Visceral Fat Mass Has Stronger Associations with Diabetes and Prediabetes than Other Anthropometric Obesity Indicators among Korean Adults
- Affiliations
-
- 1Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- 2Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. djkim@ajou.ac.kr
- 3Cardiovascular and Metabolic Disease Etiology Research Center, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- KMID: 2374088
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2016.57.3.674
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study determined which obesity measurement correlates the best with diabetes and prediabetes.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This cross-sectional study enrolled 1603 subjects (611 men, 992 women; age 30-64 years) at the Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases Etiology Research Center. Body mass index, waist circumference, waist-height ratio, waist-hip ratio, waist-thigh ratio, and visceral fat were used as measures of obesity. Visceral fat was acquired using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA). The prevalences of diabetes and prediabetes were defined using the criteria in the American Diabetes Association 2015 guidelines.
RESULTS
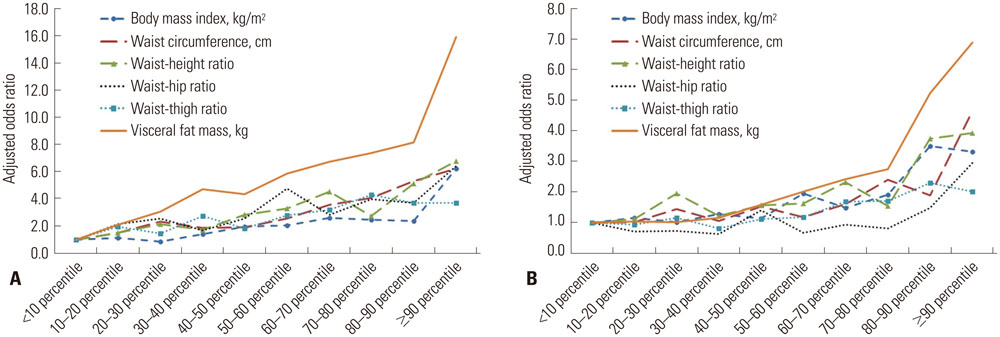
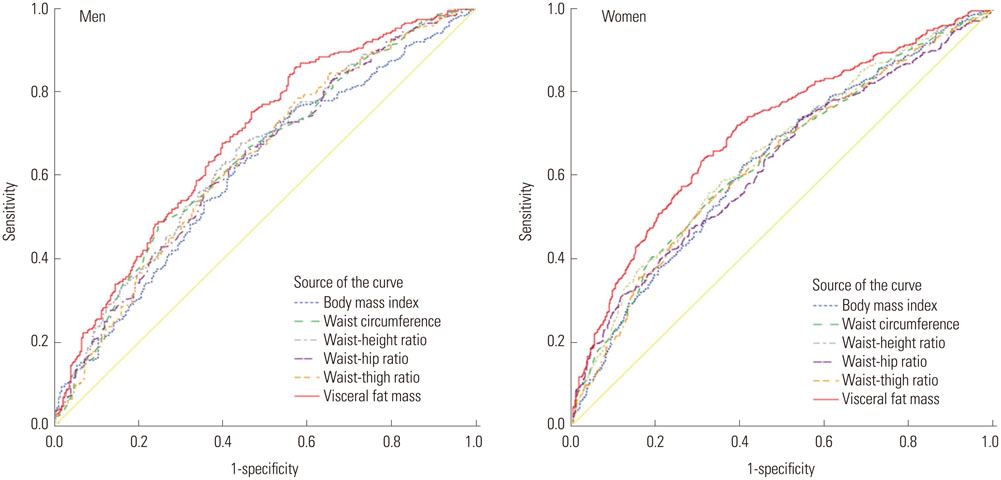
After adjusting for age and other potential confounding factors, participants with a visceral fat mass in the upper 10th percentile had a higher odds ratio (OR) for diabetes and prediabetes than the upper 10th percentile of other adiposity indices [men, OR=15.9, 95% confidence interval (CI)=6.4-39.2; women, OR=6.9, 95% CI=3.5-13.7]. Visceral fat mass also had the highest area under the curve with diabetes and prediabetes in both men (0.69, 95% CI=0.64-0.73) and women (0.70, 95% CI=0.67-0.74) compared to other anthropometric measurements of obesity.
