J Rheum Dis.
2017 Feb;24(1):4-13. 10.4078/jrd.2017.24.1.4.
Nuclear Medicine Imaging in Rheumatic Diseases
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nuclear Medicine, Hanyang University Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. yychoi@hanyang.ac.kr
- KMID: 2371672
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2017.24.1.4
Abstract
- The rapid development of medical imaging technologies has greatly enhanced the utility of nuclear medicine imaging modalities over the last decade. Hybrid imaging technology merging computed tomography (CT) with single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) or positron emission tomography (PET) allows superimposing the physiologic data obtained by SPECT or PET on the detailed anatomy of CT, yielding a better understanding of the disease status and improving diagnostic performance. However, the conventional whole body bone scan and three phase bone scan still have their own distinct role as diagnostic imaging, reflecting the changes of bone metabolism in benign and malignant diseases, including rheumatic diseases. A review of each nuclear medicine imaging technique and clinical applications in various conditions of rheumatic diseases will be presented in this article.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Subramanian G, McAfee JG, Bell EG, Blair RJ, O'Mara RE, Ralston PH. 99m Tc-labeled polyphosphate as a skeletal imaging agent. Radiology. 1972; 102:701–4.2. Subramanian G. Radiopharmaceuticals for bone scanning. Collier BD, Fogelman I, Rosenthall L, editors. Skeletal nuclear medicine. St. Louis (MO): Mosby;1996. p. 9–20.3. Freeman LM, Blaufox MD. Letter from the Editors: planar imaging in the age of SPECT. Semin Nucl Med. 2012; 42:1–2.
Article4. Davila D, Antoniou A, Chaudhry MA. Evaluation of osseous metastasis in bone scintigraphy. Semin Nucl Med. 2015; 45:3–15.
Article5. Brenner AI, Koshy J, Morey J, Lin C, DiPoce J. The bone scan. Semin Nucl Med. 2012; 42:11–26.
Article6. Palestro CJ. Radionuclide imaging of osteomyelitis. Semin Nucl Med. 2015; 45:32–46.
Article7. Scharf SC. Bone SPECT/CT in skeletal trauma. Semin Nucl Med. 2015; 45:47–57.
Article8. Palestro CJ. FDG-PET in musculoskeletal infections. Semin Nucl Med. 2013; 43:367–76.
Article9. Jadvar H, Desai B, Conti PS. Sodium 18F-fluoride PET/CT of bone, joint, and other disorders. Semin Nucl Med. 2015; 45:58–65.
Article10. Fischer DR. Musculoskeletal imaging using fluoride PET. Semin Nucl Med. 2013; 43:427–33.
Article11. Jones AG, Francis MD, Davis MA. Bone scanning: radio-nuclidic reaction mechanisms. Semin Nucl Med. 1976; 6:3–18.
Article12. Elgazzar AH. Orthopedic nuclear medicine. Berlin: SpringerVerlag;2004. p. 13–31.13. Lee WW, So Y. Skeletal system. In: Chung JK, Lee MC. Nuclear medicine. 3rd ed.Seoul: Korea Medical Book Publisher;2008. p. 509–71.14. Eggli DF, Tulchinsky M. Normal planar bone scan. Collier BD, Fogelman I, Rosenthall L, editors. Skeletal nuclear medicine. St. Louis (MO): Mosby;1996. p. 25–6.15. Grassi W, De Angelis R, Lamanna G, Cervini C. The clinical features of rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Radiol. 1998; 27(Suppl 1):S18–24.
