Ann Lab Med.
2016 Nov;36(6):614-616. 10.3343/alm.2016.36.6.614.
A Case of Flavobacterium ceti Meningitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. nhryoo@dsmc.or.kr
- KMID: 2373604
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2016.36.6.614
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
-
Aged
Aneurysm/surgery
Anti-Bacterial Agents/pharmacology
Brain Diseases/surgery
Craniotomy/adverse effects
DNA, Bacterial/chemistry/genetics/metabolism
Female
Flavobacteriaceae Infections/etiology/microbiology
Flavobacterium/classification/drug effects/*isolation & purification
Humans
Meningitis/*diagnosis/microbiology
Microbial Sensitivity Tests
Phylogeny
Postoperative Complications
Sequence Analysis, DNA
Anti-Bacterial Agents
DNA, Bacterial
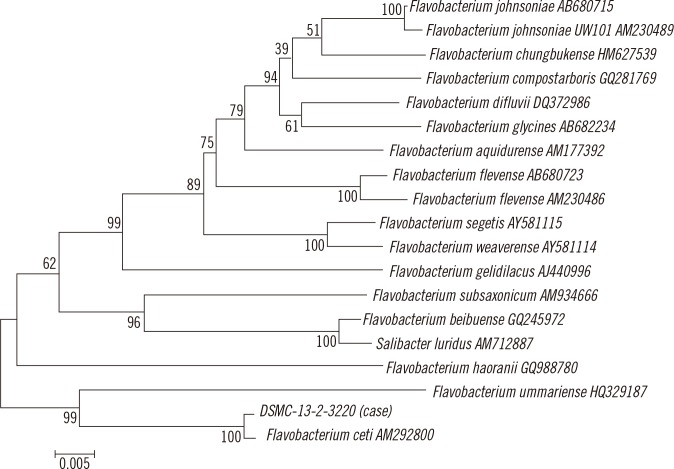
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bernardet JF, Bowman JP. The genus Flavobacterium. In : Dworkin M, Falkow S, Rosenberg E, Schleifer KH, Stackebrandt E, editors. The prokaryotes: a hand book on the biology of bacteria. 3rd ed. New York: Springer;2006. p. 455–480.2. Vela AI, Fernandez A, Sánchez-Porro C, Sierra E, Mendez M, Arbelo M, et al. Flavobacterium ceti sp. nov., isolated from beaked whales (Ziphius cavirostris). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2007; 57:2604–2608. PMID: 17978226.3. Kuai S, Huang L, Pei H, Chen Y, Liu J. Imipenem resistance due to class A carbapenemase KPC-2 in a Flavobacterium odoratum isolate. J Med Microbiol. 2011; 60:1408–1409. PMID: 21474611.4. Mosayebi Z, Movahedian AH, Soori T. Flavobacterium sepsis outbreak due to contaminated distilled water in a neonatal intensive care unit. J Hosp Infect. 2011; 78:214–215. PMID: 21316811.5. Tian GZ, Piao DR, Zhao HY, Jiang H, Cui BY, Li JY. A Flavobacterium lindanitolerans strain isolated from the ascites sample of a Chinese patient with EV71 virus infection. Biomed Environ Sci. 2011; 24:694–696. PMID: 22365408.6. Sung JY, Kim TS, Shin S, Roh EY, Yoon JH, Kim EC. Flavobacterium ceti from blood samples of a Korean patient with alcoholic liver cirrhosis. Ann Lab Med. 2015; 35:384–386. PMID: 25932454.7. CLSI. Interpretive criteria for identification of bacteria and fungi by DNA target sequencing; Approved guideline, MM18-A. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standard Institute;2008.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Flavobacterium Indologenes Meningitis in Neonate
- A Case of Flavobacterium Indologenes Keratitis
- Flavobacterium ceti From Blood Samples of a Korean Patient With Alcoholic Liver Cirrhosis
- Ventriculitis by nosocomial flavobacterium meningosepticum inneonates: neurosonographic findings
- A Case Report of Benign Recurrent Aseptic Meningitis Mollaret`s Meningitis