Clin Orthop Surg.
2016 Sep;8(3):268-273. 10.4055/cios.2016.8.3.268.
Evaluation of Outcome of Posterior Decompression and Instrumented Fusion in Lumbar and Lumbosacral Tuberculosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedics, Shri Aurobindo Institute of Medical Sciences, Indore, India. drakshayjain@yahoo.co.in
- KMID: 2374272
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.3.268
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
For surgical treatment of lumbar and lumbosacral tuberculosis, the anterior approach has been the most popular approach because it allows direct access to the infected tissue, thereby providing good decompression. However, anterior fixation is not strong, and graft failure and loss of correction are frequent complications. The posterior approach allows circumferential decompression of neural elements along with three-column fixation attained via pedicle screws by the same approach. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the outcome (functional, neurological, and radiological) in patients with lumbar and lumbosacral tuberculosis operated through the posterior approach.
METHODS
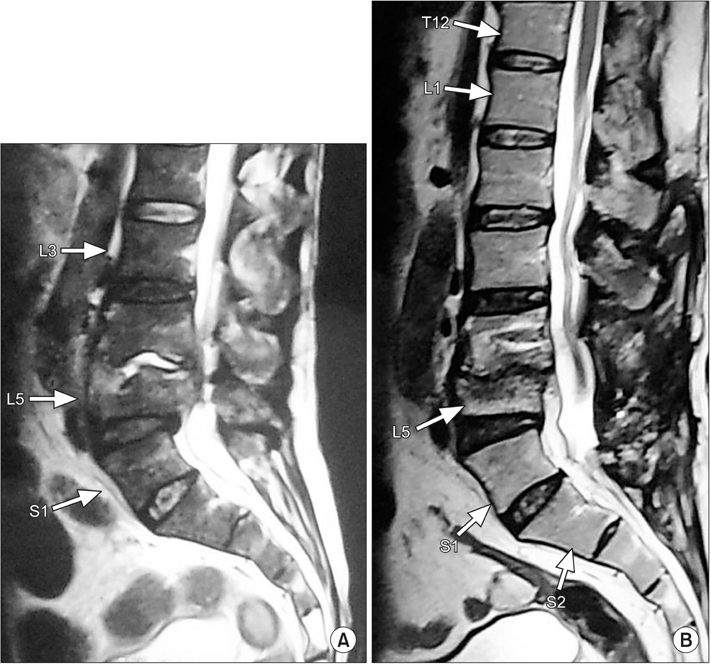
Twenty-eight patients were diagnosed with tuberculosis of the lumbar and lumbosacral region from August 2012 to August 2013. Of these, 13 patients had progressive neurological deterioration or increasing back pain despite conservative measures and underwent posterior decompression and pedicle screw fixation with posterolateral fusion. Antitubercular therapy was given till signs of radiological healing were evident (9 to 16 months). Functional outcome (visual analogue scale [VAS] score for back pain), neurological recovery (Frankel grading), and radiological improvement were evaluated preoperatively, immediately postoperatively and 3 months, 6 months, and 1 year postoperatively.
RESULTS
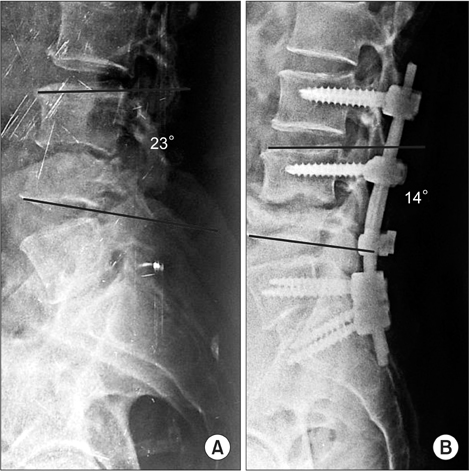
The mean VAS score for back pain improved from 7.89 (range, 9 to 7) preoperatively to 2.2 (range, 3 to 1) at 1-year follow-up. Frankel grading was grade B in 3, grade C in 7, and grade D in 3 patients preoperatively, which improved to grade D in 7 and grade E in 6 patients at the last follow-up. Radiological healing was evident in the form of reappearance of trabeculae formation, resolution of pus, fatty marrow replacement, and bony fusion in all patients. The mean correction of segmental kyphosis was 9.85° postoperatively. The mean loss of correction at final follow-up was 3.15°.
CONCLUSIONS
Posterior decompression with instrumented fusion is a safe and effective approach for management of patients with lumbar and lumbosacral tuberculosis.
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Back Pain
Cohort Studies
*Decompression, Surgical/adverse effects/methods/statistics & numerical data
Female
Humans
Lumbosacral Region/*surgery
Male
Middle Aged
Pain Measurement
Postoperative Complications
*Spinal Fusion/adverse effects/methods/statistics & numerical data
Tuberculosis, Spinal/*surgery
Young Adult
Figure
Reference
-
1. World Health Organization. Global tuberculosis report 2015. 20th ed. Geneva: World Health Organization;2015.2. Trecarichi EM, Di Meco E, Mazzotta V, Fantoni M. Tuberculous spondylodiscitis: epidemiology, clinical features, treatment, and outcome. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2012; 16:Suppl 2. 58–72.3. Turgut M. Spinal tuberculosis (Pott's disease): its clinical presentation, surgical management, and outcome. A survey study on 694 patients. Neurosurg Rev. 2001; 24(1):8–13.