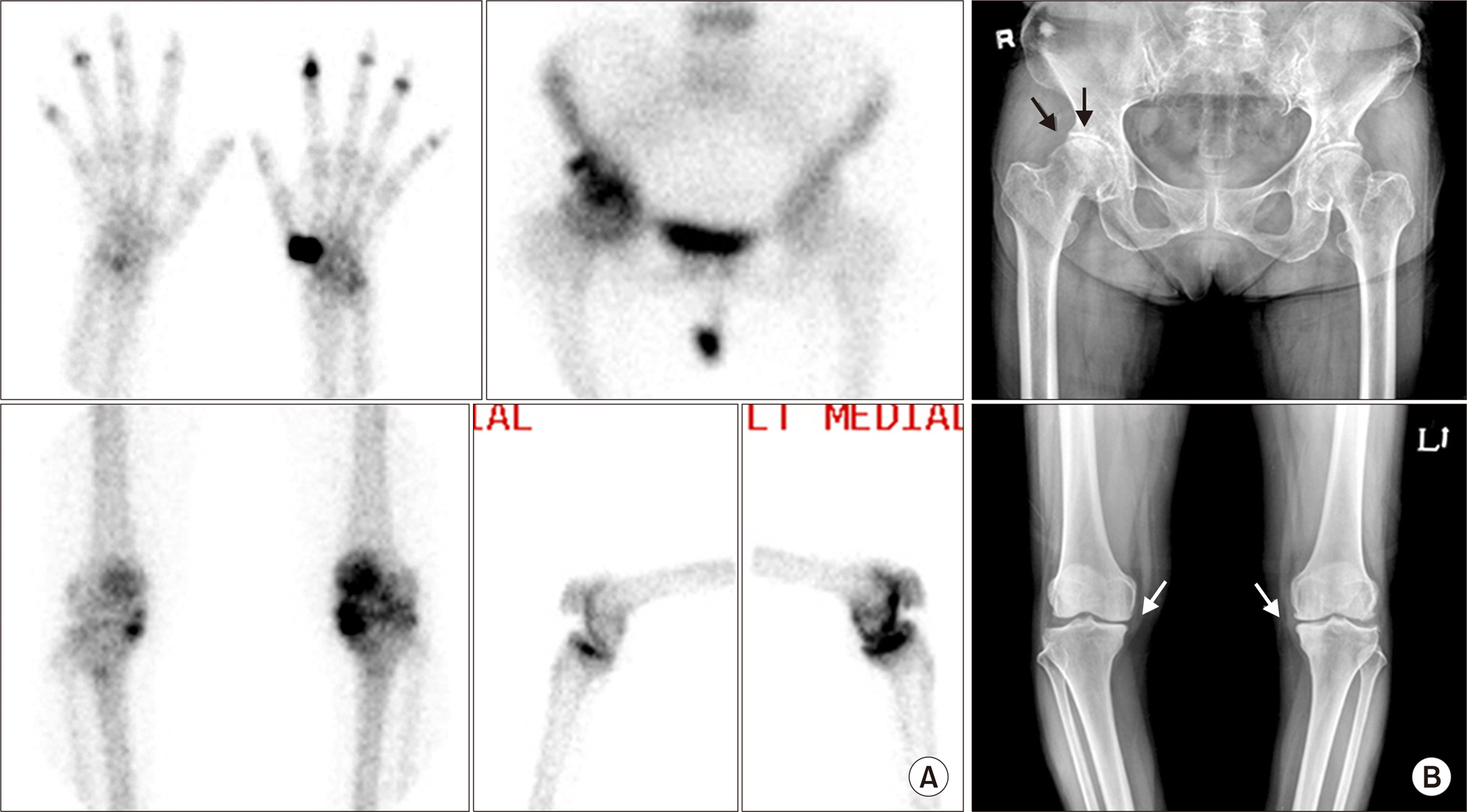
Article16. Ziff M. General mechanisms of inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Bull Schweiz Akad Med Wiss. 1979; 35:275–81.17. Kim JY, Choi YY, Kim CW, Sung YK, Yoo DH. Bone scintigraphy in the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis: is there additional value of bone scintigraphy with blood pool phase over conventional bone scintigraphy? J Korean Med Sci. 2016; 31:502–9.
Article18. Elgazzar AH, Silberstein EB. Skeletal scintigraphy in non-neoplastic osseous disorders. Henkin RE, Bova D, Dilehay GL, Halama JR, Karesh SM, Wagner RH, editors. Nuclear medicine. 2nd ed.Philadelphia (PA): Mosby;2006. p. 1121–81.19. Rosenthall L. Nuclear medicine techniques in arthritis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1991; 17:585–97.
Article20. Chalmers J, Gray DH, Rush J. Observations on the induction of bone in soft tissues. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1975; 57:36–45.
Article21. Craven PL, Urist MR. Osteogenesis by radioisotope labelled cell populations in implants of bone matrix under the influence of ionizing radiation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1971; 76:231–43.
