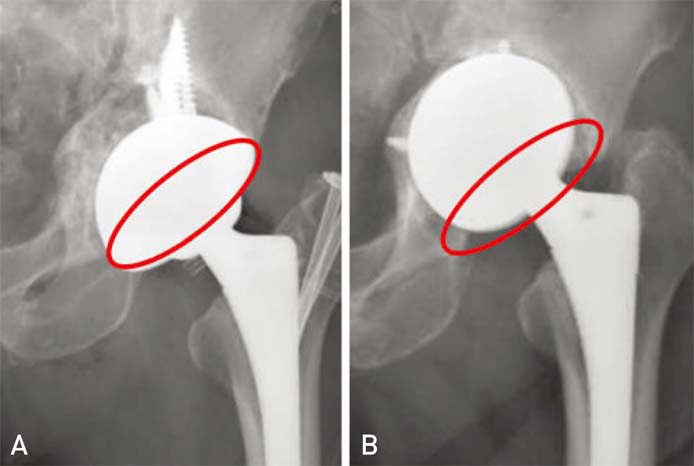
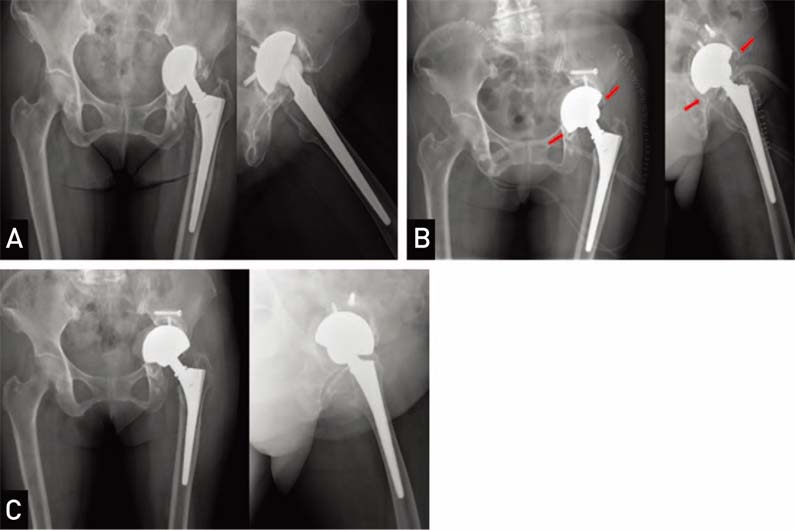
Hip Pelvis.
2017 Mar;29(1):24-29. 10.5371/hp.2017.29.1.24.
Comparative Study of Peripheral Rim Fixation Using Jumbo Cup in Revisional Hip Arthroplasty
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, Seoul, Korea. albire00@naver.com
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Gyeongsang National University Changwon Hospital, Changwon, Korea.
- 3Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, The Catholic University of Korea, Yeoeuido St. Mary's Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2371764
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5371/hp.2017.29.1.24
Abstract
- PURPOSE
It is challenging procedure to revise acetabular component in acetabulum with severe bone defect or deformity. The jumbo cup is good option for revisional arthroplasty in large bone defect. The purpose of this study is to compare the prognosis of revisional total hip arthroplasty using jumbo cup with peripheral rim fixation and no rim fixation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We included the patients who had performed acetabular revisional total hip arthroplasty from January 2002 to March 2015 in our institute. Total of 51 hips (51 patients) were included. The mean follow up period was 51 months (range, 12 to 154 months) and mean age was 60.7 years (range, 30 to 81 years). We divided into two groups (peripheral rim fixation group and no rim fixation group) by anteroposterior and lateral plain radiograph. We compared survival rate, hip center change and clinical outcomes between two groups.