Article4. Nussbaum ES, Rockswold GL, Bergman TA, Erickson DL, Seljeskog EL. Spinal tuberculosis: a diagnostic and management challenge. J Neurosurg. 1995; 83(2):243–247.
Article5. Lee TC, Lu K, Yang LC, Huang HY, Liang CL. Transpedicular instrumentation as an adjunct in the treatment of thoracolumbar and lumbar spine tuberculosis with early stage bone destruction. J Neurosurg. 1999; 91:2 Suppl. 163–169.
Article6. Zaveri G. The role of posterior surgery in spinal tuberculosis. ArgoSpine News J. 2011; 23(3):112–119.
Article7. Huskisson EC. Measurement of pain. Lancet. 1974; 2(7889):1127–1131.
Article8. Frankel HL, Hancock DO, Hyslop G, et al. The value of postural reduction in the initial management of closed injuries of the spine with paraplegia and tetraplegia: I. Paraplegia. 1969; 7(3):179–192.
Article9. Khoo LT, Mikawa K, Fessler RG. A surgical revisitation of Pott distemper of the spine. Spine J. 2003; 3(2):130–145.
Article10. Hodgson AR, Stock FE, Fang HS, Ong GB. Anterior spinal fusion: the operative approach and pathological findings in 412 patients with Pott's disease of the spine. Br J Surg. 1960; 48(208):172–178.
Article11. Benli IT, Kaya A, Acaroglu E. Anterior instrumentation in tuberculous spondylitis: is it effective and safe? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007; 460:108–116.12. Jain AK, Dhammi IK, Prashad B, Sinha S, Mishra P. Simultaneous anterior decompression and posterior instrumentation of the tuberculous spine using an anterolateral extrapleural approach. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008; 90(11):1477–1481.
Article13. Hee HT, Majd ME, Holt RT, Pienkowski D. Better treatment of vertebral osteomyelitis using posterior stabilization and titanium mesh cages. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2002; 15(2):149–156.
Article14. Krodel A, Kruger A, Lohscheidt K, Pfahler M, Refior HJ. Anterior debridement, fusion, and extrafocal stabilization in the treatment of osteomyelitis of the spine. J Spinal Disord. 1999; 12(1):17–26.15. Fukuta S, Miyamoto K, Masuda T, et al. Two-stage (posterior and anterior) surgical treatment using posterior spinal instrumentation for pyogenic and tuberculotic spondylitis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003; 28(15):E302–E308.
Article16. Moon MS, Woo YK, Lee KS, Ha KY, Kim SS, Sun DH. Posterior instrumentation and anterior interbody fusion for tuberculous kyphosis of dorsal and lumbar spines. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1995; 20(17):1910–1916.
Article17. Campbell PG, Malone J, Yadla S, et al. Early complications related to approach in thoracic and lumbar spine surgery: a single center prospective study. World Neurosurg. 2010; 73(4):395–401.
Article18. Moon MS. Combined posterior instrumentation and anterior interbody fusion for active tuberculous kyphosis of the thoraco-lumbar spine. Orthop Trauma. 1991; 5(3):177–179.
Article19. Sundararaj GD, Behera S, Ravi V, Venkatesh K, Cherian VM, Lee V. Role of posterior stabilisation in the management of tuberculosis of the dorsal and lumbar spine. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2003; 85(1):100–106.
Article20. Bezer M, Kucukdurmaz F, Aydin N, Kocaoglu B, Guven O. Tuberculous spondylitis of the lumbosacral region: long-term follow-up of patients treated by chemotherapy, transpedicular drainage, posterior instrumentation, and fusion. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2005; 18(5):425–429.21. Sahoo MM, Mahapatra SK, Sethi GC, Dash SK. Posterior-only approach surgery for fixation and decompression of thoracolumbar spinal tuberculosis: a retrospective study. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2012; 25(7):E217–E223.22. Jain AK, Srivastava A, Saini NS, Dhammi IK, Sreenivasan R, Kumar S. Efficacy of extended DOTS category I chemotherapy in spinal tuberculosis based on MRI-based healed status. Indian J Orthop. 2012; 46(6):633–639.
Article23. Zhang H, Sheng B, Tang M, et al. One-stage surgical treatment for upper thoracic spinal tuberculosis by internal fixation, debridement, and combined interbody and posterior fusion via posterior-only approach. Eur Spine J. 2013; 22(3):616–623.
Article24. Ito M, Sudo H, Abumi K, et al. Minimally invasive surgical treatment for tuberculous spondylodiscitis. Minim Invasive Neurosurg. 2009; 52(5-6):250–253.
Article25. Garg N, Vohra R. Minimally invasive surgical approaches in the management of tuberculosis of the thoracic and lumbar spine. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014; 472(6):1855–1867.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intertransverse Fusion in Spondylolisthesis: Report of a Case
- Impact on Neurological Recovery of Transforaminal Debridement and Interbody Fusion versus Transpedicular Decompression in Combination with Pedicle Screw Instrumentation for Treating Thoracic and Lumbar Spinal Tuberculosis
- Clinical Comparison between Decompression and Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion in Chronic Lower Back Pain Involving Degenerative Disc Disease and Spinal Stenosis
- Extended Posterior Decompression and Instrumented Fusion for Spinal Tuberculosis
- Radiologic Comparison of the Sacroiliac Joint Degeneration Following Lumbar or Lumbosacral Fusion