Article22. Oh SN, Jee WH, Cho SM, Kim SH, Kang HS, Ryu KN, et al. Osteonecrosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: MR imaging and scintigraphic evaluation. Clin Imaging. 2004; 28:305–9.23. Ostendorf B, Mattes-György K, Reichelt DC, Blondin D, Wirrwar A, Lanzman R, et al. Early detection of bony alterations in rheumatoid and erosive arthritis of finger joints with high-resolution single photon emission computed tomography, and differentiation between them. Skeletal Radiol. 2010; 39:55–61.
Article24. McQueen FM. Imaging in early rheumatoid arthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2013; 27:499–522.
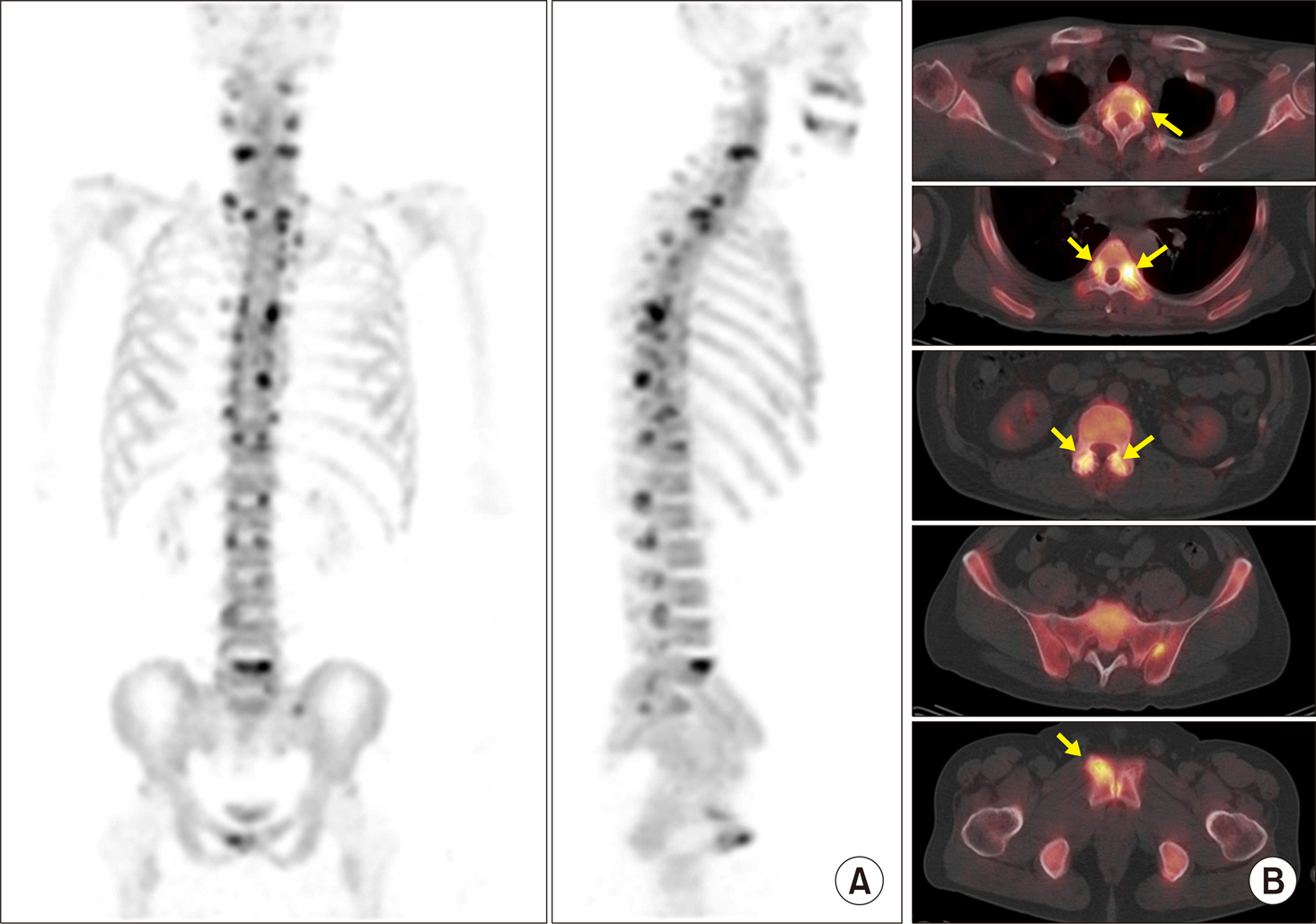
Article25. Zilber K, Gorenberg M, Rimar D, Boulman N, Kaly L, Rozenbaum M, et al. Radionuclide methods in the diagnosis of sacroiliitis in patients with spondyloarthritis: an update. Rambam Maimonides Med J. 2016; 7:e0037.
