Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr.
2017 Mar;20(1):22-26. 10.5223/pghn.2017.20.1.22.
Pooled Analysis of the Cow's Milk-related-Symptom-Score (CoMiSSâ„¢) as a Predictor for Cow's Milk Related Symptoms
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Universitair Ziekenhuis Brussel, Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Brussels, Belgium. yvan.vandenplas@uzbrussel.be
- 2Nestlé Health Science, Vevey, Switzerland.
- 3United Pharmaceuticals/Novalac, Paris, France.
- 4Cytel, Cambridge, MA, USA.
- KMID: 2375274
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2017.20.1.22
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The diagnosis of cow's milk (CM) allergy is a challenge. The Cow's Milk-related-Symptom-Score (CoMiSSâ„¢) was developed to offer primary health care providers a reliable diagnostic tool for CM related symptoms. The predictive prospective value of the CoMiSSâ„¢ was evaluated in three clinical trials.
METHODS
Pooled analyses of the three studies were conducted based on regressing the results of the month-1 challenge test on the month-1 CoMiSSâ„¢, adjusting for baseline CoMiSSâ„¢ using a logistic regression model. In addition a logistic regression model was also fitted to the month-1 challenge test result with the change in CoMiSSâ„¢ from baseline as a predictor.
RESULTS
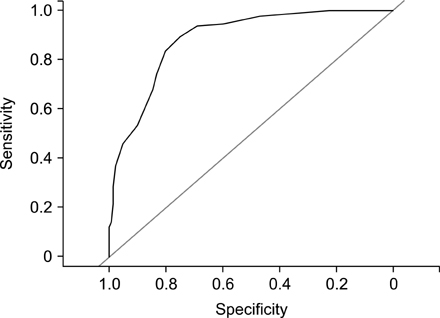
Results suggest that infants having a low CoMiSSâ„¢ (median, 5) after 1 month dietary treatment free from intact CM protein have a significant risk of having a positive challenge test (odds ratio, 0.83; 95% confidence interval, 0.75-0.93; p=0.002). Pooled data suggest that the change in CoMiSSâ„¢ from baseline to month-1 can predict CM related symptoms as a confirmed diagnosis according to the challenge test at month-1. However, in order to validate such a tool, infants without CM related symptoms would also need to be enrolled in a validation trial. A concern is that it may not be ethical to expose healthy infants to a therapeutic formula and a challenge test.
CONCLUSION
Pooled data analysis emphasizes that the CoMiSSâ„¢ has the potential to be of interest in infants suspected to have CM-related-symptoms. A prospective validation trial is needed.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Cow's Milk-related Symptom Score as a predictive tool for cow's milk allergy in Indian children aged 0–24 months
Rajniti Prasad, Ravi Shankar Ayathu Venkata, Praveen Ghokale, Pavitra Chakravarty, Fahmina Anwar
Asia Pac Allergy. 2018;8(4):. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.2018.8.e36.
Reference
-
1. Robbins KA, Wood RA, Keet CA. Milk allergy is associated with decreased growth in US children. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014; 134:1466–1468.e6.
Article2. Vieira MC, Morais MB, Spolidoro JV, Toporovski MS, Cardoso AL, Araujo GT, et al. A survey on clinical presentation and nutritional status of infants with suspected cow' milk allergy. BMC Pediatr. 2010; 10:25.
Article3. Vandenplas Y, Dupont C, Eigenmann P, Host A, Kuitunen M, Ribes-Koninckx C, et al. A workshop report on the development of the cow's milk-related symptom score awareness tool for young children. Acta Paediatr. 2015; 104:334–339.
Article4. Vandenplas Y, Steenhout P, Planoudis Y, Grathwohl D. Althera Study Group. Treating cow's milk protein allergy: a double-blind randomized trial comparing two extensively hydrolysed formulas with probiotics. Acta Paediatr. 2013; 102:990–998.
Article5. Vandenplas Y, De Greef E, Hauser B. Paradice Study Group. Safety and tolerance of a new extensively hydrolyzed rice protein-based formula in the management of infants with cow's milk protein allergy. Eur J Pediatr. 2014; 173:1209–1216.
Article6. Vandenplas Y, De Greef E, Xinias I, Vrani O, Mavroudi A, Hammoud M, et al. Safety of a thickened extensive casein hydrolysate formula. Nutrition. 2016; 32:206–212.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Cow's Milk Allergy with Atopic Dermatitis
- Cow's Milk-Related Symptom Score in Presumed Healthy Polish Infants Aged 0–6 Months
- A Case of Hemorrhagic Gastritis due to Cow's Milk Allergy
- Fecal Calprotectin and Cow’s MilkRelated-Symptoms Score in Children with Cow’s Milk Protein Allergy
- Factors which affect the serum ferritin in whole cow's milk related iron deficiency anemia children