Ann Lab Med.
2017 Jan;37(1):66-70. 10.3343/alm.2017.37.1.66.
Using Array-Based Comparative Genomic Hybridization to Diagnose Pallister-Killian Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Green Cross Laboratories, Yongin, Korea.
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sunnyhk@skku.edu
- KMID: 2373617
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2017.37.1.66
Abstract
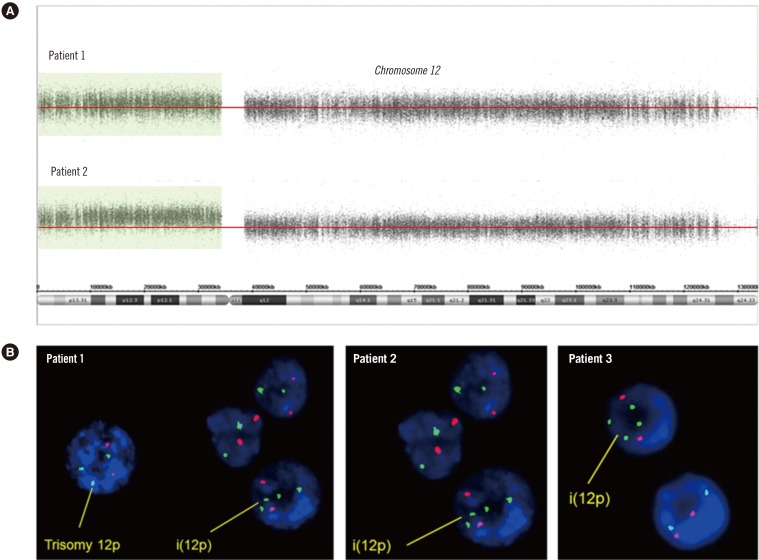
- Pallister-Killian syndrome (PKS) is a rare multisystem disorder characterized by isochromosome 12p and tissue-limited mosaic tetrasomy 12p. In this study, we diagnosed three pediatric patients who were suspicious of having PKS using array-based comparative genomic hybridization (array CGH) and FISH analyses performed on peripheral lymphocytes. Patients 1 and 2 presented with craniofacial dysmorphic features, hypotonia, and a developmental delay. Array CGH revealed two to three copies of 12p in patient 1 and three copies in patient 2. FISH analysis showed trisomy or tetrasomy 12p. Patient 3, who had clinical features comparable to those of patients 1 and 2, was diagnosed by using FISH analysis alone. Here, we report three patients with mosaic tetrasomy 12p. There have been only reported cases diagnosed by chromosome analysis and FISH analysis on skin fibroblast or amniotic fluid. To our knowledge, patient 1 was the first case diagnosed by using array CGH performed on peripheral lymphocytes in Korea.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Advantages of Array Comparative Genomic Hybridization Using Buccal Swab DNA for Detecting Pallister-Killian Syndrome
Veronica Bertini, Simone Gana, Alessandro Orsini, Alice Bonuccelli, Diego Peroni, Valetto Angelo
Ann Lab Med. 2019;39(2):232-234. doi: 10.3343/alm.2019.39.2.232.
