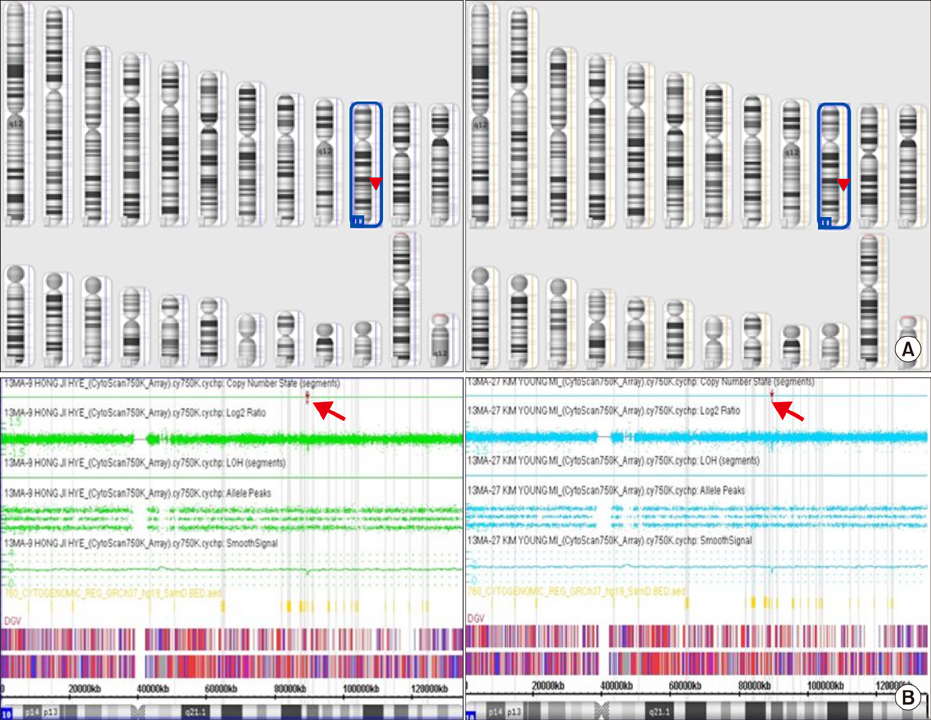
- Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome (BRRS) is one of the phosphatase and tensin homolog hamartoma tumor syndrome with a PTEN gene mutation. It is a rare dominant autosomal disorder characterized by cutaneous lipomas, macrocephaly, intestinal polyps, and developmental delay. Diagnosing this syndrome is important, because it may represent the pediatric phenotype of Cowden syndrome, in which there is an increased risk for malignant tumors in children. Until now, the prevalence of BRRS is unknown. Several dozen cases have been reported in the medical literature, but no case has been reported in Korea. Here we report a case of a 19-year-old girl who was diagnosed with BRRS because of macrocephaly, intellectual disability, and intestinal polyps. Her mother had similar findings and a PTEN mutation. Neither patient had mutations detected by conventional mutation-detection techniques, but a PTEN gene deletion was demonstrated by chromosomal microarray analysis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Buisson P, Leclair MD, Jacquemont S, Podevin G, Camby C, David A, et al. Cutaneous lipoma in children: 5 cases with Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome. J Pediatr Surg. 2006; 41:1601–1603.
Article2. Schreibman IR, Baker M, Amos C, McGarrity TJ. The hamartomatous polyposis syndromes: a clinical and molecular review. Am J Gastroenterol. 2005; 100:476–490.
Article3. Bannayan GA. Lipomatosis, angiomatosis, and macrencephalia. A previously undescribed congenital syndrome. Arch Pathol. 1971; 92:1–5.4. Genetics Home Reference. Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome [Internet]. Bethesda: U. S. National Library of Medicine;2012. cited 2016 Mar 13. Available from: https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/bannayan-riley-ruvalcaba-syndrome.5. Genetics Home Reference. Cowden syndrome [Internet]. Bethesda: U. S. National Library of Medicine;2012. cited 2016 Mar 13. Available from: https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/cowden-syndrome.6. Blumenthal GM, Dennis PA. PTEN hamartoma tumor syndromes. Eur J Hum Genet. 2008; 16:1289–1300.
