J Korean Med Sci.
2017 Apr;32(4):695-699. 10.3346/jkms.2017.32.4.695.
Report on the Project for Establishment of the Standardized Korean Laboratory Terminology Database, 2015
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. labmd@korea.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Laboratory Medicine, Inje University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea.
- 5Department of Laboratory Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Laboratory Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 7Department of Laboratory Medicine, Sungkyunkwan University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 8Department of Laboratory Medicine, Hallym University College of Medicine, Anyang, Korea.
- 9Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seegene Medical Foundation, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2371458
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2017.32.4.695
Abstract
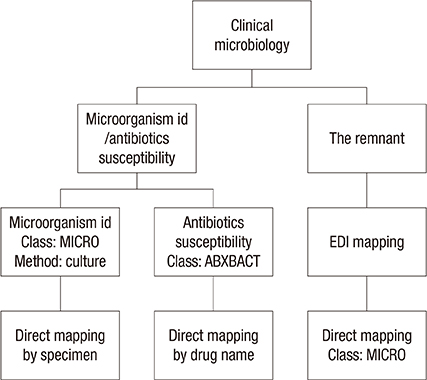
- The National Health Information Standards Committee was established in 2004 in Korea. The practical subcommittee for laboratory test terminology was placed in charge of standardizing laboratory medicine terminology in Korean. We aimed to establish a standardized Korean laboratory terminology database, Korea-Logical Observation Identifier Names and Codes (K-LOINC) based on former products sponsored by this committee. The primary product was revised based on the opinions of specialists. Next, we mapped the electronic data interchange (EDI) codes that were revised in 2014, to the corresponding K-LOINC. We established a database of synonyms, including the laboratory codes of three reference laboratories and four tertiary hospitals in Korea. Furthermore, we supplemented the clinical microbiology section of K-LOINC using an alternative mapping strategy. We investigated other systems that utilize laboratory codes in order to investigate the compatibility of K-LOINC with statistical standards for a number of tests. A total of 48,990 laboratory codes were adopted (21,539 new and 16,330 revised). All of the LOINC synonyms were translated into Korean, and 39,347 Korean synonyms were added. Moreover, 21,773 synonyms were added from reference laboratories and tertiary hospitals. Alternative strategies were established for mapping within the microbiology domain. When we applied these to a smaller hospital, the mapping rate was successfully increased. Finally, we confirmed K-LOINC compatibility with other statistical standards, including a newly proposed EDI code system. This project successfully established an up-to-date standardized Korean laboratory terminology database, as well as an updated EDI mapping to facilitate the introduction of standard terminology into institutions.
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Incorporation of Korean Electronic Data Interchange Vocabulary into Observational Medical Outcomes Partnership Vocabulary
Yeonchan Seong, Seng Chan You, Anna Ostropolets, Yeunsook Rho, Jimyung Park, Jaehyeong Cho, Dmitry Dymshyts, Christian G. Reich, Yunjung Heo, Rae Woong Park
Healthc Inform Res. 2021;27(1):29-38. doi: 10.4258/hir.2021.27.1.29.Application Guidelines of Logical Observation Identifiers Names and Codes (LOINC) for General Chemistry and Hematology Tests
Kuenyoul Park, Hyejin Ryu, Min-Sun Kim, Ye-Jin Oh, Shinae Yu, Eun-Jung Cho, Sollip Kim, Jae-Woo Chung, Yeo-Min Yun, Young Kyung Lee, Sail Chun
Lab Med Online. 2025;15(1):28-35. doi: 10.47429/lmo.2025.15.1.28.
Reference
-
1. Kume N, Suzuki K, Kobayashi S, Araki K, Yoshihara H. Development of unified lab test result master for multiple facilities. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2015; 216:1050.2. Forrey AW, McDonald CJ, DeMoor G, Huff SM, Leavelle D, Leland D, Fiers T, Charles L, Griffin B, Stalling F, et al. Logical observation identifier names and codes (LOINC) database: a public use set of codes and names for electronic reporting of clinical laboratory test results. Clin Chem. 1996; 42:81–90.3. Kopanitsa G. Mapping Russian laboratory terms to LOINC. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2015; 210:379–383.4. Yoon SY, Yoon JH, Min WK, Lim HS, Song J, Chae SL, Lee CK, Kwon JA, Lee KN. Standardization of terminology in laboratory medicine I. Korean J Lab Med. 2007; 27:151–155.5. Lee KN, Yoon JH, Min WK, Lim HS, Song J, Chae SL, Jang S, Ki CS, Bae SY, Kim JS, et al. Standardization of terminology in laboratory medicine II. J Korean Med Sci. 2008; 23:711–713.6. Regenstrief Institute (US). LOINC database (v. 2.48) [Internet]. accessed on 27 June 2014. Available at https://loinc.org/.7. McDonald C, Huff S, Deckard J, Armson S, Abhyankar S, Vreeman DJ. LOINC user's guide [Internet]. accessed on 27 June 2014. Available at http://loinc.org/downloads/files/LOINCManual.pdf.8. Korean Medical Association. English-Korean, Korean-English Medical Terminology. 5th ed. Seoul: Korean Medical Association;2009.9. Dhakal S, Burrer SL, Winston CA, Dey A, Ajani U, Groseclose SL. Coding of electronic laboratory reports for biosurveillance, selected United States hospitals, 2011. Online J Public Health Inform. 2015; 7:e220.10. Vreeman DJ, Hook J, Dixon BE. Learning from the crowd while mapping to LOINC. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2015; 22:1205–1211.11. Sakurabayashi I. Coding for clinical laboratory information. Jpn J Clin Pathol. 1997; 45:573–576.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Systematic Review of Audiology Terminology
- Standardization of Terminology in Laboratory Medicine I
- Transition of the Korean Name for the Department of Radiology and Korean Medical Terminology: A Note Ahead of Publication for the Sixth Edition of the Korean Medical Terminology
- The Endoscopic Report for Endoscopic Electronic Medical Records
- Standardization of Terminology in Laboratory Medicine ll