Reference
-
1. Pallister PD, Meisner LF, Elejalde BR, Francke U, Herrmann J, Spranger J, et al. The pallister mosaic syndrome. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1977; 13:103–110.2. Peltomäki P, Knuutila S, Ritvanen A, Kaitila I, de la Chapelle A. Pallister-Killian syndrome: cytogenetic and molecular studies. Clin Genet. 1987; 31:399–405. PMID: 2887316.3. Wenger SL, Boone LY, Steele MW. Mosaicism in Pallister i(12p) syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1990; 35:523–525. PMID: 2333883.4. Schinzel A. Tetrasomy 12p (Pallister-Killian syndrome). J Med Genet. 1991; 28:122–125. PMID: 2002482.5. Wilkens A, Liu H, Park K, Campbell LB, Jackson M, Kostanecka A, et al. Novel clinical manifestations in Pallister-Killian syndrome: comprehensive evaluation of 59 affected individuals and review of previously reported cases. Am J Med Genet A. 2012; 158A:3002–3017. PMID: 23169767.6. Priest JH, Rust JM, Fernhoff PM. Tissue specificity and stability of mosaicism in Pallister-Killian +i(12p) syndrome: relevance for prenatal diagnosis. Am J Med Genet. 1992; 42:820–824. PMID: 1554021.7. Reeser SL, Wenger SL. Failure of PHA-stimulated i(12p) lymphocytes to divide in Pallister-Killian syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1992; 42:815–819. PMID: 1554020.8. Pagon RA, Hall JG, Davenport SL, Aase J, Norwood TH, Hoehn HW. Abnormal skin fibroblast cytogenetics in four dysmorphic patients with normal lymphocyte chromosomes. Am J Hum Genet. 1979; 31:54–61. PMID: 155399.9. Kulharya AS, Lovell CM, Flannery DB. Unusual mosaic karyotype resulting from adjacent 1 segregation of t(11;22): importance of performing skin fibroblast karyotype in patients with unexplained multiple congenital anomalies. Am J Med Genet. 2002; 113:367–370. PMID: 12457409.10. Theisen A, Rosenfeld JA, Farrell SA, Harris CJ, Wetzel HH, Torchia BA, et al. aCGH detects partial tetrasomy of 12p in blood from Pallister-Killian syndrome cases without invasive skin biopsy. Am J Med Genet A. 2009; 149A:914–918. PMID: 19353629.11. Ballif BC, Rorem EA, Sundin K, Lincicum M, Gaskin S, Coppinger J, et al. Detection of low-level mosaicism by array CGH in routine diagnostic specimens. Am J Med Genet A. 2006; 140:2757–2767. PMID: 17103431.12. Polityko AD, Goncharova E, Shamgina L, Drozdovskaja N, Podleschuk L, Abramchik E, et al. Pallister-Killian syndrome: rapid decrease of isochromosome 12p frequency during amniocyte subculturing. Conclusion for strategy of prenatal cytogenetic diagnostics. J Histochem Cytochem. 2005; 53:361–364. PMID: 15750020.13. Tang W, Wenger SL. Cell death as a possible mechanism for tissue limited mosaicism in Pallister-Killian syndrome. J Assoc Genet Technol. 2005; 31:168–169. PMID: 16354943.14. Hall BD. Mosaic tetrasomy 21 is mosaic tetrasomy 12p some of the time. Clin Genet. 1985; 27:284–285. PMID: 3987079.15. Lopes V, Mak E, Wyatt PR. Prenatal diagnosis of tetrasomy 21. Prenat Diagn. 1985; 5:233–235. PMID: 3161017.16. Shaffer LG, Kashork CD, Saleki R, Rorem E, Sundin K, Ballif BC, et al. Targeted genomic microarray analysis for identification of chromosome abnormalities in 1500 consecutive clinical cases. J Pediatr. 2006; 149:98–102. PMID: 16860135.17. Bejjani BA, Theisen AP, Ballif BC, Shaffer LG. Array-based comparative genomic hybridization in clinical diagnosis. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2005; 5:421–429. PMID: 15934818.18. Spinner NB, Conlin LK. Mosaicism and clinical genetics. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2014; 166C:397–405. PMID: 25424979.19. Hodge JC, Hulshizer RL, Seger P, St Antoine A, Bair J, Kirmani S. Array CGH on unstimulated blood does not detect all cases of Pallister-Killian syndrome: a skin biopsy should remain the diagnostic gold standard. Am J Med Genet A. 2012; 158A:669–673. PMID: 22315202.20. Cobben JM, Engelen M, Polstra A. Array CGH on unstimulated blood does not detect all cases of Pallister-Killian syndrome: buccal smear analysis should remain the diagnostic procedure of first choice. Am J Med Genet A. 2013; 161A:1517–1519. PMID: 23613446.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Advantages of Array Comparative Genomic Hybridization Using Buccal Swab DNA for Detecting Pallister-Killian Syndrome
- A Case of Pallister-Killian Syndrome
- Current Status and Future Clinical Applications of Array.based Comparative Genomic Hybridization
- Next generation sequencing and array-based comparative genomic hybridization for molecular diagnosis of pediatric endocrine disorders
- Array-based Comparative Genomic Hybridization and Its Application to Cancer Genomes and Human Genetics