Yonsei Med J.
2016 Jul;57(4):1016-1021. 10.3349/ymj.2016.57.4.1016.
Factors Contributing to Increases in Prescription Drug Expenditures Borne by National Health Insurance in South Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Pharmaceutical Benefits Department I Director, Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Division of TB Epidemic Investigation, Center for Disease Control & Prevention, Cheongju, Korea.
- 3Division of Social Welfare, Baekseok University, Cheonan, Korea.
- 4Department of Preventive Medicine and Public Health, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. ajoujkh@ajou.ac.kr
- 5Health Administration, Baekseok Arts University, Seoul, Korea. sjlee0820@bau.ac.kr
- KMID: 2374137
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2016.57.4.1016
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Rapid growth of prescription drug expenditures is a problem in South Korea. The objective of this study was to assess the contributions of four variables (therapeutic choice, drug-mix, original use, and price changes) to increases in drug expenditures paid by the National Health Insurance (NHI) in Korea.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A retrospective cohort study was conducted between January 1, 2008 and June 30, 2012 utilizing data from the NHI Claims Database of the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service. The number of target drug types for final analysis was 13959. To analyze the growth rates of drug expenditures, this study used Fisher ideal index and the Laspeyres and Paasche indexes.
RESULTS
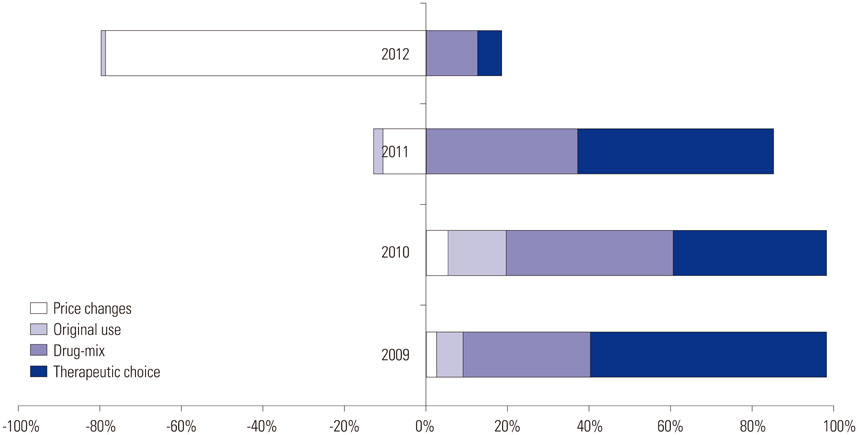
With the exception of 2012, therapeutic choice contributed to about 40-60% of the increase in drug expenditures every year, while drug-mix contributed to another 30-40%.
CONCLUSION
The rapid growth in prescription drug expenditure was found to be largely due to drug-mix and therapeutic choice over time. Original use had little impact on drug spending.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Park M, Chol Y, Tae Y, Chol J, Paek S, Lee H. 2010 Survey on National Health Insurance out-of-pocket expenditure. Seoul: National Health Insurance Service Health Insurance Police Research Institute;2011.2. Ministry of Health and Welfare. Evaluation of price cuts for drugs whose patents are expired after one year. Ministry of Health and Welfare;2013. accessed on 2013 July 24. http://www.129.go.kr/news/news02_view.jsp?n=7293.3. OECD. Health at a glance 2011: OECD indicators. Paris: OECD Publishing;2013.4. Lee YK, Chang S, Sin JK, Park JY. Separation of prescription and dispensing: changes in pharmaceutical costs and related policy issues. Seoul: Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs;2001.5. Ess SM, Schneeweiss S, Szucs TD. European healthcare policies for controlling drug expenditure. Pharmacoeconomics. 2003; 21:89–103.
Article6. Lee IH, Park S, Lee EK. Generic utilization in the Korean National Health Insurance Market; cost, volume and influencing factors. Yakhak Hoeji. 2014; 58:99–106.7. Shin Y, Whang D, Kang K, Bae EY, Lee S, Lee C. The National Health Insurance and its policy tasks. Seoul: Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs;2010.8. Bae EY. Study on the drug expenditure trend in Korea. Korean J Health Econ Policy. 2007; 13:39–54.9. Choi YJ, Shalowitz JI. Major growths of Korean pharmaceutical expenditure. J Korea Soc Health Inform Stat. 2011; 36:15–24.10. Morgan S. Drug expenditure trends in the Canadian provinces: magnitude and causes from 1998 to 2004. Healthc Policy. 2005; 1:85–99.
Article11. Cheong I, Lee S. A study on an incentive system for reducing pharmaceutical expenditure in Korea. Health Soc Welf Rev. 2009; 29:243–267.
Article12. Chernew ME, Smith DG, Kirking DM, Fendrick AM. Decomposing pharmaceutical cost growth in different types of health plans. Am J Manag Care. 2001; 7:667–673.13. Morgan SG. Quantifying components of drug expenditure inflation: the British Columbia seniors' drug benefit plan. Health Serv Res. 2002; 37:1243–1266.
Article14. Prieto L, Flöter S. The new EMCDDA standard table on public expenditure: a step forward in quantifying drug-related costs in Europe. Suchttherapie. 2009; 10:S211.
Article15. Jang S, Park CM, Bae G, Lee HJ, Kim HS. Determinants of publicly funded drug expenditure in South Korea. Seoul: Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service;2011.16. Park SE, Lim SH, Choi HW, Lee SM, Kim DW, Yim EY, et al. Evaluation on the first 2 years of the positive list system in South Korea. Health Policy. 2012; 104:32–39.
Article17. Bae G, Park C, Lee H, Han E, Kim DS, Jang S. Effective policy initiatives to constrain lipid-lowering drug expenditure growth in South Korea. BMC Health Serv Res. 2014; 14:100.
Article18. IMS Health intelligence applied, HIRA. Benchmarking prescribing behaviour for 207 disease conditions in Korea against those in specific reference markets, and to explore the drivers of any disparities in prescribing behaviour. Seoul: IMS Health intelligence applied, Health Insurence Review & Assecement;2006.19. National Health Insurance Service, Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service. 2012 National Health Insurance statistical yearbook. Seoul: National Health Insurance Service, Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service;2013.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- An analysis of contributing factors to financial status of regional health insurance
- Trend and Prediction of Urban Family Expenditure for Health Care
- Constructing a Real-Time Prescription Drug Monitoring System
- Factors Affecting Perceived Financial Burden of Medical Expenditures
- The fantasy of a new healthcare policy in Korea