J Korean Orthop Assoc.
1968 Feb;3(1):11-15. 10.4055/jkoa.1968.3.1.11.
Intertransverse Fusion in Spondylolisthesis: Report of a Case
- KMID: 2464772
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.1968.3.1.11
Abstract
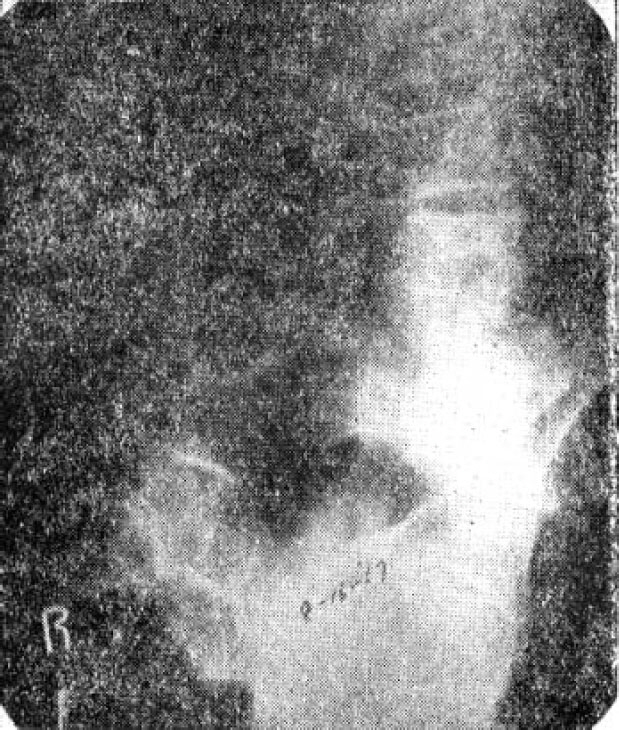
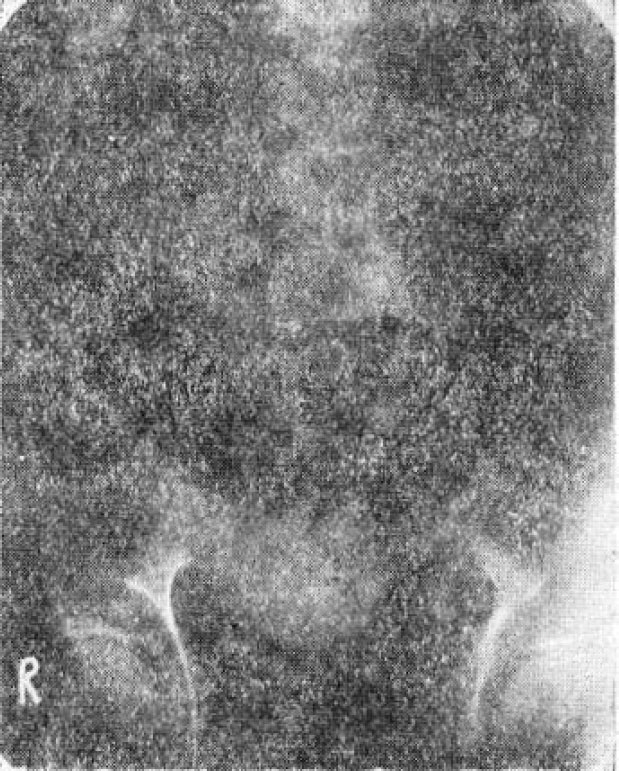
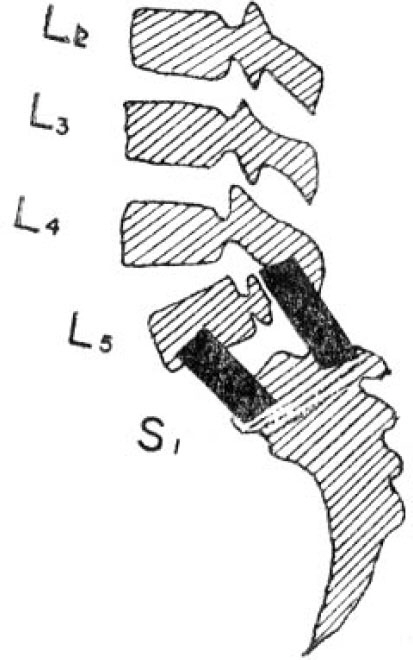
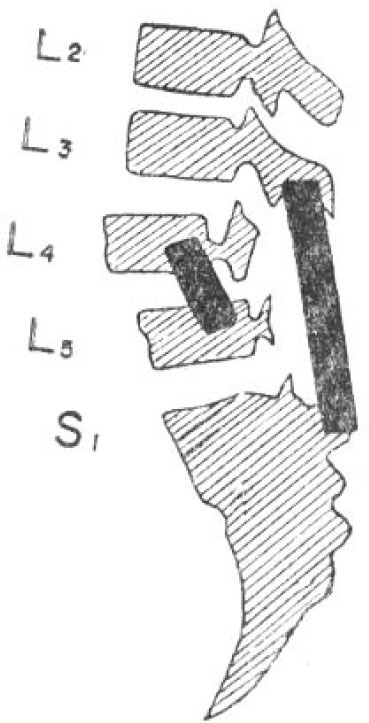
- There have been described a number of techniques and their combinations in the treatment of spondlolisthesis. The most widely used of this is excision of the posterior element combined by posterior fusion with a H-graft. However some advise decompression alone, while others recommend fusion without decompression. Anterior interbody fusion and posterolateral fusion have also been reported. Recently Rombold described intertransverse fusion combined with standard posterior fusion. The rationale of this procedure is best on the fact that a posterior fusion above and below the affected vetebra after the decompression stablized the body of the affected vetebra only indirectly, and stabilization of the affected vetebra to the one below come be achieved by fusion of the transverse processes which are anterior to the isthmus defect. The authors experience a case of spondylolisthesis of the 4th Lumbar vetebra associated with a cystic mass both subcutaneous and intraspinal connected by a defect in the lamina of the 5th Lumbar vetebra. They treated this case by laminectomy of the 5th Lumbar vetebra and excision of the posterior element of the 4th Lumbar vetebra, excision of the cystic mass and H-graft between L3 and Sl, inclusive, and reinforced this fusion with bilateral intertransverse fusion between 4th and 3th Lumbar vetebrae.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Spondylolisthesis. J.B.J.S. 37–A:878–879. 