Korean J Ophthalmol.
2017 Apr;31(2):177-179. 10.3341/kjo.2017.31.2.177.
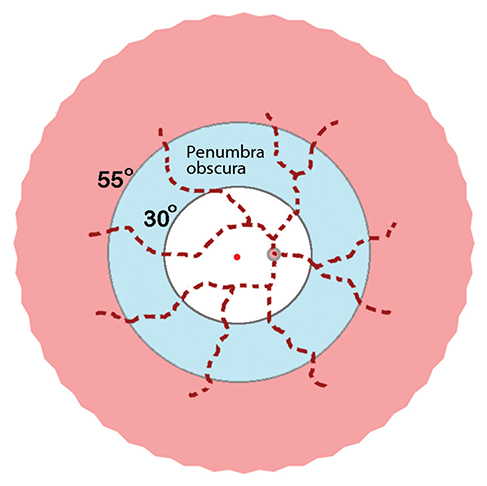
The Penumbra Obscura Stimulates Iris Neovascularisation after Isolated Central Retinal Artery Occlusion
- Affiliations
-
- 1Manchester Royal Eye Hospital, Manchester, UK. david.mcleod@nhs.net
- KMID: 2373477
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2017.31.2.177
Abstract
- No abstract available.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jung YH, Ahn SJ, Hong JH, et al. Incidence and clinical features of neovascularization of the iris following acute central retinal artery occlusion. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2016; 30:352–359.2. Duker JS, Brown GC. Iris neovascularization associated with obstruction of the central retinal artery. Ophthalmology. 1988; 95:1244–1250.3. McLeod D, Beatty S. Evidence for an enduring ischaemic penumbra following central retinal artery occlusion, with implications for fibrinolytic therapy. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2015; 49:82–119.4. Hayreh SS. Acute retinal arterial occlusive disorders. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2011; 30:359–394.5. McLeod D. Ischemic penumbra in retina endures: vascular neuropathology is reconciled. Neural Regen Res. 2016; 11:737–739.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Incomplete Central Retinal Artery Occlusion
- The Successful Treatment of a Case of Central Retinal Artery Occlusion
- Central Retinal Artery Occlusion Masquerading as Branch Retinal Artery Occlusion
- A Case of Cilioretinal Artery Occlusion Associated with Central Retinal Vein Occlusion
- A Clinical Study of 36 Cases of Retinal Artery Occlusion