Korean J Gastroenterol.
2015 May;65(5):306-311. 10.4166/kjg.2015.65.5.306.
A Case of Paradoxical Reaction Development during Antituberculosis Therapy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Digestive Disease Research Institute, Wonkwang University School of Medicine, Iksan, Korea. medsgs@wonkwang.ac.kr
- KMID: 2373227
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2015.65.5.306
Abstract
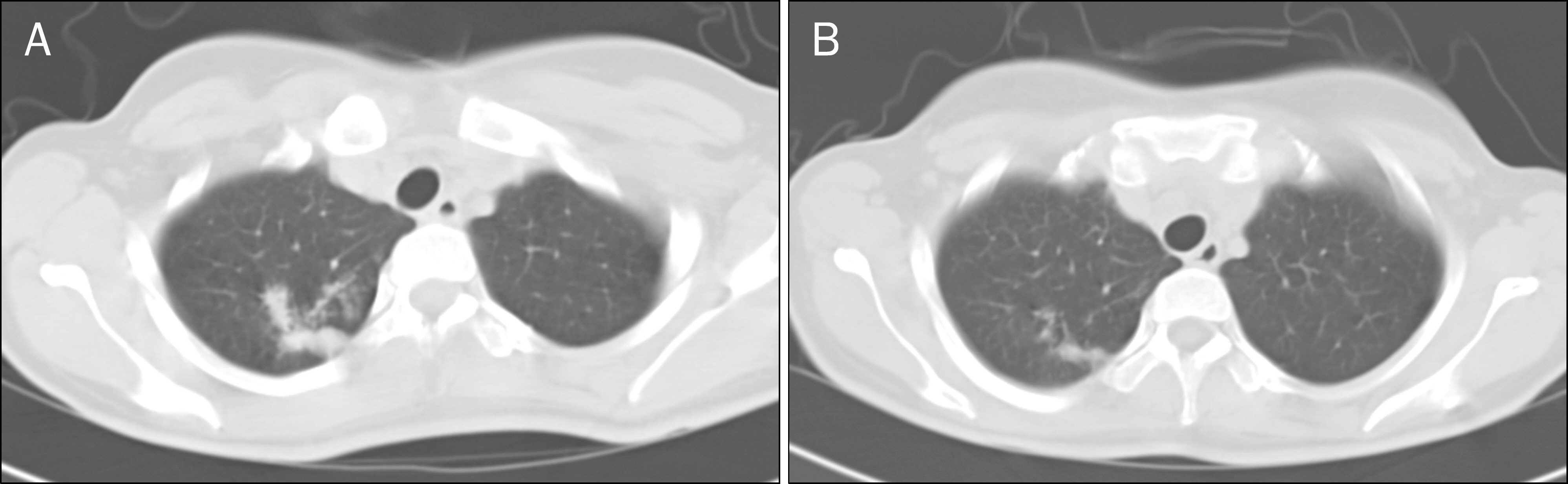
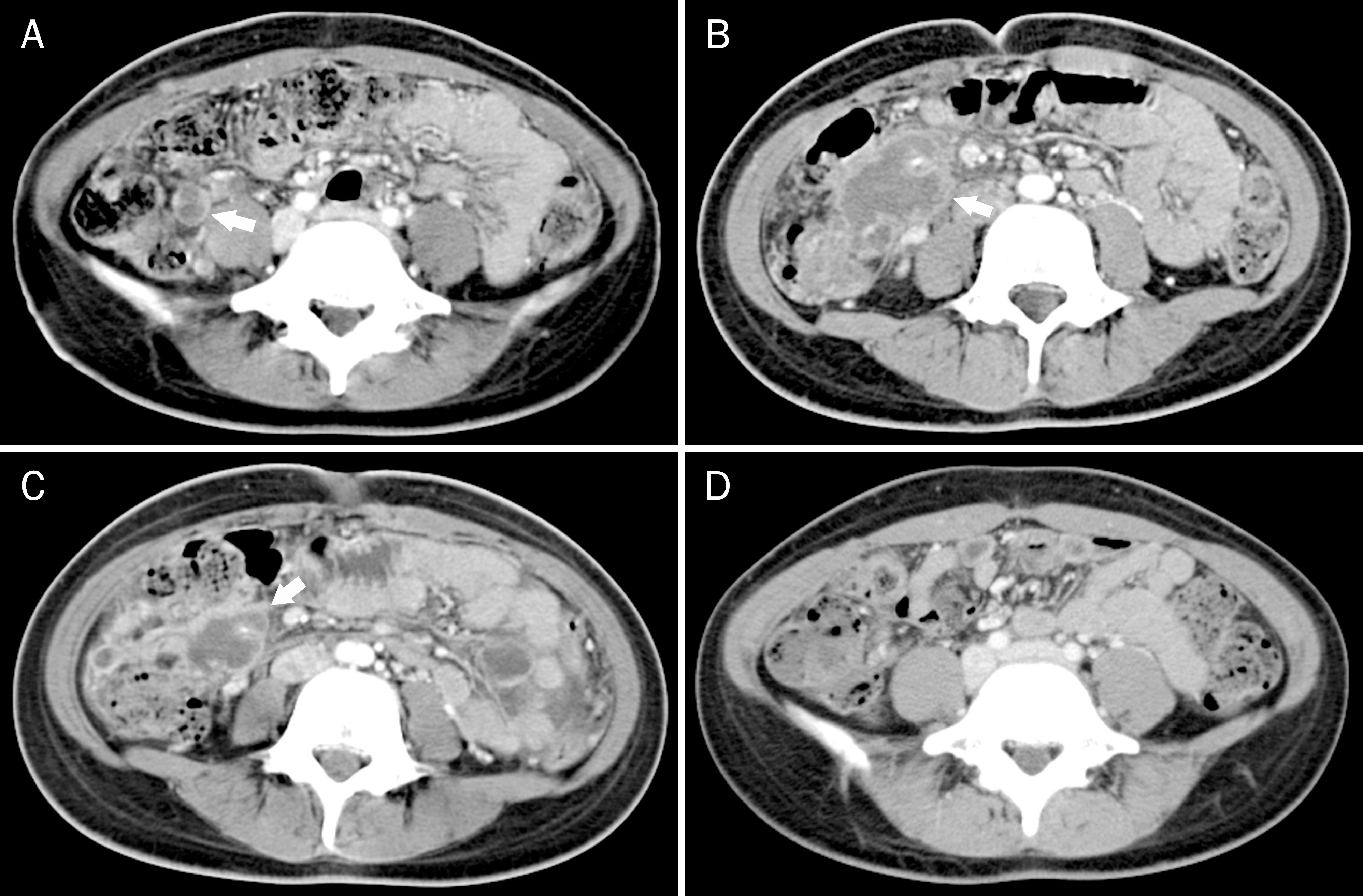
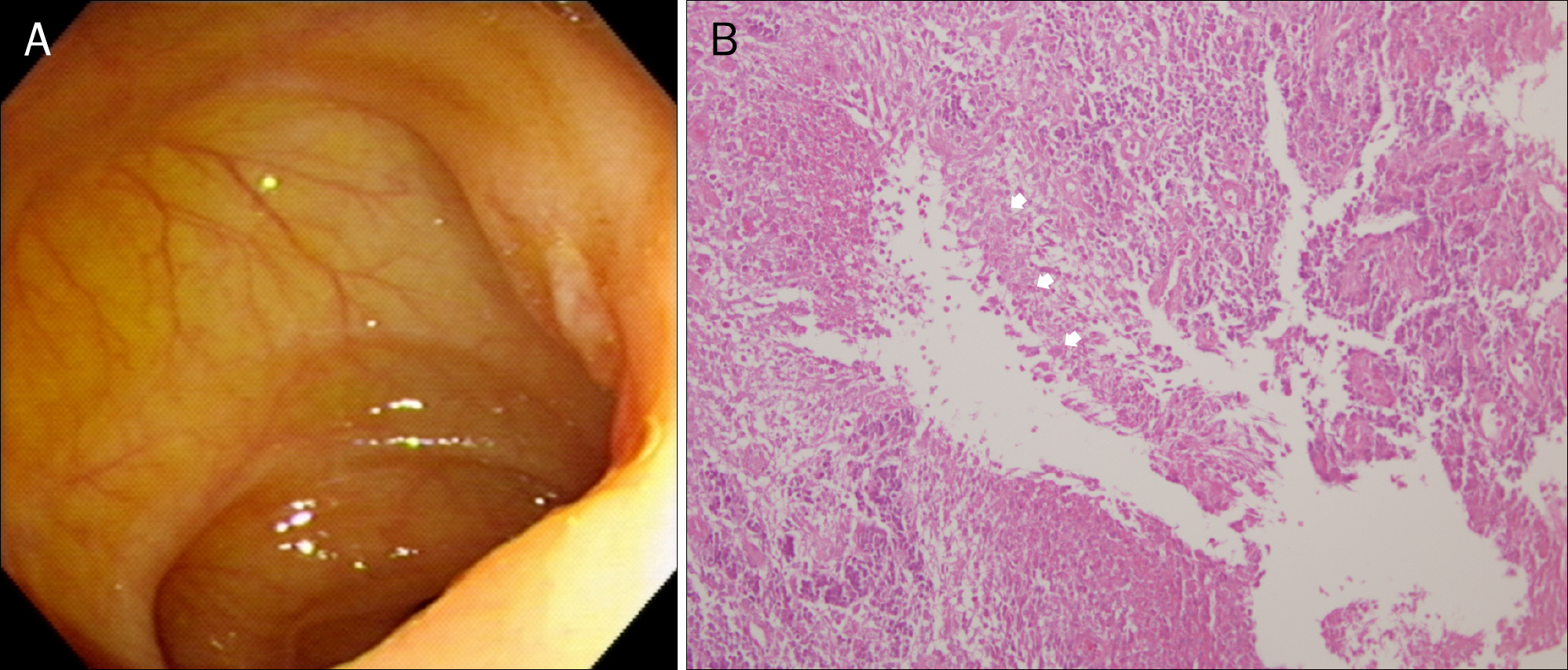
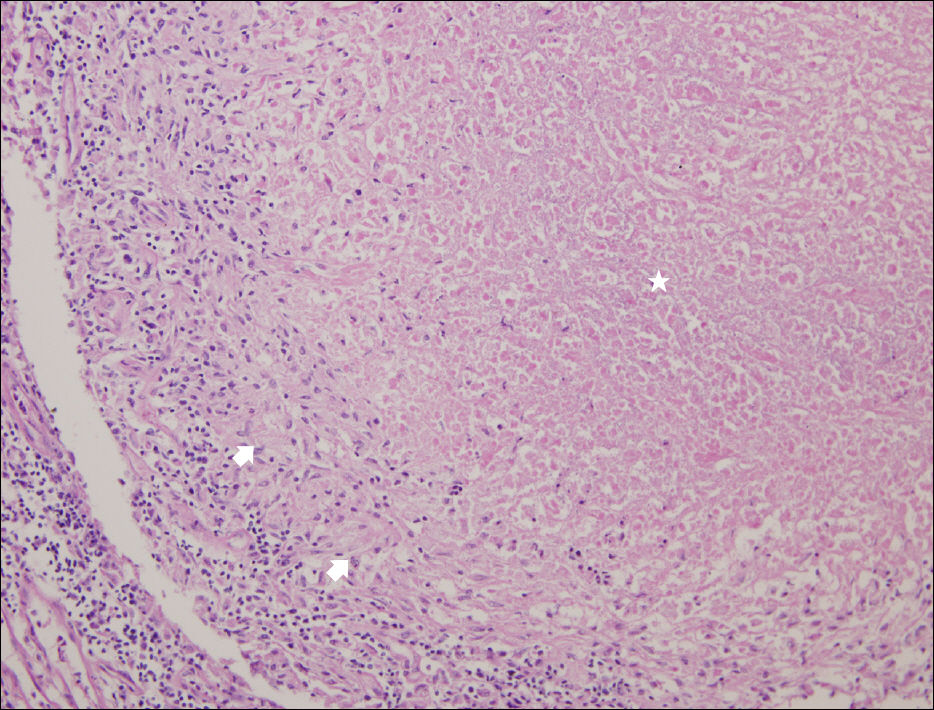
- Paradoxical reaction during antituberculosis therapy is defined as aggravation of preexisting tuberculous lesions or the development of new lesions. A 24-year-old female college student diagnosed with abdominal and pulmonary tuberculosis presented with fever and abdominal pain after having been treated with antituberculosis agents for 4 months. Tuberculous mesenteric lymphadenitis was suspected on abdominal CT scan and enlarged necrotic abscess was also present. These findings were considered to be due to paradoxical reaction rather than treatment failure during antituberculosis treatment. Although laparoscopic bowel adhesiolysis and abscess drainage were performed, high fever and severe abdominal pain did not improve. However, the patient eventually made a completely recovery after corticosteroid therapy combined with antituberculosis agents. Herein, we report a case of paradoxical reaction which developed in a patient with abdominal and pulmonary tuberculosis during antituberculosis therapy.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Cheng VC, Ho PL, Lee RA, et al. Clinical spectrum of paradoxical deterioration during antituberculosis therapy in non-HIV-in-fected patients. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2002; 21:803–809.
