Ann Lab Med.
2016 May;36(3):209-214. 10.3343/alm.2016.36.3.209.
Usefulness of Flow Cytometric Analysis for Detecting Leptomeningeal Diseases in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea.
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine & Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. LEE.ST@yuhs.ac sunnyhk@skku.edu
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Patholgy, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2373529
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2016.36.3.209
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The clinical usefulness of flow cytometry (FCM) for the diagnosis of leptomeningeal diseases (LMD) in non-Hodgkin lymphomas has been suggested in previous studies but needs to be further validated. With this regards, we evaluated the use of FCM for LMD in a series of Korean patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
METHODS
FCM and cytomorphology were conducted using samples obtained from clinically suspected LMD patients, follow-up LMD patients, and those with high risk of developing tumorigenic diseases. We then compared results of FCM and cytomorphology. In total, 55 and 47 CSF samples were analyzed by FCM and cytomorphology, respectively.
RESULTS
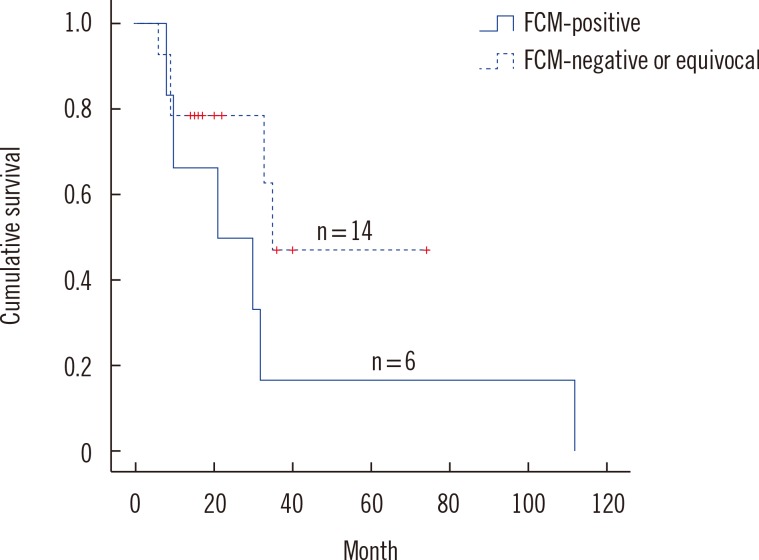
Of the samples analyzed, 25.5% (14/55) and 12.8% (6/47) were positive by FCM and cytomorphology, respectively. No samples were determined as negative by FCM but positive by cytomorphology. Seven patients were positive only by FCM and negative by cytomorphology, and six among them were clinically confirmed to have LMD either by follow-up cytomorphology or imaging study.
CONCLUSIONS
We observed a high detection rate of tumor cells by FCM compared with cytomorphology. FCM study can be useful in early sensitive detection of LMD.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Wilson WH, Bromberg JE, Stetler-Stevenson M, Steinberg SM, Martin-Martin L, Muniz C, et al. Detection and outcome of occult leptomeningeal disease in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and Burkitt lymphoma. Haematologica. 2014; 99:1228–1235. PMID: 24727817.
Article2. Hill QA, Owen RG. CNS prophylaxis in lymphoma: who to target and what therapy to use. Blood Rev. 2006; 20:319–332. PMID: 16884838.
Article3. Woo J, Baumann A, Arguello V. Recent advancements of flow cytometry: new applications in hematology and oncology. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2014; 14:67–81. PMID: 24308362.
Article4. Craig FE, Foon KA. Flow cytometric immunophenotyping for hematologic neoplasms. Blood. 2008; 111:3941–3967. PMID: 18198345.
Article5. de Graaf MT, de Jongste AH, Kraan J, Boonstra JG, Sillevis Smitt PA, Gratama JW. Flow cytometric characterization of cerebrospinal fluid cells. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2011; 80:271–281. PMID: 21567940.
Article6. Kentrou NA, Tsagarakis NJ, Tzanetou K, Damala M, Papadimitriou KA, Skoumi D, et al. An improved flow cytometric assay for detection and discrimination between malignant cells and atypical mesothelial cells, in serous cavity effusions. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2011; 80:324–334. PMID: 21695775.
Article7. Cesana C, Klersy C, Scarpati B, Brando B, Faleri M, Bertani G, et al. Flow cytometry and cytomorphology evaluation of hematologic malignancy in cerebrospinal fluids: comparison with retrospective clinical outcome. Ann Hematol. 2011; 90:827–835. PMID: 21212952.
Article8. Chizuka A, Kanda Y, Nannya Y, Oshima K, Kaneko M, Yamamoto R, et al. The diagnostic value of kappa/lambda ratios determined by flow cytometric analysis of biopsy specimens in B-cell lymphoma. Clin Lab Haematol. 2002; 24:33–36. PMID: 11843896.