1955.2. Paul C, Colona M.D.Spondylolisthesis. Analysis of Two Hundred One Cases. J.B.J.S. 154:398–402. 1954398–402. 1954.3. David M., Bosworth M.D., J William, Fieldings M.D., Lawrence Demarest, M.D., Mario Bonaquist, M.D.Spondylolisthesis A Critical Review of A Consecutive Series of Cases Treated by Arthrodesis. J.B.J.S. 37–A:767–786. 1955.4. Gerald G., Gill M.D., John G., Manning M. D., Hugh L., White M.D.Surgical Treatment of Spodylolisthesis without Spine Fusion 1. J.B.J.S. 37–A:493–520. 1955.5. Beckett Howorth, M.D.Low Bachache and Sciatica. Part III. Surgical Treatment of Spondylolisthesis. J.B.J.S. 46–A:1515–9. 1961.6. Adkins E.W.O.Spondylolisthesis. J.B.J.S. 37–B:48–62. 1955.
Article7. Geoge Truchly M.D.,, Walter A.L., Thompson M.D.Posterolateral Fusion of the Lumbarsacral Spine. J.B.J.S. 44–A:505–512. 1962.8. Edward D Henderson. Result of the Surgical Treatment Spondylolisthesis. J.B.J.S. 48–A:619. 1966.9. Cleveland Borthworth, M.D., Thompson F.R.Pseudoarthrosis in The Lumbosacral Spine. J.B.J.S. 30–A:302–312. 1948.10. Watkins M.B.Posterolateral Fusion of Lumbar and Lumbaosacral Spine. J.B.J.S. 35–A:1014–1018. 1953.11. Watkins M.B.Posterolateral Bone-Grafting for Fusion of the Lumbar and Lumbaosacral Spine. J. B.J.S. 41–A:388–396. 1959.12. Charles Rombold M.D.Treatment of Spondylolisthesis by Posterolateral Fusion. Resection of the Pars Interarticularis and Prompt Mobilization of the Patients. J.B.J.S. 48–A:1287. 1966.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Surgical Treatment of Spondylolysis: A Report of 7 Cases
- Intertransverse Fusion Versus Posterior Interbody Fusion for the Treatment of the Degenerative Lumbar Spondylolisthesis
- Surgical Treatment of Lumbar Spondylolisthesis
- Anterior Spinal Fusion in the Treatment of Spondylolisthesis: A Report of Three Cases
- A Case of Juxtafacet Cyst of the Lumbar Spine Accompanied by Spinal Instability