CONCLUSION
Visceral fat mass measured using DXA is an indicator of diabetes or prediabetes, due to its ability to differentiate between abdominal visceral and subcutaneous fat.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Absorptiometry, Photon
*Adiposity
Adult
Anthropometry
Asian Continental Ancestry Group/*statistics & numerical data
Biomarkers/blood
Body Mass Index
Cross-Sectional Studies
Diabetes Mellitus/*ethnology
Female
Humans
*Intra-Abdominal Fat
Male
Middle Aged
Obesity/complications/*ethnology
Odds Ratio
Prediabetic State/*ethnology
Prevalence
Prospective Studies
Republic of Korea/epidemiology
Waist Circumference
Biomarkers
Figure
Cited by 5 articles
-
The Association of Adiponectin and Visceral Fat with Insulin Resistance and β-Cell Dysfunction
Hyun Uk Moon, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Seung Jin Han, Hae Jin Kim, Dae Jung Kim
J Korean Med Sci. 2019;34(1):. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2019.34.e7.Serum Chemerin Levels are Associated with Visceral Adiposity, Independent of Waist Circumference, in Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetic Subjects
Dae Young Cheon, Jun Goo Kang, Seong Jin Lee, Sung Hee Ihm, Eun Jig Lee, Moon Gi Choi, Hyung Joon Yoo, Chul Sik Kim
Yonsei Med J. 2017;58(2):319-325. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2017.58.2.319.Cohort Profile: The Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases Etiology Research Center Cohort in Korea
Jee-Seon Shim, Bo Mi Song, Jung Hyun Lee, Seung Won Lee, Ji Hye Park, Dong Phil Choi, Myung Ha Lee, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim, Sungha Park, Won-Woo Lee, Yoosik Youm, Eui-Cheol Shin, Hyeon Chang Kim
Yonsei Med J. 2019;60(8):804-810. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2019.60.8.804.Sex Differences of Visceral Fat Area and Visceral-to-Subcutaneous Fat Ratio for the Risk of Incident Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Eun Hee Kim, Hong-Kyu Kim, Min Jung Lee, Sung-Jin Bae, Jaewon Choe, Chang Hee Jung, Chul-Hee Kim, Joong-Yeol Park, Woo Je Lee
Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):486-498. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2021.0095.Association of Body Composition Changes with the Development of Diabetes Mellitus: A Nation-Wide Population Study
Hyung Jun Kim, Hyung-Woo Lee, Min-Kyoung Kang, Gwang Hyun Leem, Min-Ho Kim, Tae-Jin Song
Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(6):1093-1104. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2023.0243.
Reference
-
1. Kim DJ. The epidemiology of diabetes in Korea. Diabetes Metab J. 2011; 35:303–308.
Article2. Kelly T, Yang W, Chen CS, Reynolds K, He J. Global burden of obesity in 2005 and projections to 2030. Int J Obes (Lond). 2008; 32:1431–1437.
Article3. Seidell JC. The impact of obesity on health status: some implications for health care costs. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1995; 19:Suppl 6. S13–S16.4. Taylor AE, Ebrahim S, Ben-Shlomo Y, Martin RM, Whincup PH, Yarnell JW, et al. Comparison of the associations of body mass index and measures of central adiposity and fat mass with coronary heart disease, diabetes, and all-cause mortality: a study using data from 4 UK cohorts. Am J Clin Nutr. 2010; 91:547–556.
Article5. Wang Y, Rimm EB, Stampfer MJ, Willett WC, Hu FB. Comparison of abdominal adiposity and overall obesity in predicting risk of type 2 diabetes among men. Am J Clin Nutr. 2005; 81:555–563.
Article6. Snijder MB, Zimmet PZ, Visser M, Dekker JM, Seidell JC, Shaw JE. Independent and opposite associations of waist and hip circumferences with diabetes, hypertension and dyslipidemia: the AusDiab Study. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2004; 28:402–409.
Article7. Snijder MB, Dekker JM, Visser M, Bouter LM, Stehouwer CD, Kostense PJ, et al. Associations of hip and thigh circumferences independent of waist circumference with the incidence of type 2 diabetes: the Hoorn Study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2003; 77:1192–1197.
Article8. Kodama S, Horikawa C, Fujihara K, Heianza Y, Hirasawa R, Yachi Y, et al. Comparisons of the strength of associations with future type 2 diabetes risk among anthropometric obesity indicators, including waist-to-height ratio: a meta-analysis. Am J Epidemiol. 2012; 176:959–969.
Article9. Bouchard C. BMI, fat mass, abdominal adiposity and visceral fat: where is the 'beef'? Int J Obes (Lond). 2007; 31:1552–1553.
Article10. Després JP, Lemieux S, Lamarche B, Prud'homme D, Moorjani S, Brun LD, et al. The insulin resistance-dyslipidemic syndrome: contribution of visceral obesity and therapeutic implications. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1995; 19:Suppl 1. S76–S86.11. Hayashi T, Boyko EJ, Leonetti DL, McNeely MJ, Newell-Morris L, Kahn SE, et al. Visceral adiposity and the risk of impaired glucose tolerance: a prospective study among Japanese Americans. Diabetes Care. 2003; 26:650–655.12. Choi YJ, Seo YK, Lee EJ, Chung YS. Quantification of visceral fat using dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry and its reliability according to the amount of visceral fat in Korean adults. J Clin Densitom. 2015; 18:192–197.
Article13. Maurovich-Horvat P, Massaro J, Fox CS, Moselewski F, O'Donnell CJ, Hoffmann U. Comparison of anthropometric, area- and volume-based assessment of abdominal subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue volumes using multi-detector computed tomography. Int J Obes (Lond). 2007; 31:500–506.