RESULTS
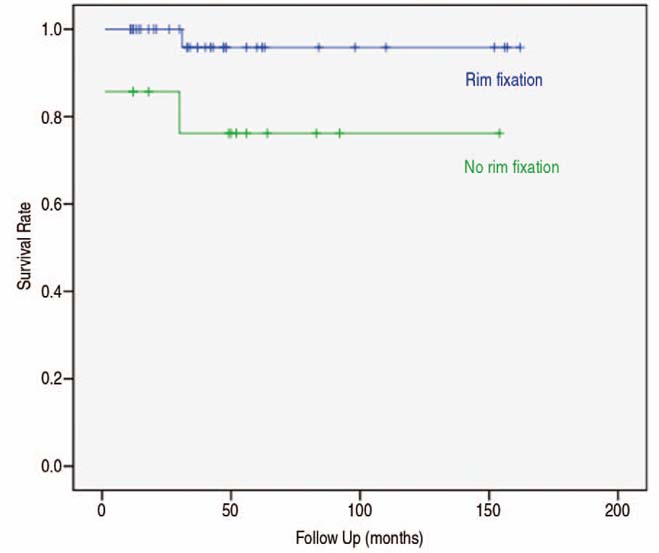
There were 37 patients in peripheral rim fixation group and 14 patients in no rim fixation group. There was one patient who had aseptic loosening necessary to re-revision in rim fixation group and 3 patients in no rim fixation group. And one patient had superficial infection in rim fixation group and one patient had periprosthetic fracture in no rim fixation group. Survival rate was higher in the peripheral rim fixation group (97.3%) than no rim fixation group (78.6%, P=0.028)
CONCLUSION
Based on our findings, peripheral rim fixation might be recommended to improve short-term outcome after revision total hip arthroplasty using jumbo cup.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Herberts P, Ahnfelt L, Malchau H, Strömberg C, Andersson GB. Multicenter clinical trials and their value in assessing total joint arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989; (249):48–55.
Article2. Pieringer H, Auersperg V, Böhler N. Reconstruction of severe acetabular bone-deficiency: the Burch-Schneider antiprotrusio cage in primary and revision total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2006; 21:489–496.3. Chen WM, Engh CA Jr, Hopper RH Jr, McAuley JP, Engh CA. Acetabular revision with use of a bilobed component inserted without cement in patients who have acetabular bone-stock deficiency. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000; 82:197–206.
Article4. Whaley AL, Berry DJ, Harmsen WS. Extra-large uncemented hemispherical acetabular components for revision total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001; 83-A:1352–1357.
Article5. Fan CY, Chen WM, Lee OK, Huang CK, Chiang CC, Chen TH. Acetabular revision arthroplasty using jumbo cups: an experience in Asia. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2008; 128:809–813.
Article6. Patel JV, Masonis JL, Bourne RB, Rorabeck CH. The fate of cementless jumbo cups in revision hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2003; 18:129–133.
Article7. Lachiewicz PF, Soileau ES. Fixation, survival, and dislocation of jumbo acetabular components in revision hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013; 95:543–548.
Article8. Wedemeyer C, Neuerburg C, Heep H, et al. Jumbo cups for revision of acetabular defects after total hip arthroplasty: a retrospective review of a case series. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2008; 128:545–550.
Article9. Jasty M. Jumbo cups and morsalized graft. Orthop Clin North Am. 1998; 29:249–254.10. Hansen E, Ries MD. Revision total hip arthroplasty for large medial (protrusio) defects with a rim-fit cementless acetabular component. J Arthroplasty. 2006; 21:72–79.
Article11. Engh CA, Hooten JP Jr, Zettl-Schaffer KF, et al. Porous-coated total hip replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994; (298):89–96.
Article12. Faizan A, Black BJ, Fay BD, Heffernan CD, Ries MD. Comparison of head center position and screw fixation options between a jumbo cup and an offset center of rotation cup in revision total hip arthroplasty: a computer simulation study. J Arthroplasty. 2016; 31:307–311.
Article13. Harris WH. Traumatic arthritis of the hip after dislocation and acetabular fractures: treatment by mold arthroplasty. An end-result study using a new method of result evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1969; 51:737–755.
Article14. Gustke KA, Levering MF, Miranda MA. Use of jumbo cups for revision of acetabulae with large bony defects. J Arthroplasty. 2014; 29:199–203.
Article15. MacKenzie JR, Callaghan JJ, Pedersen DR, Brown TD. Areas of contact and extent of gaps with implantation of oversized acetabular components in total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994; (298):127–136.
Article16. Paprosky WG, Perona PG, Lawrence JM. Acetabular defect classification and surgical reconstruction in revision arthroplasty. A 6-year follow-up evaluation. J Arthroplasty. 1994; 9:33–44.
Article17. Nwankwo CD, Ries MD. Do jumbo cups cause hip center elevation in revision THA? A radiographic evaluation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014; 472:2793–2798.
Article18. Gustke KA. Jumbo cup or high hip center: is bigger better? J Arthroplasty. 2004; 19:4 Suppl 1. 120–123.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Acetabular Cup Revision
- Liner Dissociation by Extrusion of the Acetabular Cup Fixation Screw after Total Hip Replacement: Two Cases Report
- Periprosthetic Acetabular Fracture after Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Report on Two Cases
- The Role of Intraoperative Frozen Section as a Guide to Sepsis in Hip Arthroplasty for Teatment of painful Hip Disease
- Navigated Acetabular Cup Fixation for Acetabular Deformity or Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty