Hip Pelvis.
2014 Sep;26(3):150-156. 10.5371/hp.2014.26.3.150.
Navigated Acetabular Cup Fixation for Acetabular Deformity or Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Seoul Veterans Hospital, Seoul, Korea. 3188yun@naver.com
- KMID: 2054178
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5371/hp.2014.26.3.150
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the usefulness of navigated acetabular cup fixation for total hip arthroplasty in patients with acetabular deformity or revision total hip arthroplasty.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
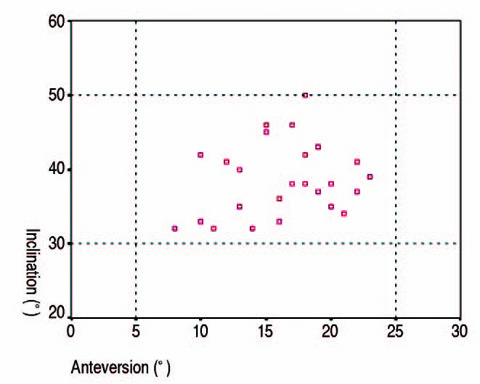
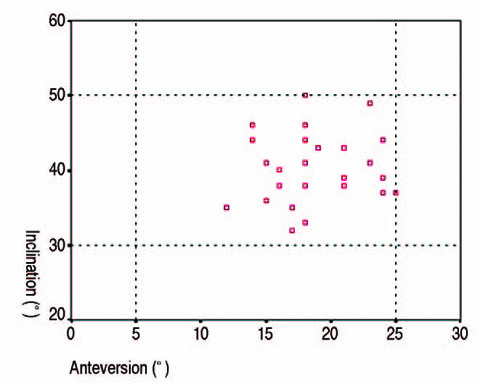
This study enrolled 28 patients with at least 12 months' follow-up. The safe zone of the acetabular cup was defined as 40degrees+/-10degreesin inclination and 15degrees+/-10degreesin anteversion. The authors used the navigation and radiographic data to determine whether the acetabular cup was located within the safe zone or not. To evaluate the clinical outcomes, preoperative and last follow-up Harris hip scores were checked, and the occurrence of complications was evaluated.
RESULTS
According to the navigation data, the mean inclination and anteversion were 38.5degrees+/-4.7degrees(range, 32degrees-50degrees) and 16.6degrees+/-4.0degrees(range, 8degrees-23degrees), respectively. According to the radiographic data the mean inclination and anteversion were 40.5degrees+/-4.6degrees(range, 32degrees-50degrees) and 19.4degrees+/-4.2degrees(range, 8degrees-25degrees), respectively. In both cases, all values were within the safe zone. Harris hip score was improved in all patients from preoperative 52.3+/-14.4 points (range, 29-87 points) to 88.0+/-9.0 points (range, 65-99 points) at the last follow-up. There was no dislocation or loosening of both cases.
CONCLUSION
Navigated acetabular cup fixation is a useful technique for total hip arthroplasty in patients with acetabular deformity or revision total hip arthroplasty because it prevents the malposition and related complications.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
The Evolution of Computer-Assisted Total Hip Arthroplasty and Relevant Applications
Jun-Dong Chang, In-Sung Kim, Atul M. Bhardwaj, Ramachandra N. Badami
Hip Pelvis. 2017;29(1):1-14. doi: 10.5371/hp.2017.29.1.1.Efficacy of Computed Tomography-Based Navigation for Cup Placement in Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty
Yuta Kubota, Nobuhiro Kaku, Tomonori Tabata, Hiroaki Tagomori, Hiroshi Tsumura
Clin Orthop Surg. 2019;11(1):43-51. doi: 10.4055/cios.2019.11.1.43.
Reference
-
1. Gandhi R, Marchie A, Farrokhyar F, Mahomed N. Computer navigation in total hip replacement: a meta-analysis. Int Orthop. 2009; 33:593–597.
Article2. Del Schutte H Jr, Lipman AJ, Bannar SM, Livermore JT, Ilstrup D, Morrey BF. Effects of acetabular abduction on cup wear rates in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1998; 13:621–626.
Article3. Kennedy JG, Rogers WB, Soffe KE, Sullivan RJ, Griffen DG, Sheehan LJ. Effect of acetabular component orientation on recurrent dislocation, pelvic osteolysis, polyethylene wear, and component migration. J Arthroplasty. 1998; 13:530–534.
Article4. Paterno SA, Lachiewicz PF, Kelley SS. The influence of patient-related factors and the position of the acetabular component on the rate of dislocation after total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1997; 79:1202–1210.
Article5. Lewinnek GE, Lewis JL, Tarr R, Compere CL, Zimmerman JR. Dislocations after total hip-replacement arthroplasties. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1978; 60:217–220.
Article6. Steppacher SD, Kowal JH, Murphy SB. Improving cup positioning using a mechanical navigation instrument. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011; 469:423–428.
Article7. Beckmann J, Stengel D, Tingart M, Götz J, Grifka J, Lüring C. Navigated cup implantation in hip arthroplasty. Acta Orthop. 2009; 80:538–544.
Article8. Inori F, Ohashi H, Yo H, Okajima Y, Matsui Y, Shintani K. Accuracy of cup height and medialization in THA for dysplastic hip osteoarthritis using an imageless navigation system. Orthopedics. 2012; 35:10 Suppl. 7–12.