Article7. Marsh DJ, Coulon V, Lunetta KL, Rocca-Serra P, Dahia PL, Zheng Z, et al. Mutation spectrum and genotype-phenotype analyses in Cowden disease and Bannayan-Zonana syndrome, two hamartoma syndromes with germline PTEN mutation. Hum Mol Genet. 1998; 7:507–515.
Article8. Parisi MA, Dinulos MB, Leppig KA, Sybert VP, Eng C, Hudgins L. The spectrum and evolution of phenotypic findings in PTEN mutation positive cases of Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome. J Med Genet. 2001; 38:52–58.
Article9. Latiff ZA, Atmawidjaja RW, RajaLope RJ, Syed Omar SA, Syed Zakaria SZ, Jamal RA. Bannayan Riley Ruvalcaba syndrome. Ann Acad Med Singap. 2010; 39:578–582.10. Lachlan KL, Lucassen AM, Bunyan D, Temple IK. Cowden syndrome and Bannayan Riley Ruvalcaba syndrome represent one condition with variable expression and age-related penetrance: results of a clinical study of PTEN mutation carriers. J Med Genet. 2007; 44:579–585.
Article11. Hobert JA, Eng C. PTEN hamartoma tumor syndrome: an overview. Genet Med. 2009; 11:687–694.
Article12. Gontijo GM, Pinto CA, Rogatto SR, Cunha IW, Aguiar S Jr, Alves CA. Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome with deforming lipomatous hamartomas in infant--case report. An Bras Dermatol. 2013; 88:982–985.
Article13. Zhou XP, Waite KA, Pilarski R, Hampel H, Fernandez MJ, Bos C, et al. Germline PTEN promoter mutations and deletions in Cowden/Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome result in aberrant PTEN protein and dysregulation of the phosphoinositol-3-kinase/Akt pathway. Am J Hum Genet. 2003; 73:404–411.
Article14. Eng C. PTEN hamartoma tumor syndrome (PHTS) [Internet]. Pagon RA, Adam MP, Ardinger HH, editors. GeneReviews. Seattle: University of Washington;2001. 11. 29. 2014 Jan 23. 2016 Mar 13. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1488/.15. Shaffer LG, Bejjani BA. Using microarray-based molecular cytogenetic methods to identify chromosome abnormalities. Pediatr Ann. 2009; 38:440–447.
Article16. Menko FH, Kneepkens CM, de Leeuw N, Peeters EA, Van Maldergem L, Kamsteeg EJ, et al. Variable phenotypes associated with 10q23 microdeletions involving the PTEN and BMPR1A genes. Clin Genet. 2008; 74:145–154.
Article17. Seo EJ. Clinical applications of chromosomal microarray analysis. J Genet Med. 2010; 7:111–118.
Article18. Manning M, Hudgins L. Array-based technology and recommendations for utilization in medical genetics practice for detection of chromosomal abnormalities. Genet Med. 2010; 12:742–745.
Article19. Miller DT, Adam MP, Aradhya S, Biesecker LG, Brothman AR, Carter NP, et al. Consensus statement: chromosomal microarray is a first-tier clinical diagnostic test for individuals with developmental disabilities or congenital anomalies. Am J Hum Genet. 2010; 86:749–764.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Pediatric Case of Bannayan–Riley–Ruvalcaba Syndrome with Recurrent Iron Deficiency Anemia
- PTEN Mutation Identified in Patient Diagnosed with Simultaneous Multiple Cancers
- Identification of a Novel p53 Intronic Mutation in Cowden's Disease
- A Case of Cowden Syndrome with Novel PTEN Gene Mutation
- Usefulness of Chromosomal Microarray in Hematologic Malignancies: A Case of Aggressive NK-cell Leukemia with 1q Abnormality