Article14. Kim HJ, Kim YG, Park JS, Ahn YH, Ha KH, Kim DJ. Association between blood glucose level derived using the oral glucose tolerance test and hemoglobin A1C level. Korean J Intern Med. 2015; in press.15. Kaul S, Rothney MP, Peters DM, Wacker WK, Davis CE, Shapiro MD, et al. Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry for quantification of visceral fat. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2012; 20:1313–1318.
Article16. American Diabetes Association. (2) Classification and diagnosis of diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2015; 38:Suppl. S8–S16.17. Freedman DS, Rimm AA. The relation of body fat distribution, as assessed by six girth measurements, to diabetes mellitus in women. Am J Public Health. 1989; 79:715–720.
Article18. Qian Y, Lin Y, Zhang T, Bai J, Chen F, Zhang Y, et al. The characteristics of impaired fasting glucose associated with obesity and dyslipidaemia in a Chinese population. BMC Public Health. 2010; 10:139.
Article19. Lee YH, Bang H, Kim HC, Kim HM, Park SW, Kim DJ. A simple screening score for diabetes for the Korean population: development, validation, and comparison with other scores. Diabetes Care. 2012; 35:1723–1730.20. Tulloch-Reid MK, Williams DE, Looker HC, Hanson RL, Knowler WC. Do measures of body fat distribution provide information on the risk of type 2 diabetes in addition to measures of general obesity? Comparison of anthropometric predictors of type 2 diabetes in Pima Indians. Diabetes Care. 2003; 26:2556–2561.
Article21. Vazquez G, Duval S, Jacobs DR Jr, Silventoinen K. Comparison of body mass index, waist circumference, and waist/hip ratio in predicting incident diabetes: a meta-analysis. Epidemiol Rev. 2007; 29:115–128.
Article22. Rajpathak SN, Wylie-Rosett J. High prevalence of diabetes and impaired fasting glucose among Chinese immigrants in New York City. J Immigr Minor Health. 2011; 13:181–183.
Article23. Garnett SP, Baur LA, Cowell CT. Waist-to-height ratio: a simple option for determining excess central adiposity in young people. Int J Obes (Lond). 2008; 32:1028–1030.
Article24. Xu Z, Qi X, Dahl AK, Xu W. Waist-to-height ratio is the best indicator for undiagnosed type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med. 2013; 30:e201–e207.25. Han TS, McNeill G, Seidell JC, Lean ME. Predicting intra-abdominal fatness from anthropometric measures: the influence of stature. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1997; 21:587–593.
Article26. Kim YL, Kim TK, Cheong ES, Shin DG, Choi GS, Jung J, et al. Relation of absolute or relative adiposity to insulin resistance, retinol binding protein-4, leptin, and adiponectin in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab J. 2012; 36:415–421.
Article27. Després JP. Is visceral obesity the cause of the metabolic syndrome? Ann Med. 2006; 38:52–63.
Article28. Kahn BB, Flier JS. Obesity and insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 2000; 106:473–481.
Article29. Boden G. Free fatty acids, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Proc Assoc Am Physicians. 1999; 111:241–248.
Article30. Nielsen S, Guo Z, Johnson CM, Hensrud DD, Jensen MD. Splanchnic lipolysis in human obesity. J Clin Invest. 2004; 113:1582–1588.
Article31. Oka R, Miura K, Sakurai M, Nakamura K, Yagi K, Miyamoto S, et al. Comparison of waist circumference with body mass index for predicting abdominal adipose tissue. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2009; 83:100–105.
Article32. Preis SR, Massaro JM, Robins SJ, Hoffmann U, Vasan RS, Irlbeck T, et al. Abdominal subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue and insulin resistance in the Framingham heart study. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2010; 18:2191–2198.
Article33. Han JH, Park HS, Kim SM, Lee SY, Kim DJ, Choi WH. Visceral adipose tissue as a predictor for metabolic risk factors in the Korean population. Diabet Med. 2008; 25:106–110.
Article34. Rhee SY, Park SW, Kim DJ, Woo J. Gender disparity in the secular trends for obesity prevalence in Korea: analyses based on the KNHANES 1998-2009. Korean J Intern Med. 2013; 28:29–34.
Article35. Malin SK, Kashyap SR. Effects of metformin on weight loss: potential mechanisms. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2014; 21:323–329.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Association of Genetically Predicted Obesity and Stool Frequency: Evidence From an Observational and Mendelian Randomization Study
- The Association of Visceral Fat Area with Anthropometric Variables and its Risk for Metabolic Syndrome
- The correlation between simple anthropometric indices and abdominal visceral fat accumulation by computed tomography
- Correlation between risk of atherosclerosis and anthropometric parameters in premenopausal women
- Association of Hemoglobin A1c with Visceral Fat Measured by Computed Tomography in Nondiabetic Adults