Neurointervention.
2017 Mar;12(1):50-53. 10.5469/neuroint.2017.12.1.50.
Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Manifested as Rapid Progressive Dementia Successfully Treated by Endovascular Embolization Only
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kzoo@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Radiology, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2371759
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5469/neuroint.2017.12.1.50
Abstract
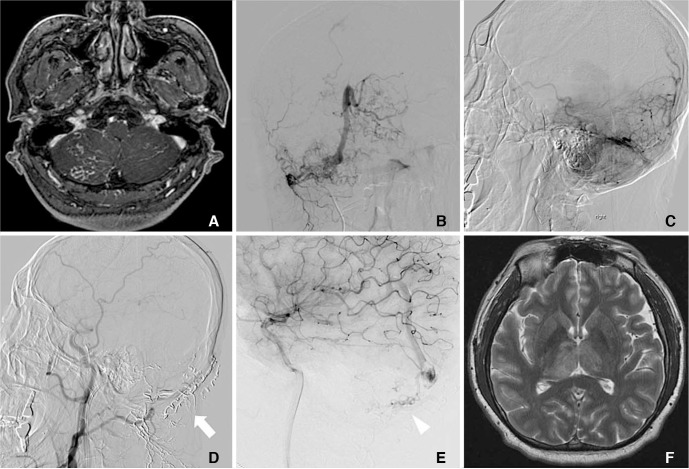
- A 43-year-old male presented with daytime sleepiness at work and indifferent behavior like never before. Two weeks prior to hospital admission, he had episodic memory loss with well preserved remote memory. Brain MRI showed a dural arteriovenous fistula (DAVF) in the right lateral transverse sinus with a bilateral thalamic venous infarction. Cerebral angiography confirmed a right transverse sigmoid dural arteriovenous fistula with a feeding artery of the right occipital artery and left posterior meningeal artery. The DAVF was completely eliminated through multiple endovascular interventions. Recently, endovascular treatment has become one of the main therapeutic options to obliterate a fistulous site, which has led to a rapid diagnostic approach and management of DAVFs with high curative rates. We report a rare case of posterior fossa located at a dural arteriovenous fistula that caused rapid progressive dementia and was successfully eliminated through only endovascular treatment.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Endovascular Treatment of Bilateral Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula: Therapeutic Strategy and Follow-Up Outcomes
Jong Kook Rhim, Young Dae Cho, Dong Hyun Yoo, Hyun-Seung Kang, Won-Sang Cho, Jeong Eun Kim, Min Jae Cho, Gyojun Hwang, O-Ki Kwon, Moon Hee Han
Korean J Radiol. 2018;19(2):334-341. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2018.19.2.334.
Reference
-
1. Chaichana KL, Coon AL, Tamargo RJ, Huang J. Dural arteriovenous fistulas: epidemiology and clinical presentation. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2012; 23:7–13. PMID: 22107854.
Article2. Miller TR, Gandhi D. Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulae: Clinical Presentation and Management Strategies. Stroke. 2015; 46:2017–2025. PMID: 25999384.
Article3. Holekamp TF, Mollman ME, Murphy RK, Kolar GR, Kramer NM, Derdeyn CP, et al. Dural arteriovenous fistula-induced thalamic dementia: report of 4 cases. J Neurosurg. 2016; 124:1752–1765. PMID: 26587655.
Article4. Morparia N, Miller G, Rabinstein A, Lanzino G, Kumar N. Cognitive decline and hypersomnolence: thalamic manifestations of a tentorial dural arteriovenous fistula (dAVF). Neurocrit Care. 2012; 17:429–433. PMID: 22847398.
Article5. Gandhi D, Chen J, Pearl M, Huang J, Gemmete JJ, Kathuria S. Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas: classification, imaging findings, and treatment. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2012; 33:1007–1013. PMID: 22241393.
Article6. Hurst RW, Bagley LJ, Galetta S, Glosser G, Lieberman AP, Trojanowski J, et al. Dementia resulting from dural arteriovenous fistulas: the pathologic findings of venous hypertensive encephalopathy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1998; 19:1267–1273. PMID: 9726465.7. Matsumura A, Oda M, Hozuki T, Imai T, Shimohama S. Dural arteriovenous fistula in a case of dementia with bithalamic MR lesions. Neurology. 2008; 71:1553. PMID: 18981380.
Article8. Lasjaunias P, Chiu M, Brugge KT, Tolia A, Hurth M, Berenstein M. Neurological manifestations of intracranial dural arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg. 1986; 64:724–730. PMID: 3701421.
Article9. Van Dijk JM, Willinsky RA. Venous congestive encephalopathy related to cranial dural arteriovenous fistulas. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2003; 13:55–72. PMID: 12802941.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Endovascular Treatment of Dural Sinus Malformation in Infant: A Case Report
- Dementia and Parkinsonism-a Rare Presentation of Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulae
- Stereotactic radiosurgery for dural arteriovenous fistula
- Transvenous Coil Embolization for Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas of the Ophthalmic Sheath: Report of Two Cases and Review of the Literature
- Transvenous coil embolization of hypoglossal canal dural arteriovenous fistula using detachable coils: A case report