Clin Orthop Surg.
2016 Sep;8(3):345-348. 10.4055/cios.2016.8.3.345.
The Floating Upper Limb: Multiple Injuries Involving Ipsilateral, Proximal, Humeral, Supracondylar, and Distal Radial Limb
- Affiliations
-
- 1Government Bone & Joint Hospital, Srinagar, India.
- 2Department of Biotechnology, University of Kashmir, Srinagar, India. qazi.danish@gmail.com
- 3Multi-Disciplinary Research Unit, Government Medical College, Srinagar, India.
- KMID: 2374284
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.3.345
Abstract
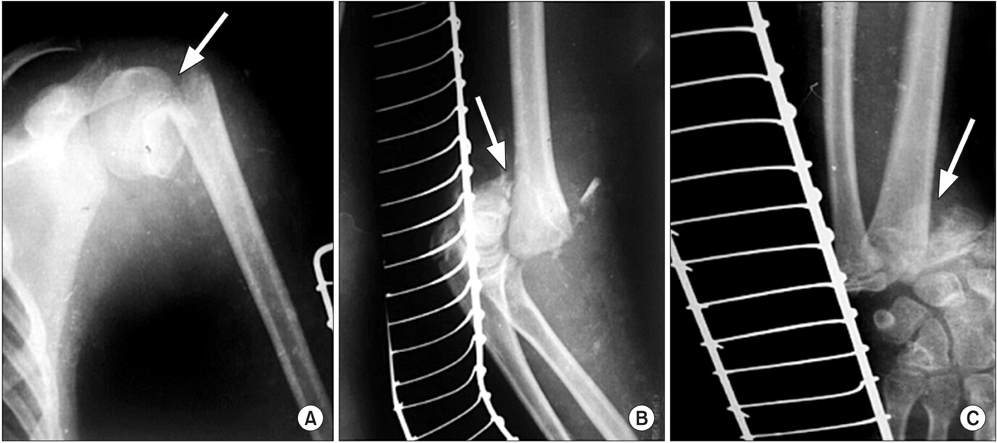
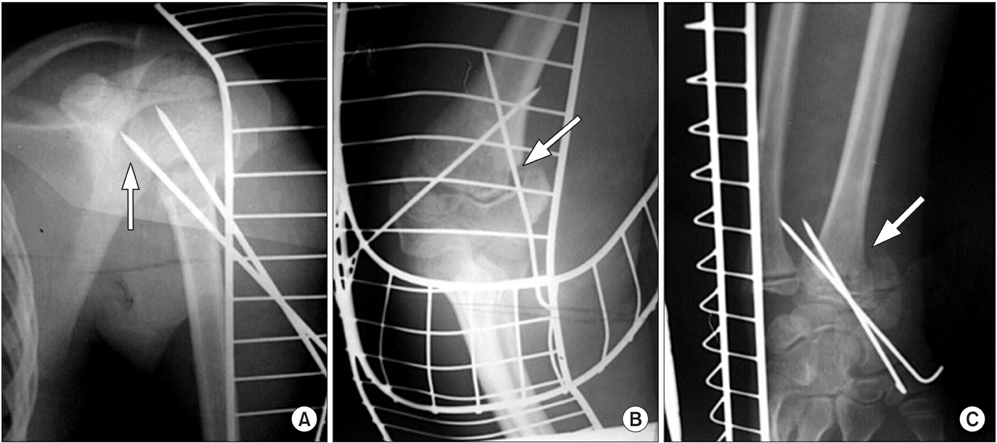
- Floating arm injury represents a common yet complicated injury of the childhood severely associated with limb deformation and even morbidity, if not precisely addressed and credibly operated. Here, we report a rare floating upper limb case of a 9-year-old boy with multiple injuries of ipsilateral proximal humeral, supracondylar and distal radial limb. This is the first report to document such a combined floating elbow and floating arm injury in the same limb. In this report, we discuss the surgical procedures used and recovery of the patient monitored to ascertain the effectiveness of the method in limb reorganisation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Stanitski CL, Micheli LJ. Simultaneous ipsilateral fractures of the arm and forearm in children. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1980; (153):218–222.
Article2. Harrington P, Sharif I, Fogarty EE, Dowling FE, Moore DP. Management of the floating elbow injury in children: simultaneous ipsilateral fractures of the elbow and forearm. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2000; 120(3-4):205–208.3. Guven M, Akman B, Kormaz T, Poyanli O, Altintas F. "Floating arm" injury in a child with fractures of the proximal and distal parts of the humerus: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2009; 3:9287.
Article4. Gul A, Sambandam S. Ipsilateral proximal and flexion supracondylar humerus fracture with an associated olecranon fracture in a 4-year-old child: a case report. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2006; 16(3):237–239.
Article5. James P, Heinrich SD. Ipsilateral proximal metaphyseal and flexion supracondylar humerus fractures with an associated olecranon avulsion fracture. Orthopedics. 1991; 14(6):713–716.
Article6. Parmaksizoglu AS, Ozkaya U, Bilgili F, Sayin E, Kabukcuoglu Y. Closed reduction of the pediatric supracondylar humerus fractures: the "joystick" method. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2009; 129(9):1225–1231.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Recovery from Motor Weakness of Ipsilateral Upper Limb Following Stroke Comparison on Recovery of Proximal Portion with That of Distal Portion
- Hirayama Disease with Proximal Involvement
- A Study of Motor Conduction Velocity of Radial Nerve: Comparision of Proximal and Distal Segments
- Change of Longitudinal Axis of Radius and Ulna in Cubitus Varus Deformity
- Reconstruction of Wrist Joint Using Vascularized Free Fibular Head Graft After the Wide Tumor Excision of Distal Radius