Article26. Caldarella C, Isgrò MA, Treglia I, Treglia G. Is fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography useful in monitoring the response to treatment in patients with multiple myeloma? Int J Hematol. 2012; 96:685–91.
Article27. Love C, Tomas MB, Tronco GG, Palestro CJ. FDG PET of infection and inflammation. Radiographics. 2005; 25:1357–68.
Article28. Chaudhari AJ, Ferrero A, Godinez F, Yang K, Shelton DK, Hunter JC, et al. High-resolution (18)F-FDG PET/CT for assessing disease activity in rheumatoid and psoriatic arthritis: findings of a prospective pilot study. Br J Radiol. 2016; 89:20160138.29. Dhawan R, Lokitz K, Lokitz S, Caldito G, Takalkar AM. FDG PET imaging of extremities in rheumatoid arthritis. J La State Med Soc. 2016; 168:156–61.30. Suto T, Okamura K, Yonemoto Y, Okura C, Tsushima Y, Takagishi K. Prediction of large joint destruction in patients with rheumatoid arthritis using 18F-FDG PET/CT and disease activity score. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016; 95:e2841.
Article31. Yonemoto Y, Okamura K, Takeuchi K, Kaneko T, Kobayashi T, Okura C, et al. [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose uptake as a predictor of large joint destruction in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 2016; 36:109–15.
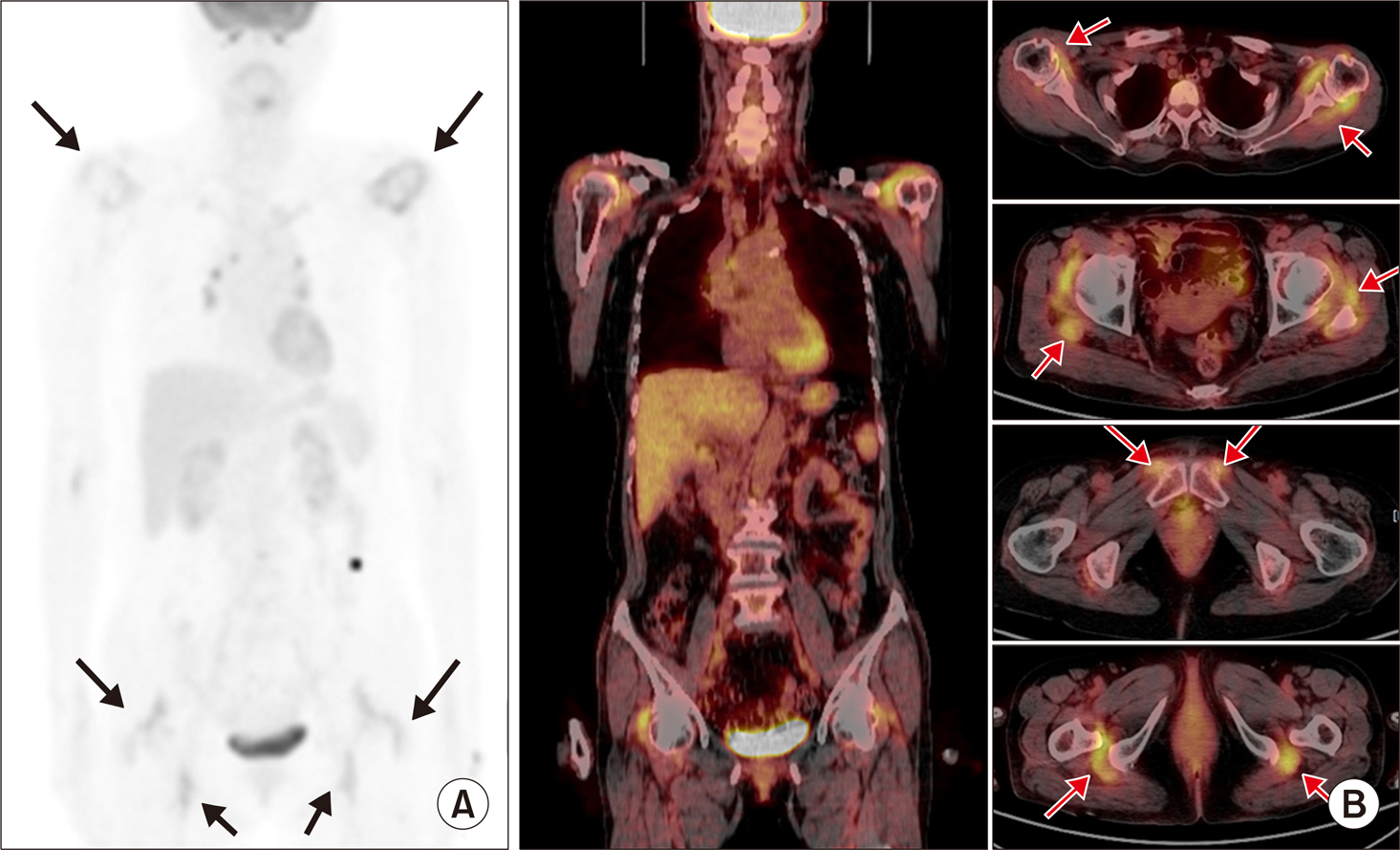
Article32. Wakura D, Kotani T, Takeuchi T, Komori T, Yoshida S, Makino S, et al. Differentiation between Polymyalgia Rheumatica (PMR) and elderly-onset rheumatoid arthritis using 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography: is enthesitis a new pathological lesion in PMR? PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0158509.
Article33. Li Y, Schiepers C, Lake R, Dadparvar S, Berenji GR. Clinical utility of (18)F-fluoride PET/CT in benign and malignant bone diseases. Bone. 2012; 50:128–39.
Article34. Czernin J, Satyamurthy N, Schiepers C. Molecular mechanisms of bone 18F-NaF deposition. J Nucl Med. 2010; 51:1826–9.
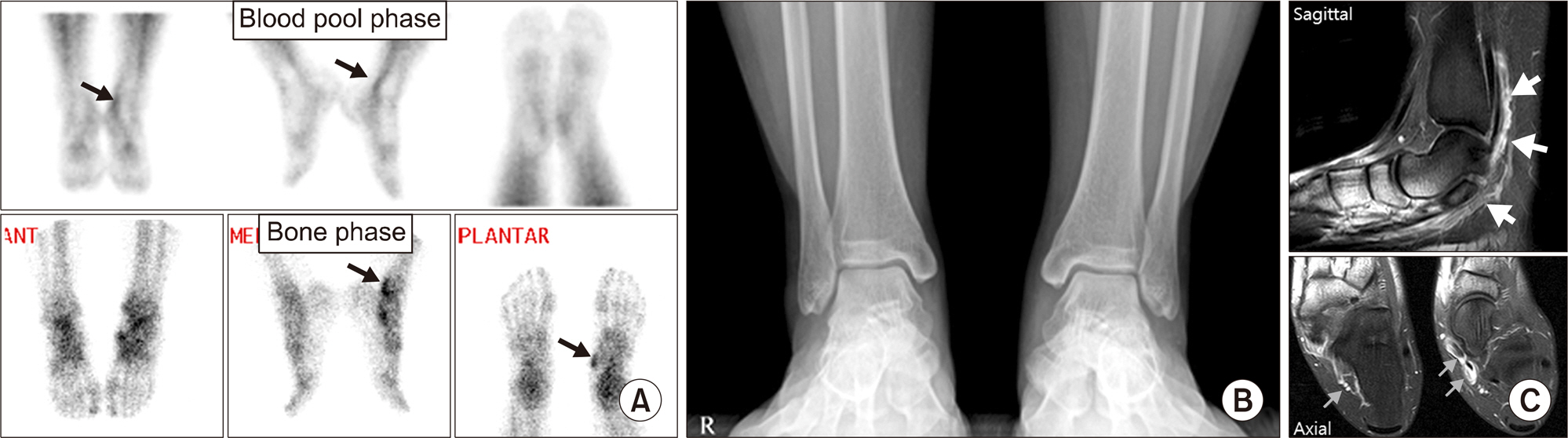
Article35. Kim JY, Choi YY, Kim YH, Park SB, Jeong MA. Role of (18)F-fluoride PET/CT over dualphase bone scintigraphy in evaluation and management of lesions causing foot and ankle pain. Ann Nucl Med. 2015; 29:302–12.
Article