Article2. Al-Majed SA. Study of paradoxical response to chemotherapy in tuberculous pleural effusion. Respir Med. 1996; 90:211–214.
Article3. Hawkey CR, Yap T, Pereira J, et al. Characterization and management of paradoxical upgrading reactions in HIV-uninfected patients with lymph node tuberculosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2005; 40:1368–1371.
Article4. Cheng VC, Yam WC, Woo PC, et al. Risk factors for development of paradoxical response during antituberculosis therapy in HIV-negative patients. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2003; 22:597–602.
Article5. Carvalho AC, De Iaco G, Saleri N, et al. Paradoxical reaction during tuberculosis treatment in HIV-seronegative patients. Clin Infect Dis. 2006; 42:893–895.
Article6. Blumberg HM, Burman WJ, Chaisson RE, et al. American Thoracic Society, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Infectious Diseases Society. American Thoracic Society/Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/Infectious Diseases Society of America: treatment of tuberculosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003; 167:603–662.7. Ahn TH, Park MB, Lee KJ, et al. A case report of tuberculous brain abscess and tuberculous peritonitis developing due to paradoxical reactions. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2009; 66:457–462.
Article8. Kasahara K, Fukuoka A, Murakawa K, et al. Tuberculous peritonitis developing during chemotherapy for pulmonary and intestinal tuberculosis: a case report. Respirology. 2005; 10:257–260.
Article9. Kim SY, Oh TH, Seo JY, et al. A case of tuberculous peritonitis developed during chemotherapy for tuberculous pleurisy as paradoxical response. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2011; 57:379–383.
Article10. Bukharie H. Paradoxical response to antituberculous drugs: resolution with corticosteroid therapy. Scand J Infect Dis. 2000; 32:96–97.
Article11. Lee YJ, Jung SH, Hyun WJ, et al. A case of obstructive jaundice caused by paradoxical reaction during antituberculous chemotherapy for abdominal tuberculosis. Gut Liver. 2009; 3:338–342.
Article12. Dixit R, Nuwal P, Arya M. Splenic abscess as a paradoxical response to chemotherapy in tuberculous pleural effusion. Ann Thorac Med. 2010; 5:50–51.
Article13. Kim YS, Kim YH, Lee KM, Kim JS, Park YS. IBD Study Group of the Korean Association of the Study of Intestinal Diseases. Diagnostic guideline of intestinal tuberculosis. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2009; 53:177–186.14. Geri G, Passeron A, Heym B, et al. Paradoxical reactions during treatment of tuberculosis with extrapulmonary manifestations in HIV-negative patients. Infection. 2013; 41:537–543.
Article15. Kim SH, Chung HY, Lee GD, et al. Clinical characteristics of paradoxical response to chemotherapy in pulmonary tuberculosis. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2002; 53:27–35.
Article16. Grange JM, Stanford JL, Rook GA. Tuberculosis and cancer: par-allels in host responses and therapeutic approaches? Lancet. 1995; 345:1350–1352.
Article17. Garcia Vidal C, Garau J. Systemic steroid treatment of paradoxical upgrading reaction in patients with lymph node tuberculosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2005; 41:915–916.18. Garcia Vidal C, Rodríguez Fernández S, Martínez Lacasa J, et al. Paradoxical response to antituberculous therapy in infliximab- treated patients with disseminated tuberculosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2005; 40:756–759.19. Wendel KA, Alwood KS, Gachuhi R, Chaisson RE, Bishai WR, Sterling TR. Paradoxical worsening of tuberculosis in HIV-in-fected persons. Chest. 2001; 120:193–197.
Article20. Cho OH, Park KH, Kim T, et al. Paradoxical responses in non-HIV-infected patients with peripheral lymph node tuberculosis. J Infect. 2009; 59:56–61.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Adverse Effects of Antituberculosis Drugs and the Solutions
- Intestinal Perforation as a Paradoxical Reaction to Antitubercular Therapy: A Case Report
- 10 Cases of Paradoxical Expansion of Intracranial Terculomas During Chemotherapy
- Paradoxical Deterioration of Intramedullary Spinal Tuberculomas during Antituberculous Therapy
- The CT findings and clinical course of intraperitoneal tuberculous abscess