Article9. Ståhlberg A, Aman P, Strömbom L, Zoric N, Diez A, Nilsson O, et al. Comparison of reverse transcription quantitative real-time PCR, flow cytometry, and immunohistochemistry for detection of monoclonality in lymphomas. ISRN Oncol. 2014; 2014:796210. PMID: 24649374.
Article10. Zembruski NC, Stache V, Haefeli WE, Weiss J. 7-Aminoactinomycin D for apoptosis staining in flow cytometry. Anal Biochem. 2012; 429:79–81. PMID: 22796502.
Article11. Argon A, Uyaroğlu MA, Nart D, Veral A, Kitapcioğlu G. The effectiveness of the liquid-based preparation method in cerebrospinal fluid cytology. Acta Cytol. 2013; 57:266–270. PMID: 23636078.
Article12. Hegde U, Filie A, Little RF, Janik JE, Grant N, Steinberg SM, et al. High incidence of occult leptomeningeal disease detected by flow cytometry in newly diagnosed aggressive B-cell lymphomas at risk for central nervous system involvement: the role of flow cytometry versus cytology. Blood. 2005; 105:496–502. PMID: 15358629.
Article13. Alvarez R, Dupuis J, Plonquet A, Christov C, Copie-Bergman C, Hemery F, et al. Clinical relevance of flow cytometric immunophenotyping of the cerebrospinal fluid in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Ann Oncol. 2012; 23:1274–1279. PMID: 21965472.
Article14. Di Noto R, Scalia G, Abate G, Gorrese M, Pascariello C, Raia M, et al. Critical role of multidimensional flow cytometry in detecting occult leptomeningeal disease in newly diagnosed aggressive B-cell lymphomas. Leuk Res. 2008; 32:1196–1199. PMID: 18262645.
Article15. Bromberg JE, Breems DA, Kraan J, Bikker G, van der Holt B, Smitt PS, et al. CSF flow cytometry greatly improves diagnostic accuracy in CNS hematologic malignancies. Neurology. 2007; 68:1674–1679. PMID: 17502548.
Article16. Benevolo G, Stacchini A, Spina M, Ferreri AJ, Arras M, Bellio L, et al. Final results of a multicenter trial addressing role of CSF flow cytometric analysis in NHL patients at high risk for CNS dissemination. Blood. 2012; 120:3222–3228. PMID: 22927246.
Article17. Sancho JM, Orfao A, Quijano S, Garcia O, Panizo C, Pérez-Ceballos E, et al. Clinical significance of occult cerebrospinal fluid involvement assessed by flow cytometry in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma patients at high risk of central nervous system disease in the rituximab era. Eur J Haematol. 2010; 85:321–328. PMID: 20528905.
Article18. Bernstein SH, Unger JM, Leblanc M, Friedberg J, Miller TP, Fisher RI. Natural history of CNS relapse in patients with aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: a 20-year follow-up analysis of SWOG 8516 -- the Southwest Oncology Group. J Clin Oncol. 2009; 27:114–119. PMID: 19047289.19. Galati D, Di Noto R, Del Vecchio L. Diagnostic strategies to investigate cerebrospinal fluid involvement in haematological malignancies. Leuk Res. 2013; 37:231–237. PMID: 23287431.
Article20. El-Sayed AM, El-Borai MH, Bahnassy AA, El-Gerzawi SM. Flow cytometric immunophenotyping (FCI) of lymphoma: correlation with histopathology and immunohistochemistry. Diagn Pathol. 2008; 3:43. PMID: 18986555.
Article21. Stacchini A, Aliberti S, Demurtas A, Benevolo G, Godio L. Ten antibodies, six colors, twelve parameters: a multiparameter flow cytometric approach to evaluate leptomeningeal disease in B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2012; 82:139–144. PMID: 22328059.
Article22. Cesana C, Klersy C, Scarpati B, Brando B, Volpato E, Bertani G, et al. Flow cytometry vs cytomorphology for the detection of hematologic malignancy in body cavity fluids. Leuk Res. 2010; 34:1027–1034. PMID: 20206995.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Bone Marrow Flow Cytometry in Staging of Patients With B-cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
- Pathologic Characteristics and Differential Diagnosis of Hodgkin Lymphoma
- Composite follicular lymphoma and classic Hodgkin lymphoma
- Mantle Cell Lymphoma, Blastoid Variant, Diagnosed on the Basis of Cytomorphology and Flow Cytometric Immunophenotyping of the Lymph Node Aspirate and Peripheral Blood
- A Case of Primary Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma of the Ovary