Article9. Ohashi H, Matsuura M, Okamoto Y, Ebara T, Kakeda K, Takahashi S. Status of navigated total hip arthroplasty in dysplastic osteoarthritis. Orthopedics. 2007; 30:10 Suppl. S117–S120.10. Kajino Y, Kabata T, Maeda T, Iwai S, Kuroda K, Tsuchiya H. Does degree of the pelvic deformity affect the accuracy of computed tomography-based hip navigation? J Arthroplasty. 2012; 27:1651–1657.
Article11. Jingushi S, Mizu-uchi H, Nakashima Y, Yamamoto T, Mawatari T, Iwamoto Y. Computed tomography-based navigation to determine the socket location in total hip arthroplasty of an osteoarthritis hip with a large leg length discrepancy due to severe acetabular dysplasia. J Arthroplasty. 2007; 22:1074–1078.
Article12. Franke J, Zheng G, Wendl K, Grützner PA, von Recum J. Clinical experience with computer navigation in revision total hip arthroplasty. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2012; 226:919–926.
Article13. Nakamura N, Nishii T, Kitada M, Iwana D, Sugano N. Application of computed tomography-based navigation for revision total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2013; 28:1806–1810.
Article14. Kuroda K, Kabata T, Maeda T, et al. The value of computed tomography based navigation in revision total hip arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2014; 38:711–716.
Article15. Yun HH, Yoon JR, Yang JH, Song SY, Park SB, Lee JW. A validation study for estimation of femoral anteversion using the posterior lesser trochanter line: an analysis of computed tomography measurement. J Arthroplasty. 2013; 28:1776–1780.
Article16. Shon WY, Yun HH, Yang JH, Song SY, Park SB, Lee JW. The use of the posterior lesser trochanter line to estimate femoral neck version: an analysis of computed tomography measurements. J Arthroplasty. 2013; 28:352–358.
Article17. Widmer KH. A simplified method to determine acetabular cup anteversion from plain radiographs. J Arthroplasty. 2004; 19:387–390.
Article18. Koo KH, Ha YC, Kim SY, Yoon KS, Min BW, Kim SR. Revision of ceramic head fracture after third generation ceramic-on-ceramic total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2014; 29:214–218.
Article19. Sharma OP, Lochab J, Berkovich Y, Safir OA, Gross AE. Severe metallosis leading to femoral head perforation. Orthopedics. 2013; 36:e241–e243.
Article20. Lopes R, Philippeau JM, Passuti N, Gouin F. High rate of ceramic sandwich liner fracture. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012; 470:1705–1710.
Article21. Jeffers JR, Walter WL. Ceramic-on-ceramic bearings in hip arthroplasty: state of the art and the future. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012; 94:735–745.22. Moskal JT, Capps SG. Improving the accuracy of acetabular component orientation: avoiding malposition. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2010; 18:286–296.
Article23. Akiyama H, Kawanabe K, Ito T, Goto K, Nangaku M, Nakamura T. Computed tomography-based navigation to determine the femoral neck osteotomy and location of the acetabular socket of an arthrodesed hip. J Arthroplasty. 2009; 24:1292.e1–1292.e4.
Article24. Minoda Y, Kadowaki T, Kim M. Acetabular component orientation in 834 total hip arthroplasties using a manual technique. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006; 445:186–191.
Article25. Kelley TC, Swank ML. Role of navigation in total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009; 91:Suppl 1. 153–158.
Article26. Lee YK, Biau DJ, Yoon BH, Kim TY, Ha YC, Koo KH. Learning curve of acetabular cup positioning in total hip arthroplasty using a cumulative summation test for learning curve (LC-CUSUM). J Arthroplasty. 2014; 29:586–589.
Article27. Parratte S, Argenson JN. Validation and usefulness of a computer-assisted cup-positioning system in total hip arthroplasty. A prospective, randomized, controlled study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007; 89:494–499.
Article28. Ybinger T, Kumpan W, Hoffart HE, Muschalik B, Bullmann W, Zweymüller K. Accuracy of navigation-assisted acetabular component positioning studied by computed tomography measurements: methods and results. J Arthroplasty. 2007; 22:812–817.
Article29. Kim TH, Lee SH, Yang JH, Oh KJ. Computed tomography assessment of image-free navigation-assisted cup placement in THA in an Asian population. Orthopedics. 2012; 35:10 Suppl. 13–17.
Article30. Zárate-Kalfópulos B, Romero-Vargas S, Otero-Cámara E, Correa VC, Reyes-Sánchez A. Differences in pelvic parameters among Mexican, Caucasian, and Asian populations. J Neurosurg Spine. 2012; 16:516–519.
Article31. Haaker RG, Tiedjen K, Ottersbach A, Rubenthaler F, Stockheim M, Stiehl JB. Comparison of conventional versus computer-navigated acetabular component insertion. J Arthroplasty. 2007; 22:151–159.
Article32. Kalteis T, Handel M, Bäthis H, Perlick L, Tingart M, Grifka J. Imageless navigation for insertion of the acetabular component in total hip arthroplasty: is it as accurate as CT-based navigation? J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006; 88:163–167.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Acetabular Cup Revision
- Liner Dissociation by Extrusion of the Acetabular Cup Fixation Screw after Total Hip Replacement: Two Cases Report
- Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty of an Acetabular Cup with Acetabular Bone Defects
- Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty: Acetabular Cup
- Cementless Acetabular Revision using microporocoated Hemispherical Cup